|
Montech
Montech (; ) is a commune in the Tarn-et-Garonne department in the Occitanie region in southern France. On the Canal de Garonne is the unique Montech water slope, a type of canal inclined plane built in 1974. The slope has been out of service since an engine failure in 2009. Population History Middle Ages In 1134, on the initiative of Raymond Séradis and d'Alphonse Jourdain, Count of Toulouse, Montech became a fortified site, a Castrum, whose function was to better protect the North of Toulouse. Ten years before Montauban a count's castle was built nearby, around which a new town developed. To the south-east, the castle is integrated with a system of fortifications which are surrounded by deep ditches. The plan adopted for this new town corresponds to a bastide-type plan (the bastides were built in the 13th century) with streets crossing at right angles, a central square, fortified gates with a drawbridge at the cardinal points which became the only access routes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
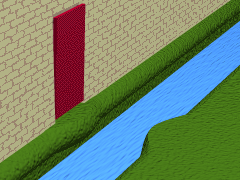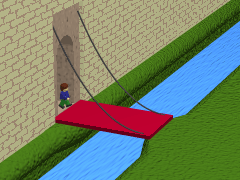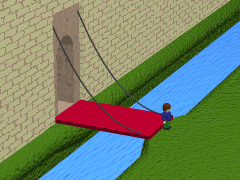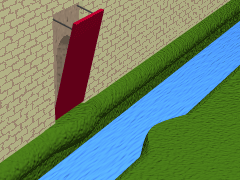
Montech Water Slope
The Montech water slope is a type of canal inclined plane built on the Canal de Garonne, in the commune of Montech, Tarn-et-Garonne, Southwest France. It is managed by the publicly owned Voies navigables de France and by-passes a series of five Lock (water navigation), locks. The slope is used for larger vessels up to 40 metres in length, while smaller boats continue to use the locks. The slope has been out of service since an engine failure in 2009, and was scheduled to reopen in the summer of 2020 but in 2023 was still not working. Operating principles The principle of the water slope is based on a sloping channel up or down which a wedge of water retained by an (almost) watertight gate is moved. This technique was invented in the 19th century by the German engineer Julius Greve and described by the French engineer Jean Aubert (engineer), Jean Aubert in 1961. The Montech water slope was inaugurated in July 1974. An evenly sloping concrete channel is fitted with a gate at the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal De Garonne
The Garonne Canal (, ) or Canal de Garonne () is a French canal dating from the mid-19th century that connects Toulouse to Castets-en-Dorthe. The remainder of the route to Bordeaux uses the river Garonne. It is the continuation of the Canal du Midi which connects the Mediterranean with Toulouse. Together, they and the Garonne form the Canal des Deux Mers which connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Atlantic Ocean. Geography Description The canal runs along the right bank of the Garonne, crosses the river in Agen via the Agen aqueduct, then continues along the left bank. It is connected to the Canal du Midi at its source in Toulouse, and emerges at Castets-en-Dorthe on the Garonne, 54 km southwest of Bordeaux, a point where the river is navigable. The canal is supplied with water from the Garonne by two sources: * The Canal de Brienne in Toulouse, taking up to 7 m3/s from the river Garonne upstream of Bazacle dam * The Brax pumping station near Agen. With the exception ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarn-et-Garonne
Tarn-et-Garonne (; ) is a Departments of France, department in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania Regions of France, region in Southern France. It is traversed by the rivers Tarn (river), Tarn and Garonne, from which it takes its name. The area was originally part of the former Provinces of France, provinces of Quercy and Languedoc. The department was created in 1808 under Napoleon, with territory taken from the neighbouring Lot (department), Lot, Haute-Garonne, Lot-et-Garonne, Gers and Aveyron departments. The department is mostly rural with fertile agricultural land in the broad river valley, but there are hilly areas to the south, east and north. The departmental Prefectures in France, prefecture is Montauban; the sole Subprefectures in France, subprefecture is Castelsarrasin. In 2019, it had a population of 260,669. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of Tarn-et-Garonne
The following is a list of the 195 Communes of France, communes of the Tarn-et-Garonne Departments of France, department of France. The communes cooperate in the following Communes of France#Intercommunality, intercommunalities (as of 2025):Périmètre des groupements en 2025 BANATIC. Accessed 28 May 2025. *Communauté d'agglomération Grand Montauban *Communauté de communes des Deux Rives (partly) *Communauté de communes Grand Sud Tarn-et-Garonne *Communauté de communes de la Lomagne Tarn-et-Garonnaise *Communauté de communes du Pays de Lafrançaise *Communauté de communes du Pays de Serres en Quercy *Communauté de communes du Quercy Caussadais *Communauté de communes du Quercy Rouergue et des gorges de l'Aveyron (partly) *Communauté de communes Quercy Vert-Aveyron *Communauté de communes Terres des Conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Abbal
André Abbal (1876–1953) was a French sculptor. He was commissioned to work on several war memorials. He is best known as a pioneer of "Direct carving" and became known as "''L'Apôtre de la Taille Directe''" (the apostle of direct carving). Biography Born in Montech in the Tarn-et-Garonne department, the son and grandson of stonemasons, Abbal's parents were Léon Armand Abbal, who practiced as a sculptor, and Jeanne Cousteau. His paternal grandfather was Jacques Abbal, who worked with Violet-le-Duc restoring religious monuments. Abbal studied at the École des Beaux-Arts in Toulouse, then the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris where he was taught by Alexandre Falguière and Antonin Mercié. He was a frequent exhibitor at the Salon des Artistes Français, won the Chenavard prize twice, and was awarded two gold medals. Abbal was an advocate of "Direct carving". In 1913 he first submitted a work which had been carved directly into stone, without the convention of starting with a mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of The Tarn-et-Garonne Department
The following is a list of the 195 communes of the Tarn-et-Garonne department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025):Périmètre des groupements en 2025 BANATIC. Accessed 28 May 2025. * Communauté d'agglomération Grand Montauban * Communauté de communes des Deux Rives (partly) * Communauté de communes Grand Sud Tarn-et- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastide
Bastides are fortified new towns built in medieval Languedoc, Gascony, Aquitaine, England and Wales during the 13th and 14th centuries, although some authorities count Mont-de-Marsan and Montauban, which was founded in 1144, as the first bastides.:fr:Bastide (ville), Bastide in the French Wikipedia, retrieved March 8, 2007. Some of the first bastides were built under Raymond VII of Toulouse to replace villages destroyed in the Albigensian Crusade. He encouraged the construction of others to colonize the wilderness, especially of southwest France. Almost 700 bastides were built between 1222 (Cordes-sur-Ciel, Tarn) and 1372 (La Bastide d'Anjou, Tarn). History were developed in number under the terms of the Treaty of Paris (1229), which permitted Raymond VII of Toulouse to build new towns in his shattered domains but not to fortify them. When the Capetian Alphonse of Poitiers inherited, under a marriage stipulated by the treaty, this " founder of unparalleled energy" consolidated h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Wars Of Religion
The French Wars of Religion were a series of civil wars between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants (called Huguenots) from 1562 to 1598. Between two and four million people died from violence, famine or disease directly caused by the conflict, and it severely damaged the power of the French monarchy. One of its most notorious episodes was the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre in 1572. The fighting ended with a compromise in 1598, when Henry of Navarre, who had converted to Catholicism in 1593, was proclaimed Henry IV of France, King Henry IV of France and issued the Edict of Nantes, which granted substantial rights and freedoms to the Huguenots. However, Catholics continued to disapprove of Protestants and of Henry, and his assassination in 1610 triggered a fresh round of Huguenot rebellions in the 1620s. Tensions between the two religions had been building since the 1530s, exacerbating existing regional divisions. The death of Henry II of France in J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choir (architecture)
A choir, also sometimes called quire, is the area of a church or cathedral that provides seating for the clergy and church choir. It is in the western part of the chancel, between the nave and the sanctuary, which houses the altar and Church tabernacle. In larger medieval churches it contained choir-stalls, seating aligned with the side of the church, so at right-angles to the seating for the congregation in the nave. Smaller medieval churches may not have a choir in the architectural sense at all, and they are often lacking in churches built by all denominations after the Protestant Reformation, though the Gothic Revival revived them as a distinct feature. As an architectural term "choir" remains distinct from the actual location of any singing choir – these may be located in various places, and often sing from a choir-loft, often over the door at the liturgical western end. In modern churches, the choir may be located centrally behind the altar, or the pulpit. The place w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type building, the strict definition of the term "nave" is restricted to the central aisle. In a broader, more colloquial sense, the nave includes all areas available for the lay worshippers, including the side-aisles and transepts.Cram, Ralph Adams Nave The Catholic Encyclopedia. Vol. 10. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1911. Accessed 13 July 2018 Either way, the nave is distinct from the area reserved for the choir and clergy. Description The nave extends from the entry—which may have a separate vestibule (the narthex)—to the chancel and may be flanked by lower side-aisles separated from the nave by an arcade. If the aisles are high and of a width comparable to the central nave, the structure is sometimes said to have three nave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drawbridge
A drawbridge or draw-bridge is a type of moveable bridge typically at the entrance to a castle or tower surrounded by a moat. In some forms of English, including American English, the word ''drawbridge'' commonly refers to all types of moveable bridges, such as bascule bridges, vertical-lift bridges and swing bridges, but this article concerns the narrower historical definition where the bridge is used in a defensive structure. As used in castles or defensive structures, drawbridges provide access across defensive structures when lowered, but can quickly be raised from within to deny entry to an enemy force. Castle drawbridges Middle Ages, Medieval castles were usually defended by a ditch or moat, crossed by a wooden bridge. In early castles, the bridge might be designed to be destroyed or removed in the event of an attack, but drawbridges became very common. A typical arrangement would have the drawbridge immediately outside a gatehouse, consisting of a wooden Deck (bridge), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
A () is a level of administrative divisions of France, administrative division in the France, French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipality, municipalities in Canada and the United States; ' in Germany; ' in Italy; ' in Spain; or civil parishes in the United Kingdom. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlet (place), hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the Municipal arrondissem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |