|
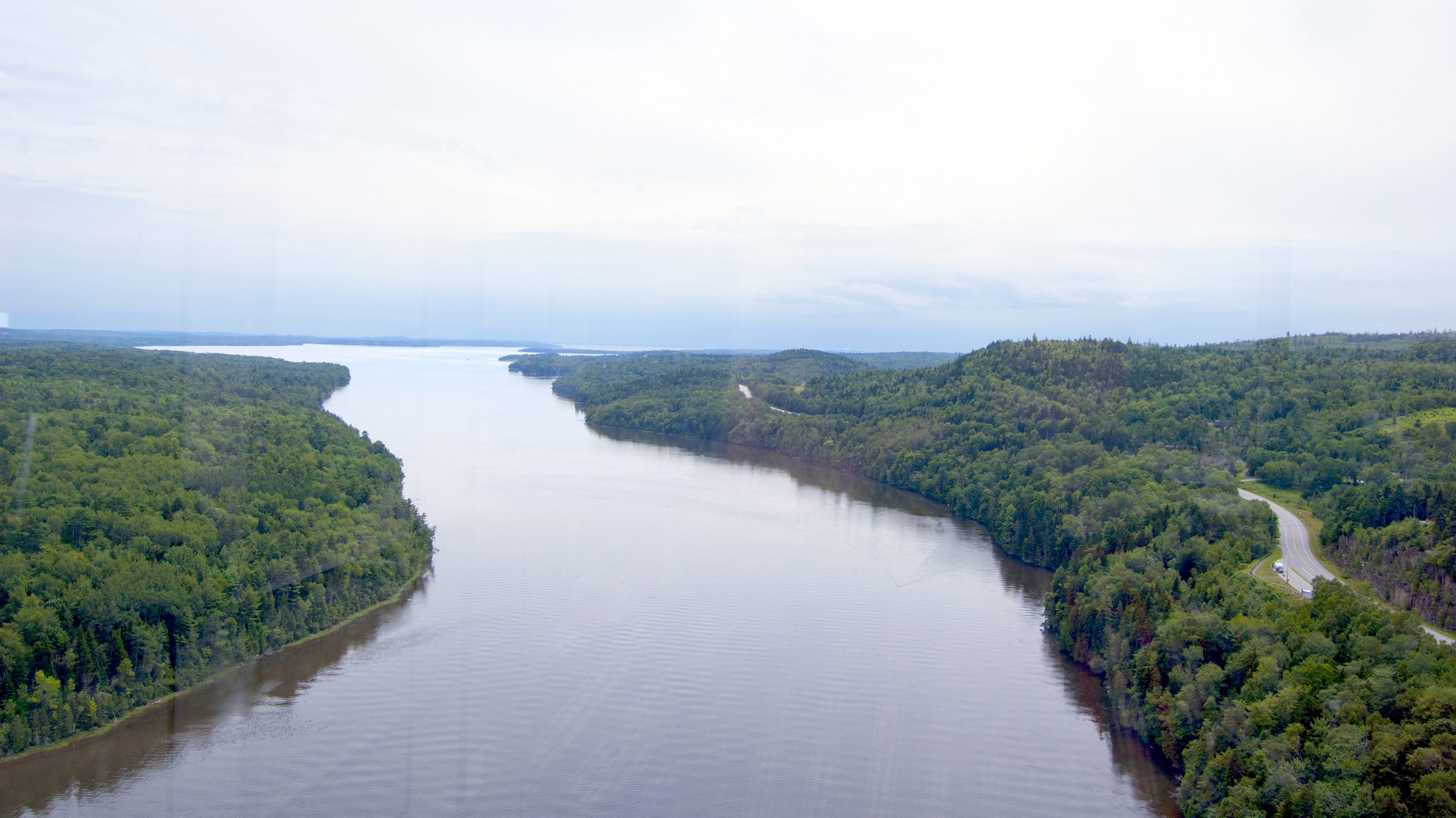
Moose Island, Maine
Moose Island is an island in Eastport, Maine located at the entrance to Cobscook Bay from Passamaquoddy Bay in the Bay of Fundy. It is part of Shackford Head State Park. Connected to the mainland portion of Washington County at Passamaquoddy Pleasant Point Reservation by a causeway, the city of Eastport occupies several islands, including its major land mass, Moose Island. Other islands comprising the city include Carlow Island, Spectacle Island, Goose Island, and Treat Island, along with other islets. Quoddy Village lies at the north-western end of Moose Island, while the city's downtown lies at the eastern end of the island. The Eastport Municipal Airport lies between Quoddy Village and downtown Eastport. History During the War of 1812, British naval forces seized Moose Island while taking control of the entire Maine coast from Penobscot Bay to the St. Croix River. Following the war, the United States relinquished its claim in 1817 on several larger islands in the Bay of Fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastport, Maine
Eastport is a city and archipelago in Washington County, Maine, United States. The population was 1,288 at the 2020 census, making Eastport the least-populous city in Maine. The principal island is Moose Island, which is connected to the mainland by a causeway. Eastport is the easternmost city in the United States (although the nearby town of Lubec is the easternmost municipality). History The native Passamaquoddy Tribe has called this area home for at least 10,000 years. Some archeologists estimate the habitation at 20,000 years. The first known European contact was the St. Croix colony founded by the French explorer Samuel de Champlain in 1604. Near present-day Calais, the unsuccessful Saint Croix Island Acadia settlement predates the first successful English settlement at Jamestown, Virginia, by three years. On June 25, 1604, Champlain and his men spent a long and severe winter on St. Croix Island with no fresh water and diminished supplies. Two-fifths of the men died of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Manan Island
Grand Manan is a Canadian island in the Bay of Fundy. Grand Manan is also the name of an incorporated village, which includes the main island and all of its adjacent islands, except White Head Island. It is governed as a village and is part of the province of New Brunswick. The point on the mainland closest to the island is near the town of Lubec, Maine, the easternmost point of the continental United States, across the Grand Manan Channel. Grand Manan is 32 kilometres south of Blacks Harbour, New Brunswick. Toponymy "Manan" is a corruption of ''mun-an-ook'' or ''man-an-ook'', meaning "island place" or "the island", from the Maliseet-Passamaquoddy-Penobscot First Nations who, according to oral history, used Grand Manan and its surrounding islands as a safe place for the elderly Passamaquoddy during winter months and as a sacred burial place (''ook'' means "people of"). In 1606 Samuel de Champlain sheltered on nearby White Head Island and produced a map calling the island "Manth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islands Of Washington County, Maine
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental and oceanic. There are also artificial islands, which are man-made. Etymology The word ''island'' derives from Middle English ''iland'', from Old English ''igland'' (from ''ig'' or ''ieg'', similarly meaning 'island' when used independently, and -land carrying its contemporary meaning; cf. Dutch ''eiland'' ("island"), German ''Eiland'' ("small island")). However, the spelling of the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Islands Of Maine
This list primarily derives from the Maine Coastal Island Registry, a database of the 3166 coastal islands from the largest (Mount Desert Island) to the smallest islets and ledges exposed above mean high tide. Some notable inland freshwater islands, like Frye Island in Sebago Lake, have been included. Description of columns Registry # refers to the Maine Coastal Island Registry ("MCIR") assigning each island an identifying number. Many islands have the same Island Name (there are over 20 "Bar Islands," for instance; more than 30 named "Little"), but each has a unique number. Some islands comprising more than one landmass have several registry numbers under one name. The table lists Cities, Towns, and Counties primarily as a finding aid, since governmental jurisdiction over Maine islands is rife with confusing historical anomalies. For instance, of Maine's 15 island communities inhabited year-round, eight are independent towns, two are part of one town, three belong to mainland mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penobscot River
The Penobscot River (Abenaki: ''Pαnawάhpskewtəkʷ'') is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed June 22, 2011 river in the U.S. state of Maine. Including the river's West Branch and South Branch increases the Penobscot's length to , making it the second-longest river system in Maine and the longest entirely in the state. Its drainage basin contains . It arises from four branches in several lakes in north-central Maine, which flow generally east. After the uniting of the West Branch with the East Branch at Medway (), the Penobscot flows south, past the city of Bangor, where it becomes navigable. Also at Bangor is the tributary Kenduskeag Stream. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean in Penobscot Bay. It is home to the Penobscot people that live on Indian Island, and considered to be The People's lifeblood. History Norumbega Most historians have accepted the Penobscot region as Jean Allefonsce's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
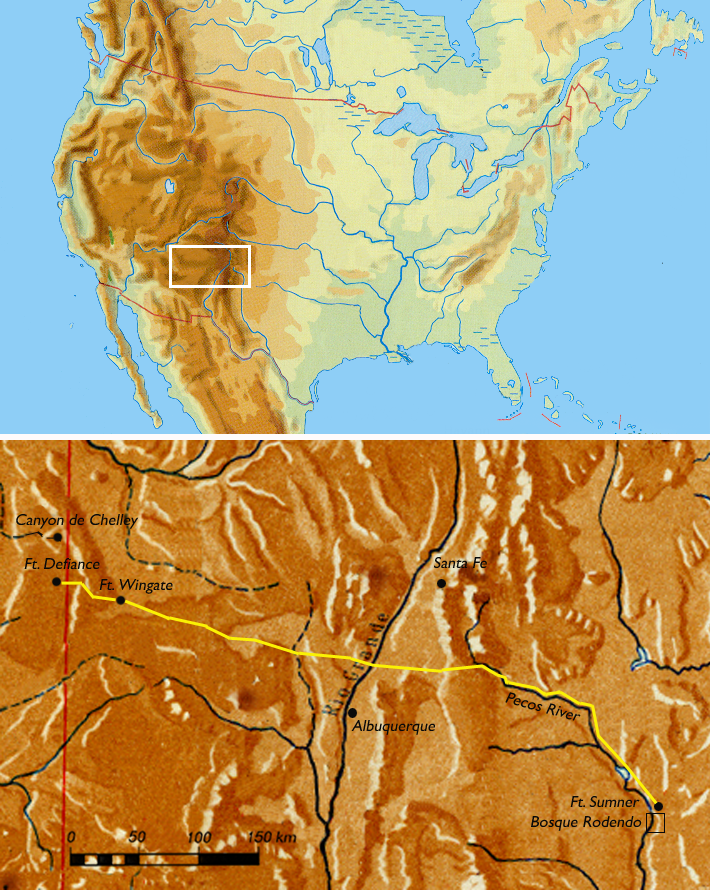
Long Walk Of The Navajo
The Long Walk of the Navajo, also called the Long Walk to Bosque Redondo ( nv, Hwéeldi), was the 1864 deportation and attempted ethnic cleansing of the Navajo people by the United States federal government. Navajos were forced to walk from their land in what is now Arizona to eastern New Mexico. Some 53 different forced marches occurred between August 1864 and the end of 1866. Some anthropologists claim that the "collective trauma of the Long Walk...is critical to contemporary Navajos' sense of identity as a people". Introduction The traditional Navajo homeland spans from Arizona through western New Mexico, where the Navajo had houses, planted crops and raised livestock. There was a long historical pattern in the Southwest of groups or bands raiding and trading with each other, with treaties being made and broken. This included interactions between Navajo, Spanish, Mexican, Pueblos, Apache, Comanche, Ute, and later European Americans. Individual civilians and Native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Mexico
) , population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano) , seat = Santa Fe , LargestCity = Albuquerque , LargestMetro = Tiguex , OfficialLang = None , Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Keres, Zuni , Governor = , Lieutenant Governor = , Legislature = New Mexico Legislature , Upperhouse = Senate , Lowerhouse = House of Representatives , Judiciary = New Mexico Supreme Court , Senators = * * , Representative = * * * , postal_code = NM , TradAbbreviation = N.M., N.Mex. , area_rank = 5th , area_total_sq_mi = 121,591 , area_total_km2 = 314,915 , area_land_sq_mi = 121,298 , area_land_km2 = 314,161 , area_water_sq_mi = 292 , area_water_km2 = 757 , area_water_percent = 0.24 , population_as_of = 2020 , population_rank = 36th , 2010Pop = 2,117,522 , population_density_rank = 45th , 2000DensityUS = 17.2 , 2000Density = 6.62 , MedianHouseholdIncome = $51,945 , IncomeRank = 45th , AdmittanceOrder = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Henry Carleton
James Henry Carleton (December 27, 1814 – January 7, 1873) was an officer in the US Army and a Union general during the American Civil War. Carleton is best known as an Indian fighter in the Southwestern United States. Biography Carleton was born in Lubec, Maine. He was commissioned as a lieutenant in the U.S. Army in 1839, during the Aroostook War, and took part in the Mexican–American War. He served in the 1st U.S. Dragoons in the American West, participating as a lieutenant in an 1844 expedition to the Pawnee and the Oto. One of Carleton's children, Henry Guy Carleton (1852–1910) was a journalist, playwright, and inventor. Mountain Meadows Massacre In May 1859, Maj. Carleton and K Company of the 1st Dragoons out of Fort Tejon, California, were detailed to escort Maj. Henry Prince, a paymaster with government funds, to the Southern Utah Territory. Arriving at Mountain Meadows, the command rendezvoused with the Santa Clara Expedition of the Department of Utah from Camp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maine Central Railroad Company
The Maine Central Railroad Company was a U. S. Class I railroad in central and southern Maine. It was chartered in 1856 and began operations in 1862. By 1884, Maine Central was the longest railroad in New England. Maine Central had expanded to when the United States Railroad Administration assumed control in 1917. The main line extended from South Portland, Maine, east to the Canada–United States border with New Brunswick, and a Mountain Division extended west from Portland to St. Johnsbury, Vermont and north into Quebec. The main line was double track from South Portland to Royal Junction, where it split into a "lower road" through Brunswick and Augusta and a "back road" through Lewiston, which converged at Waterville into single track to Bangor and points east. Branch lines served the industrial center of Rumford, a resort hotel on Moosehead Lake and coastal communities from Bath to Eastport. At the end of 1970, it operated of road on of track; that year it report ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maine State Route 190
State Route 190 (SR 190) is a state highway that travels from Water Street in Eastport to U.S. Route 1 (US 1) in Perry. It serves as the connector route to Eastport from the mainland. Though the road travels in a southeast–northwesterly direction, the road is signed as north–south. Route descriptions The state highway begins at the intersection of Water Street and Washington Street in downtown Eastport. Immediately around this intersection are businesses and the city's post office. SR 190 heads west along Washington Street where it passes numerous houses, churches, and other community buildings. At County Road and Deep Cove Road (the latter of which provides access to Eastport Municipal Airport), SR 190 curves to the north and travels along County Road. The setting becomes more rural and heads in a more northwesterly direction at Clark Street. The road skirts around the east side of Quoddy, a settlement within the city of Eastport. It exits Moose Island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Works Administration
The Public Works Administration (PWA), part of the New Deal of 1933, was a large-scale public works construction agency in the United States headed by Secretary of the Interior Harold L. Ickes. It was created by the National Industrial Recovery Act in June 1933 in response to the Great Depression. It built large-scale public works such as dams, bridges, hospitals, and schools. Its goals were to spend $3.3 billion (about $10 per person in the U.S.) in the first year, and $6 billion (about $18 dollars per person in the U.S.) in all, to supply employment, stabilize buying power, and help revive the economy. Most of the spending came in two waves in 1933–1935 and again in 1938. Originally called the ''Federal Emergency Administration of Public Works'', it was renamed the Public Works Administration in 1935 and shut down in 1944. The PWA spent over $7 billion (about $22 dollars per person in the U.S.) on contracts with private construction firms that did the actual work. It creat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC), the Works Progress Administration (WPA), the Civil Works Administration (CWA), the Farm Security Administration (FSA), the National Industrial Recovery Act of 1933 (NIRA) and the Social Security Administration (SSA). They provided support for farmers, the unemployed, youth, and the elderly. The New Deal included new constraints and safeguards on the banking industry and efforts to re-inflate the economy after prices had fallen sharply. New Deal programs included both laws passed by Congress as well as presidential executive orders during the first term of the presidency of Franklin D. Roosevelt. The programs focused on what historians refer to as the "3 R's": relief for the unemployed and for the poor, recovery of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |