|
Morenosaurus
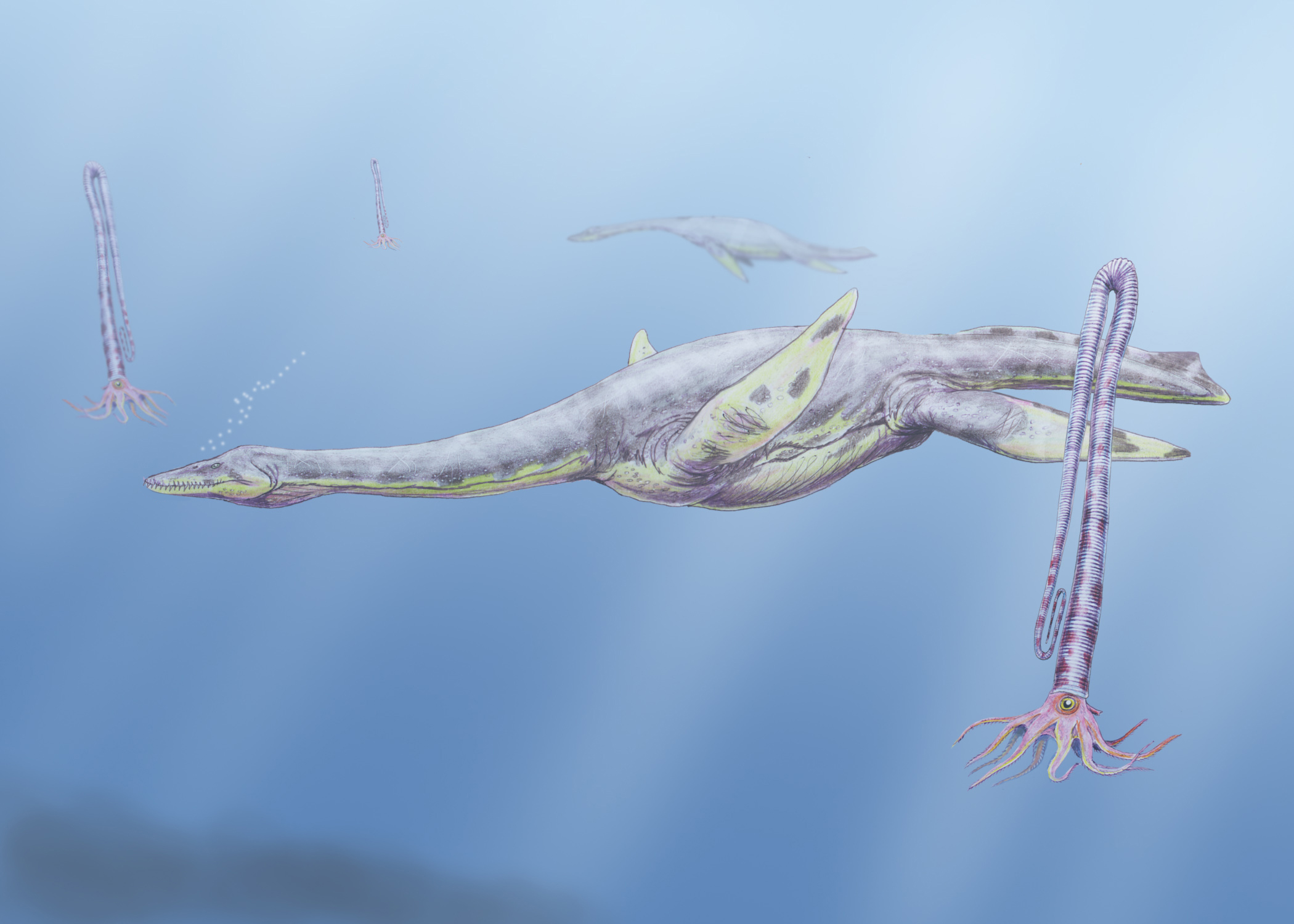
''Morenosaurus'' is an extinct genus of plesiosaur from the Cretaceous of what is now California. The type species is ''Morenosaurus stocki'', first named by Samuel Welles in 1943, in honor of Dr. Chester Stock.Hilton, Richard P., ''Dinosaurs and Other Mesozoic Animals of California'', University of California Press, Berkeley 2003 , at page 105 The species was found by Robert Wallace and Arthur Drescher in the Panoche Hills region of Fresno County. The skeleton they found was fairly complete, and lacked only the head and parts of the neck and paddles; the preserved portion of the trunk and tail is long. The skeleton was originally mounted at Caltech but is now in the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. ''Morenosaurus'' may have been similar to ''Elasmosaurus'' or ''Thalassomedon'', but studies in the early 2000s indicated that the fossils were too scrappy to identify to the family level. See also * List of plesiosaur genera * Timeline of plesiosaur research T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morenosaurus2 NT
''Morenosaurus'' is an extinct genus of plesiosaur from the Cretaceous of what is now California. The type species is ''Morenosaurus stocki'', first named by Samuel Welles in 1943, in honor of Dr. Chester Stock.Hilton, Richard P., ''Dinosaurs and Other Mesozoic Animals of California'', University of California Press, Berkeley 2003 , at page 105 The species was found by Robert Wallace and Arthur Drescher in the Panoche Hills region of Fresno County. The skeleton they found was fairly complete, and lacked only the head and parts of the neck and paddles; the preserved portion of the trunk and tail is long. The skeleton was originally mounted at Caltech but is now in the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. ''Morenosaurus'' may have been similar to ''Elasmosaurus'' or ''Thalassomedon'', but studies in the early 2000s indicated that the fossils were too scrappy to identify to the family level. See also * List of plesiosaur genera * Timeline of plesiosaur research T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
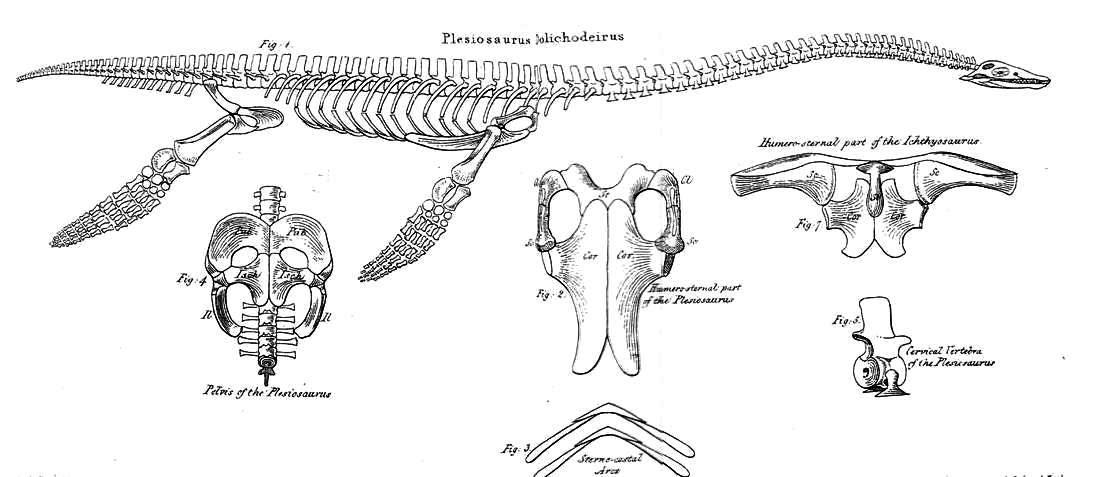
Timeline Of Plesiosaur Research
This timeline of plesiosaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, taxonomic revisions, and cultural portrayals of plesiosaurs, an order of marine reptiles that flourished during the Mesozoic Era. The first scientifically documented plesiosaur fossils were discovered during the early 19th century by Mary Anning. Plesiosaurs were actually discovered and described before dinosaurs. They were also among the first animals to be featured in artistic reconstructions of the ancient world, and therefore among the earliest prehistoric creatures to attract the attention of the lay public. Plesiosaurs were originally thought to be a kind of primitive transitional form between marine life and terrestrial reptiles. However, now plesiosaurs are recognized as highly derived marine reptiles descended from terrestrial ancestors. Early researchers thought that plesiosaurs laid eggs like most reptiles. They commonly imagined p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chester Stock
Chester Stock (28 January 1892 – 7 December 1950) was an American paleontologist who specialized in the Pleistocene mammalian fauna of the La Brea Tar Pits, Rancho La Brea tar pits. He served as a professor of geology at the California Institute of Technology, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena. Stock was born in San Francisco to John Englebert Stock and Maria Henriette Meyer, both German immigrants. He grew up in a poor neighborhood, selling newspapers to earn some money. He was educated at Starr King Primary School and Franklin Grammar School, spending weekends at a gymnasium studying German, and learned to play tuba at a local Lutheran Church. He also took an interest in science, attending the annual mechanics fair and the museum of the California Academy of Sciences. His family home was destroyed by fires caused by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, after which he joined the California National Guard. He was forced by circumstances to leave school and seek employme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasmosaurids
Elasmosauridae is an extinct family of plesiosaurs, often called elasmosaurs. They had the longest necks of the plesiosaurs and existed from the Hauterivian to the Maastrichtian stages of the Cretaceous, and represented one of the two groups of plesiosaurs present at the end of the Cretaceous alongside Polycotylidae. Their diet mainly consisted of crustaceans and molluscs. Description The earliest elasmosaurids were mid-sized, about . In the Late Cretaceous, elasmosaurids grew as large as , such as ''Styxosaurus'', ''Albertonectes'', and ''Thalassomedon''. Their necks were the longest of all the plesiosaurs, with anywhere between 32 and 76 (''Albertonectes'') cervical vertebrae. They weighed up to several tons. Classification Early three-family classification Though Cope had originally recognized ''Elasmosaurus'' as a plesiosaur, in an 1869 paper he placed it, with '' Cimoliasaurus'' and '' Crymocetus'', in a new order of sauropterygian reptiles. He named the group Strept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Plesiosaur Genera
This list of plesiosaurs is a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the order Plesiosauria, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomen dubium''), or were not formally published (''nomen nudum''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered plesiosaurs. The list currently includes 201 genera. Scope and terminology There is no official, canonical list of plesiosaur genera but one of the most thorough attempts can be found on the Plesiosauria section of Mikko Haaramo's Phylogeny Archive; also pertinent is the Plesiosaur Genera section at Adam Stuart Smith's Plesiosaur Directory.See Smith, ''Plesiosaur Genera''. Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesiosauria
The Plesiosauria (; Greek: πλησίος, ''plesios'', meaning "near to" and ''sauros'', meaning "lizard") or plesiosaurs are an order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia. Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period, possibly in the Rhaetian stage, about 203 million years ago. They became especially common during the Jurassic Period, thriving until their disappearance due to the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous Period, about 66 million years ago. They had a worldwide oceanic distribution, and some species at least partly inhabited freshwater environments. Plesiosaurs were among the first fossil reptiles discovered. In the beginning of the nineteenth century, scientists realised how distinctive their build was and they were named as a separate order in 1835. The first plesiosaurian genus, the eponymous '' Plesiosaurus'', was named in 1821. Since then, more than a hundred valid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasmosauridae
Elasmosauridae is an extinct family of plesiosaurs, often called elasmosaurs. They had the longest necks of the plesiosaurs and existed from the Hauterivian to the Maastrichtian stages of the Cretaceous, and represented one of the two groups of plesiosaurs present at the end of the Cretaceous alongside Polycotylidae. Their diet mainly consisted of crustaceans and molluscs. Description The earliest elasmosaurids were mid-sized, about . In the Late Cretaceous, elasmosaurids grew as large as , such as ''Styxosaurus'', '' Albertonectes'', and ''Thalassomedon''. Their necks were the longest of all the plesiosaurs, with anywhere between 32 and 76 (''Albertonectes'') cervical vertebrae. They weighed up to several tons. Classification Early three-family classification Though Cope had originally recognized ''Elasmosaurus'' as a plesiosaur, in an 1869 paper he placed it, with '' Cimoliasaurus'' and '' Crymocetus'', in a new order of sauropterygian reptiles. He named the group S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesiosaur
The Plesiosauria (; Greek: πλησίος, ''plesios'', meaning "near to" and ''sauros'', meaning "lizard") or plesiosaurs are an order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia. Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period, possibly in the Rhaetian stage, about 203 million years ago. They became especially common during the Jurassic Period, thriving until their disappearance due to the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous Period, about 66 million years ago. They had a worldwide oceanic distribution, and some species at least partly inhabited freshwater environments. Plesiosaurs were among the first fossil reptiles discovered. In the beginning of the nineteenth century, scientists realised how distinctive their build was and they were named as a separate order in 1835. The first plesiosaurian genus, the eponymous '' Plesiosaurus'', was named in 1821. Since then, more than a hundred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muraenosaurus
''Muraenosaurus'' (from the Latin "''Muraena''" meaning "eel" and "''Sauros''" meaning lizard) is an extinct genus of cryptoclidid plesiosaur reptile from the Oxford Clay of Southern England. The genus was given its name due to the eel-like appearance of the long neck and small head. ''Muraenosaurus'' grew up to in length and lived roughly between 160 Ma (million years ago) and 164 Ma in the Callovian of the middle Jurassic. Charles E. Leeds collected the first ''Muraenosaurus'' which was then described by H. G. Seeley.Seeley, HG. 1874. On ''Murænosaurus Leedsii'', a Plesiosaurian from the Oxford Clay. Part I. ''Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society'' 30: 197-208. The specimen may have suffered some damage due to the casual style of Charles Leeds’ collection. The first Muraenosaur was recovered with pieces missing from the skull and many of the caudal vertebrae absent. Because the animal was described from Charles Leeds’ collection it was given the name ''Muraenosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous Plesiosaurs Of North America
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) * Tardiness * Tardiness (scheduling) In scheduling, tardiness is a measure of a delay in exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the abs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalassomedon
''Thalassomedon'' (from Greek, ''thalassa'', "sea" and Greek, ''medon'', "lord" or "ruler", meaning "sea lord") is a genus of plesiosaur, named by Welles in 1943. Description ''Thalassomedon'' is among the largest elasmosaurids, with a total length of for the holotype. There is a larger skull, however, suggesting a much larger animal, potentially up to . Gregory S. Paul proposed that a long individual would have weighed , while O'Gorman and his colleagues proposed that a long individual would have weighed more than . The neck is also very long; it comprises 62 vertebraeCarpenter, K. (1999). "Revision of North American elasmosaurs from the Cretaceous western interior." ''Paludicola'', 2(2): 148-173. and is about - over half of the total length. The skull is long, with long teeth. The flippers were about long. Stones have been found in its stomach area leading some to theorize that they were used for ballast or digestion. If the latter, stomach action would cause the ston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |