|
Morchella Meiliensis
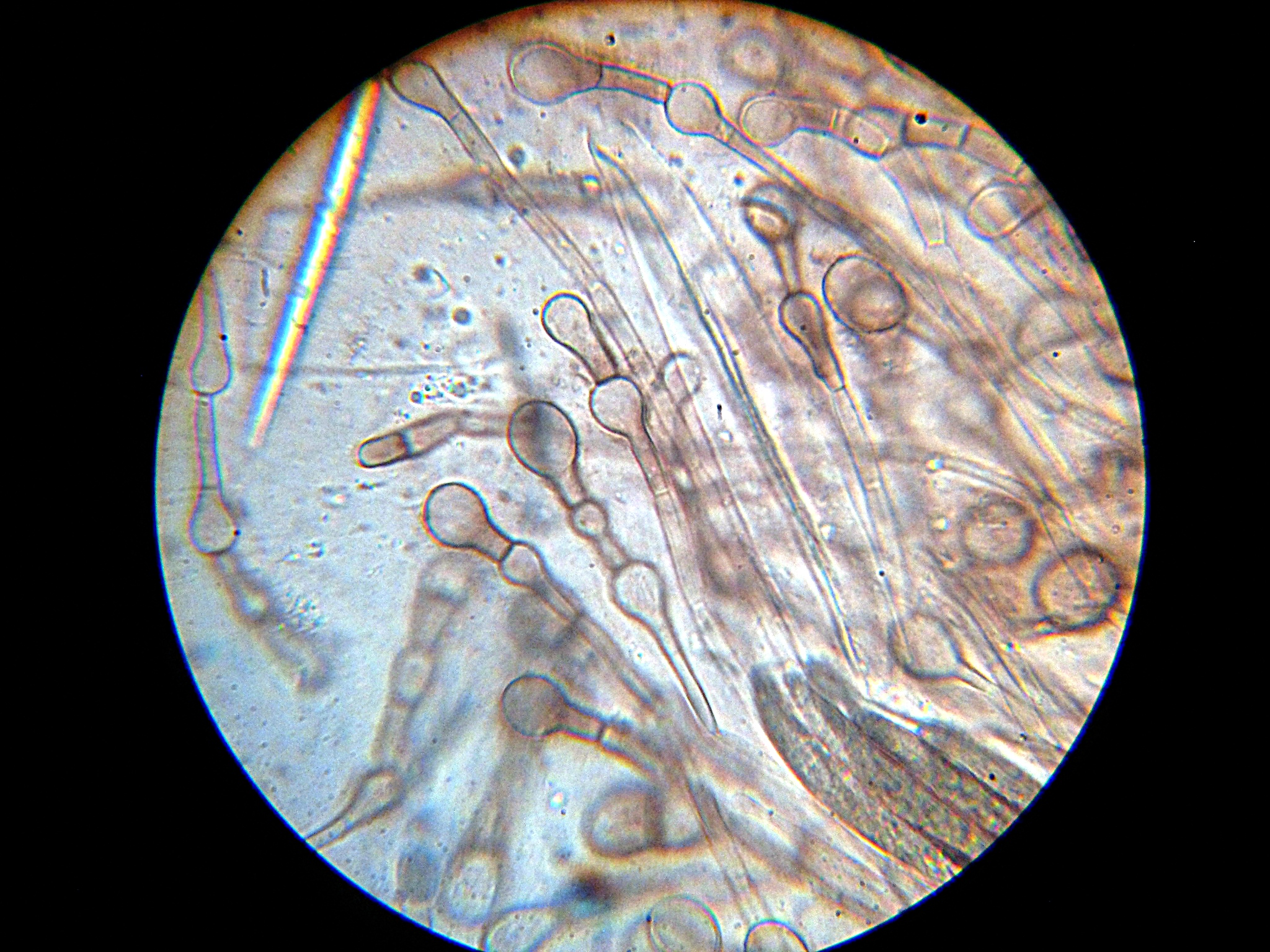
''Morchella meiliensis'' is a species of fungus in the family Morchellaceae native to China. Taxonomy The species was described as new to science in 2006. The specific epithet ''meiliensis'' refers to Meili Snow Mountain in Yunnan, where the type specimen was collected. Description The fruit bodies are with a conical cap measuring tall by wide. The surface has vertically arranged ridges that are dark brown to black in colour, while the rectangular to quadrangular pits between the ridges are merulioid (wrinkled with low, uneven ridges) and yellowish in colour. The flesh is thin, and lacks any distinctive taste or odour. The cylindrical stipe measures tall by thick. Initially whitish, it turns yellowish with a waxy sheen when dry. In deposit, ascospores are smooth, ellipsoid, hyaline (translucent), and measure 4.7–5.1 by 5.2–5.7 µm. They are thin-walled and contain oil droplets. Asci (spore-bearing cells) are eight-spored, cylindrical, and hyaline, and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyaline
A hyaline substance is one with a glassy appearance. The word is derived from el, ὑάλινος, translit=hyálinos, lit=transparent, and el, ὕαλος, translit=hýalos, lit=crystal, glass, label=none. Histopathology Hyaline cartilage is named after its glassy appearance on fresh gross pathology. On light microscopy of H&E stained slides, the extracellular matrix of hyaline cartilage looks homogeneously pink, and the term "hyaline" is used to describe similarly homogeneously pink material besides the cartilage. Hyaline material is usually acellular and proteinaceous. For example, arterial hyaline is seen in aging, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus and in association with some drugs (e.g. calcineurin inhibitors). It is bright pink with PAS staining. Ichthyology and entomology In ichthyology and entomology, ''hyaline'' denotes a colorless, transparent substance, such as unpigmented fins of fishes or clear insect wings. Resh, Vincent H. and R. T. Cardé, Eds. Encyclo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Described In 2006
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fungi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edible Fungi
Edible mushrooms are the fleshy and edible fruit bodies of several species of macrofungi (fungi which bear fruiting structures that are large enough to be seen with the naked eye). They can appear either below ground (hypogeous) or above ground (epigeous) where they may be picked by hand. Edibility may be defined by criteria that include absence of poisonous effects on humans and desirable taste and aroma. Edible mushrooms are consumed for their nutritional and culinary value. Mushrooms, especially dried shiitake, are sources of umami flavor. Edible mushrooms include many fungal species that are either harvested wild or cultivated. Easily cultivated and common wild mushrooms are often available in markets, and those that are more difficult to obtain (such as the prized truffle, matsutake, and morel) may be collected on a smaller scale by private gatherers. Some preparations may render certain poisonous mushrooms fit for consumption. Before assuming that any wild mushroom is e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunnan Province
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces of Guizhou, Sichuan, autonomous regions of Guangxi, and Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet as well as Southeast Asian countries: Vietnam, Laos, and Myanmar. Yunnan is China's fourth least developed province based on disposable income per capita in 2014. Yunnan is situated in a mountainous area, with high elevations in the northwest and low elevations in the southeast. Most of the population lives in the eastern part of the province. In the west, the altitude can vary from the mountain peaks to river valleys by as much as . Yunnan is rich in natural resources and has the largest diversity of plant life in China. Of the approximately 30,000 species of Vascular plant, higher plants in China, Yunnan has perhaps 17,000 or more. Yun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Forest
Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest is a temperate climate terrestrial habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature, with broadleaf tree ecoregions, and with conifer and broadleaf tree mixed coniferous forest ecoregions. These forests are richest and most distinctive in central China and eastern North America, with some other globally distinctive ecoregions in the Caucasus, the Himalayas, Southern Europe, Australasia, Southwestern South America and the Russian Far East. Ecology The typical structure of these forests includes four layers. * The uppermost layer is the canopy composed of tall mature trees ranging from high. Below the canopy is the three-layered, shade-tolerant understory that is roughly shorter than the canopy. * The top layer of the understory is the sub-canopy composed of smaller mature trees, saplings, and suppressed juvenile canopy layer trees awaiting an opening in the canopy. * Below the sub-canopy is the shrub layer, composed of low growi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deciduous Forest
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, after flowering; and to the shedding of ripe fruit. The antonym of ''deciduous'' in the botanical sense is evergreen. Generally, the term "deciduous" means "the dropping of a part that is no longer needed or useful" and the "falling away after its purpose is finished". In plants, it is the result of natural processes. "Deciduous" has a similar meaning when referring to animal parts, such as deciduous antlers in deer, deciduous teeth (baby teeth) in some mammals (including humans); or decidua, the uterine lining that sheds off after birth. Botany In botany and horticulture, deciduous plants, including trees, shrubs and herbaceous perennials, are those that lose all of their leaves for part of the year. This process is called abscission. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morchella Angusticeps
''Morchella angusticeps'' is a species of fungus in the family Morchellaceae native to eastern North America. Described by Charles Horton Peck Charles Horton Peck (March 30, 1833 – July 11, 1917) was an American mycologist of the 19th and early 20th centuries. He was the New York State Botanist from 1867 to 1915, a period in which he described over 2,700 species of North American fun ... in 1879, the name ''M. angusticeps'' was clarified in 2012 prior to which this species may have been referred to as either ''M. angusticeps'' or '' M. elata''. ''M. angusticeps'' is one of the black morels, and is found in eastern North America, where it occurs in association with various hardwoods in the spring. A similar, although smaller, black morel occurs in northeastern North America, '' M. septentrionalis''. References External links * * angusticeps Edible fungi Fungi described in 1879 Fungi of North America Taxa named by Charles Horton Peck {{Pezizomyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morchella Conica
''Morchella conica'' is an old binomial name previously applied to species of fungi in the family Morchellaceae. It is one of three scientific names that had been commonly used to describe black morels, the others being '' M. angusticeps'' and '' M. elata''. It was first introduced by mycologist Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1818, as a superfluous name for the old taxon ''Morchella continua''. According to Richard and colleagues, Fries’ sanctioning applies only at the subgeneric level and the name is illegitimate. Throughout the years, the name ''M. conica'' has been invariably applied to many different species by different authors, and DNA analysis in 2014 revealed that morels identified as "''M. conica''" indeed belonged to '' Morchella deliciosa'', '' Morchella purpurascens'', ''Morchella tridentina ''Morchella tridentina'' is a cosmopolitan species of ascomycete fungus in the family Morchellaceae. Commonly referred to as the mountain blond or western blond morel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyses
Paraphyses are erect sterile filament-like support structures occurring among the reproductive apparatuses of fungi, ferns, bryophytes and some thallophytes. The singular form of the word is paraphysis. In certain fungi, they are part of the fertile spore-bearing layer. More specifically, paraphyses are sterile filamentous hyphal end cells composing part of the hymenium of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota interspersed among either the asci or basidia respectively, and not sufficiently differentiated to be called cystidia A cystidium (plural cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that ar ..., which are specialized, swollen, often protruding cells. The tips of paraphyses may contain the pigments which colour the hymenium. In ferns and mosses, they are filament-like structures that are found on sporangia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascus
An ascus (; ) is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. Each ascus usually contains eight ascospores (or octad), produced by meiosis followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can occur in numbers of one (e.g. ''Monosporascus cannonballus''), two, four, or multiples of four. In a few cases, the ascospores can bud off conidia that may fill the asci (e.g. ''Tympanis'') with hundreds of conidia, or the ascospores may fragment, e.g. some ''Cordyceps'', also filling the asci with smaller cells. Ascospores are nonmotile, usually single celled, but not infrequently may be coenocytic (lacking a septum), and in some cases coenocytic in multiple planes. Mitotic divisions within the developing spores populate each resulting cell in septate ascospores with nuclei. The term ocular chamber, or oculus, refers to the epiplasm (the portion of cytoplasm not used in ascospore formation) that is surrounded by the "bourrelet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |