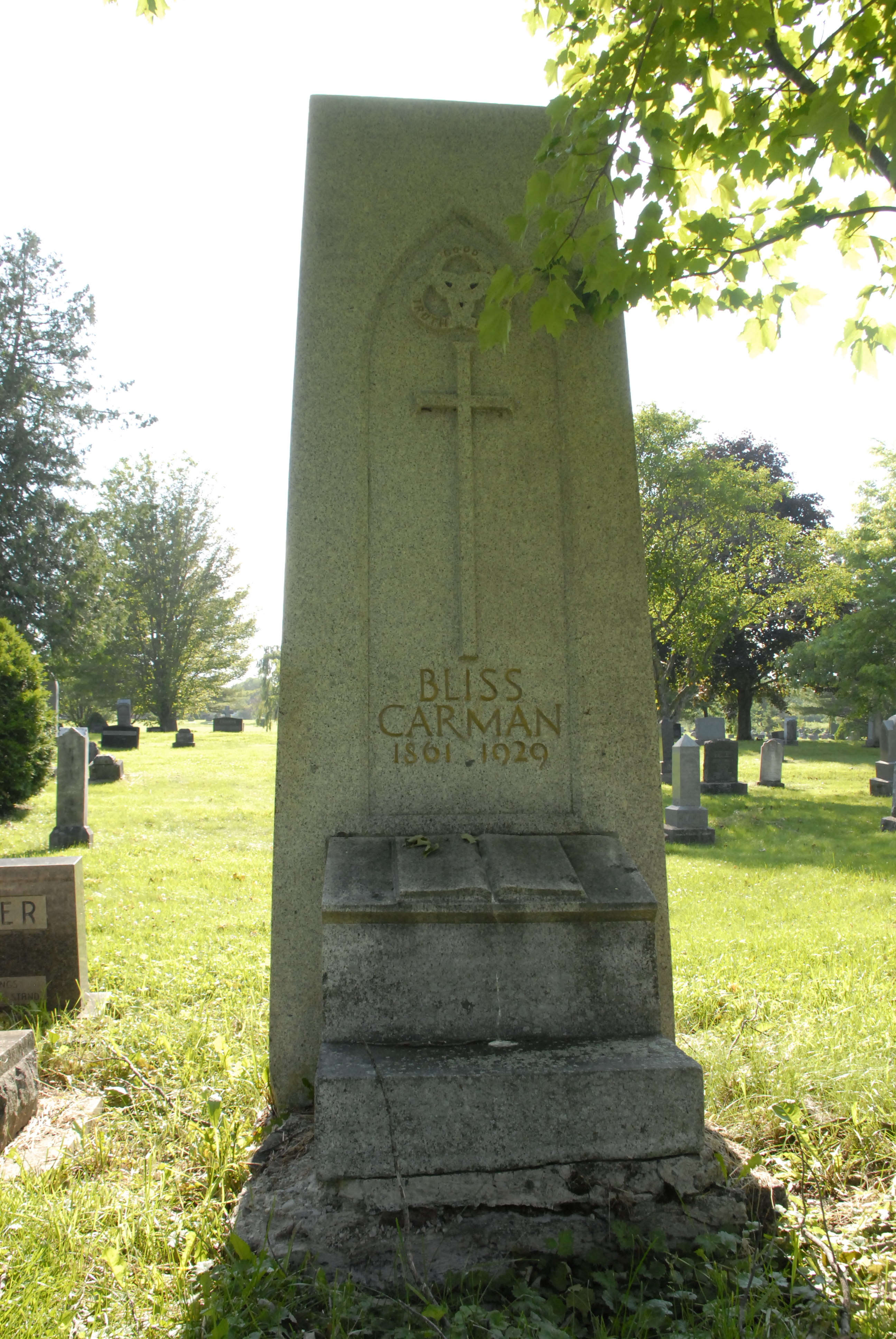|
Montreal Group
The Montreal Group, sometimes referred to as the McGill Group or McGill Movement,Dean Irvine,Montreal Group" ''Oxford Companion to Canadian History''. Answers.com, Web, March 25, 2011. was a circle of Canadian modernist writers formed in the mid-1920s at McGill University in Montreal, Quebec. The Group included Leon Edel, John Glassco, A. M. Klein, Leo Kennedy, F. R. Scott, and A. J. M. Smith, most of whom attended McGill as undergraduates. The group championed the theory and practice of modernist poetry over the Victorian-style versification, exemplified by the Confederation Poets, that predominated in Canadian poetry at the time. The Montreal Group is associated with the rise of the "little magazines", which published contemporary innovative prose and poetry in the style of British and American modernism, and later works from Europe's aesthetic and decadent movements. ''The Encyclopædia Britannica'' credits the group and its members with having "precip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modernist Literature
Literary modernism, or modernist literature, originated in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and is characterized by a self-conscious break with traditional ways of writing, in both poetry and prose fiction writing. Modernism experimented with literary form and expression, as exemplified by Ezra Pound's maxim to "Make it new." This literary movement was driven by a conscious desire to overturn traditional modes of representation and express the new sensibilities of their time. The horrors of the First World War saw the prevailing assumptions about society reassessed, and much modernist writing engages with the technological advances and societal changes of modernity moving into the 20th century. Origins and precursors In the 1880s, increased attention was given to the idea that it was necessary to push aside previous norms entirely, instead of merely revising past knowledge in light of contemporary techniques. The theories of Sigmund Freud (1856–1939), and Ernst Mach (183 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expressionist
Expressionism is a modernist movement, initially in poetry and painting, originating in Northern Europe around the beginning of the 20th century. Its typical trait is to present the world solely from a subjective perspective, distorting it radically for emotional effect in order to evoke moods or ideas. Expressionist artists have sought to express the meaningVictorino Tejera, 1966, pages 85,140, Art and Human Intelligence, Vision Press Limited, London of emotional experience rather than physical reality. Expressionism developed as an avant-garde style before the First World War. It remained popular during the Weimar Republic,Bruce Thompson, University of California, Santa Cruzlecture on Weimar culture/Kafka'a Prague particularly in Berlin. The style extended to a wide range of the arts, including expressionist architecture, painting, literature, theatre, dance, film and music. The term is sometimes suggestive of angst. In a historical sense, much older painters such as Matthia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Waste Land
''The Waste Land'' is a poem by T. S. Eliot, widely regarded as one of the most important poems of the 20th century and a central work of modernist poetry. Published in 1922, the 434-line poem first appeared in the United Kingdom in the October issue of Eliot's ''The Criterion'' and in the United States in the November issue of ''The Dial''. It was published in book form in December 1922. Among its famous phrases are "April is the cruellest month", "I will show you fear in a handful of dust", and the Sanskrit mantra " Shantih shantih shantih". Eliot's poem combines the legend of the Holy Grail and the Fisher King with vignettes of contemporary British society. Eliot employs many literary and cultural allusions from the Western canon such as Ovid's Metamorphoses and Dante's ''Divine Comedy'', as well as Shakespeare, Buddhism, and the Hindu Upanishads. The poem shifts between voices of satire and prophecy featuring abrupt and unannounced changes of speaker, location, and time a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortnightly Review
''The Fortnightly Review'' was one of the most prominent and influential magazines in nineteenth-century England. It was founded in 1865 by Anthony Trollope, Frederic Harrison, Edward Spencer Beesly, and six others with an investment of £9,000; the first edition appeared on 15 May 1865. George Henry Lewes, the partner of George Eliot, was its first editor, followed by John Morley. The print magazine ceased publication in 1954. An online "new series" started to appear in 2009. History ''The Fortnightly Review'' aimed to offer a platform for a range of ideas, in reaction to the highly partisan journalism of its day. Indeed, in announcing the first issue of the ''Fortnightly'' in the ''Saturday Review'' of 13 May 1865, G. H. Lewes wrote, "The object of ''THE FORTNIGHTLY REVIEW'' is to become the organ of the unbiassed expression of many and various minds on topics of general interest in Politics, Literature, Philosophy, Science, and Art." But by the time Lewes left due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorian Era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardian period, and its later half overlaps with the first part of the '' Belle Époque'' era of Continental Europe. There was a strong religious drive for higher moral standards led by the nonconformist churches, such as the Methodists and the evangelical wing of the established Church of England. Ideologically, the Victorian era witnessed resistance to the rationalism that defined the Georgian period, and an increasing turn towards romanticism and even mysticism in religion, social values, and arts. This era saw a staggering amount of technological innovations that proved key to Britain's power and prosperity. Doctors started moving away from tradition and mysticism towards a science-based approach; medicine advanced thanks to the adoption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Dudek
Louis Dudek, (February 6, 1918 – March 23, 2001) was a Canadians, Canadian poet, academic, and publisher known for his role in defining Modernism in poetry, and for his literary criticism. He was the author of over two dozen books. In ''A Digital History of Canadian Poetry,'' writer Heather Prycz said that "As a critic, teacher and theoretician, Dudek influenced the teaching of Canadian poetry in most [Canadian] schools and universities". Life Dudek was born in Montreal, Quebec, the son of Vincent and Stanislawa Dudek, part of an extended Catholic family which had emigrated from Poland, and was raised in that city's East End.William H. New,Dudek, Louis" ''Encyclopedia of Literature in Canada'' (Toronto: U of Toronto P, 2002), 316-317, Google Books, Web, May 6, 2011. He was lean and sickly as a child, which made him introverted and hypersensitive. His mother died at 31, when he was eight. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Verse
Free verse is an open form of poetry, which in its modern form arose through the French ''vers libre'' form. It does not use consistent meter patterns, rhyme, or any musical pattern. It thus tends to follow the rhythm of natural speech. Definition Free verse does not "proceed by a strict set of rules … is not a literary type, and does not conform to a formal structure." It is not considered to be completely free. In 1948, Charles Allen wrote, "The only freedom cadenced verse obtains is a limited freedom from the tight demands of the metered line." Free verse contains some elements of form, including the poetic line, which may vary freely; rhythm; strophes or strophic rhythms; stanzaic patterns and rhythmic units or cadences. It is said that verse is free "when it is not primarily obtained by the metered line." Donald Hall goes as far as to say that "the ''form'' of free verse is as binding and as liberating as the ''form'' of a rondeau," and T. S. Eliot wrote, "No verse is fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorothy Livesay
Dorothy Kathleen May Livesay, (October 12, 1909 – December 29, 1996) was a Canadian poet who twice won the Governor General's Award in the 1940s, and was "senior woman writer in Canada" during the 1970s and 1980s.Mathews, R.D.. "Dorothy Livesay". ''The Canadian Encyclopedia'', 16 December 2013, ''Historica Canada''. https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/dorothy-livesay. Accessed 15 May 2020. Life Livesay was born in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Her mother, Florence Randal Livesay, was a poet and journalist; her father, J.F.B. Livesay was the General Manager of Canadian Press. Livesay moved to Toronto, Ontario, with her family in 1920. She graduated with a BA in 1931 from Trinity College in the University of Toronto and received a diploma from the University of Toronto's Faculty of Social Work in 1934. She also studied at the University of British Columbia and the Sorbonne. In 1931 in Paris, Livesay became a committed Communist. She joined the Communist Party of Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond Knister
John Raymond Knister (27 May 1899 – 29 August 1932) was a Canadian poetry, Canadian poet, novelist, story writer, columnist, and reviewer, "known primarily for his Realistic fiction, realistic narratives set in rural Canada ... Knister was a highly respected member of the Canadians, Canadian literary community during the 1920s and early 1930s, and recent criticism has acknowledged him as a pioneer in establishing a distinctively modern voice in Canadian literature."Raymond Knister 1899–1932 " Twentieth-Century Literary Criticism, eNotes.com, Web, Apr. 1, 2011. Life Born at Ruscom (now part of Lakeshore, Ontario, Lakeshore), Ontario, near Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Knister attended Victoria University, Toronto, Victoria College at the University of Toronto,[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duncan Campbell Scott
Duncan Campbell Scott (August 2, 1862 – December 19, 1947) was a Canadian civil servant and poet and prose writer. With Charles G.D. Roberts, Bliss Carman, and Archibald Lampman, he is classed as one of Canada's Confederation Poets. A career civil servant, Scott served as deputy superintendent of the Department of Indian Affairs from 1913 to 1932. Life and legacy Scott was born in Ottawa, Ontario, the son of Rev. William Scott, a Methodist preacher, and Janet MacCallum. He was educated at Stanstead Wesleyan College. Early in life, he became an accomplished pianist. Scott wanted to be a doctor, but family finances were precarious, so in 1879 he joined the federal civil service. William Scott might not have money uthe had connections in high places. Among his acquaintances was the prime minister, Sir John A. Macdonald, who agreed to meet with Duncan. As chance would have it, when Duncan arrived for his interview, the prime minister had a memo on his desk from the Indian B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archibald Lampman
Archibald Lampman (17 November 1861 – 10 February 1899) was a Canadian poet. "He has been described as 'the Canadian Keats;' and he is perhaps the most outstanding exponent of the Canadian school of nature poets." ''The Canadian Encyclopedia'' says that he is "generally considered the finest of Canada's late 19th-century poets in English." Lampman is classed as one of Canada's Confederation Poets, a group which also includes Charles G.D. Roberts, Bliss Carman, and Duncan Campbell Scott. Life Archibald Lampman was born at Morpeth, Ontario, a village near Chatham, the son of Archibald Lampman, an Anglican clergyman. "The Morpeth that Lampman knew was a small town set in the rolling farm country of what is now western Ontario, not far from the shores of Lake Erie. The little red church just east of the town, on the Talbot Road, was his father's charge." In 1867 the family moved to Gore's Landing on Rice Lake, where young Archie Lampman attended at the Barron's School.Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bliss Carman
William Bliss Carman (April 15, 1861 – June 8, 1929) was a Canadian poet who lived most of his life in the United States, where he achieved international fame. He was acclaimed as Canada's poet laureate during his later years. In Canada, Carman is classed as one of the Confederation Poets, a group which also included Charles G.D. Roberts (his cousin), Archibald Lampman, and Duncan Campbell Scott. "Of the group, Carman had the surest lyric touch and achieved the widest international recognition. But unlike others, he never attempted to secure his income by novel writing, popular journalism, or non-literary employment. He remained a poet, supplementing his art with critical commentaries on literary ideas, philosophy, and aesthetics." Life William Bliss Carman was born on April 15, 1861 in Fredericton, New Brunswick. "Bliss" was his mother's maiden name. He was the great grandson of United Empire Loyalists who fled to Nova Scotia after the American Revolution, settling in New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)