|
Monte Bolca
Monte Bolca is a lagerstätte near Verona, Italy that was one of the first fossil sites with high quality preservation known to Europeans, and is still an important source of fossils from the Eocene. Geology Monte Bolca was uplifted from the Tethys Ocean floor during the formation of the Alps, in two stages: one 24 million years ago, and one between 30 and 50 million years ago. The entire formation consists of of limestone, all of which contain fossils, but interspersed in which are the lagerstätte layers that contain the highly preserved specimens. Within these layers, the fish and other specimens are so highly preserved that their organs are often completely intact in fossil form, and even the skin colorWilliams, MattTaphonomy of Monte Bolca University of Bristol can sometimes be determined. The normal rearrangement of the specimens caused by mud-dwelling organisms in the layer before it turned to stone has been avoided—it is assumed that the mud in question was low in ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturkundemuseum Berlin - Archaeophis Proavus Massalongo - Monte Bolca
The Natural History Museum (german: Museum für Naturkunde) is a natural history museum located in Berlin, Germany. It exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history and in such domain it is one of three major museums in Germany alongside ''Naturmuseum Senckenberg'' in Frankfurt and ''Museum Koenig'' in Bonn. The museum houses more than 30 million Zoology, zoological, Paleontology, paleontological, and Mineralogy, mineralogical specimens, including more than ten thousand type specimens. It is famous for two exhibits: the largest mounted dinosaur in the world (a ''Giraffatitan'' skeleton), and a well-preserved specimen of the earliest known bird, ''Archaeopteryx''. The museum's mineral collections date back to the Prussian Academy of Sciences of 1700. Important historic zoological specimens include those recovered by the German deep-sea Valdiva expedition (1898–99), the German Southpolar Expedition (1901–03), and the German Sunda Expedition (1929� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eolactoria
''Eolactoria sorbinii'' is an extinct prehistoric boxfish that lived during the Lutetian epoch of the middle Eocene, in Monte Bolca. It had two pairs of long spines, one over each eye, and one pair beneath the anal and caudal fins, arranged very similarly to those possessed by the modern genus ''Lactoria'' (e.g., "cowfish"), but were, in comparison, much longer. ''E. sorbinii'' had a fifth spine between the two eye-spines, arranged and looking very much like a nose. The only known fossil specimen is about 5 cm (2 in) long. See also * ''Proaracana'' another boxfish that lived in Monte Bolca * ''Oligolactoria'' a possible descendant from the Oligocene * Prehistoric fish The evolution of fish began about 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion. It was during this time that the early chordates developed the skull and the vertebral column, leading to the first craniates and vertebrates. The first fis ... * List of prehistoric bony fish References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mene Oblonga
''Mene oblonga'' is a species of ray-finned fish that first appeared in the Monte Bolca Lagerstatten during the Lutetian epoch of the Eocene. For a menid, it has a very shallow body, especially in comparison with the sympatric '' Mene rhombea''. Its fossils are very rare in Monte Bolca. A single fossil from the early Oligocene, referred to as "''Mene oblonga'' var. ''pusilla''," was found in Chiavon, Italy Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical .... References"A new species of Mene (Perciformes: Menidae) from the Paleocene of South America, with notes on paleoenvironment and a brief review of menid fishes." Menidae Eocene fish Oligocene fish Rupelian species extinctions Prehistoric life of Europe {{paleo-perciformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mene Rhombea
''Mene rhombea'' is an extinct perciform fish belonging to the family Menidae. During the Middle Eocene (Lutetian epoch), about 48 to 40 mya, these fishes lived in the Tethys Ocean, a large tropical sea in the area corresponding to the current Mediterranean. This ocean was extended between the continents of Gondwana and Laurasia. At this time, where Monte Bolca is today, ''M. rhombea'', and its relative, '' M. oblonga'', lived in a tropical lagoon. Description ''Mene rhombea'' had a laterally compressed body, very long and slim pelvic fins and a wide triangular tail fin. As suggested by their fossils' small, upturned mouths, and by comparison of its living relative, as ''Mene maculata'', fishes of this species were planktivore. The species shows close affinities with contemporary species inhabiting the coral reef environment of the Indo-Pacific warm seas. Distribution Their greatly valued fossils comes from the laggerstat Monte Bolca, about 30 kilometres north-east of Verona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
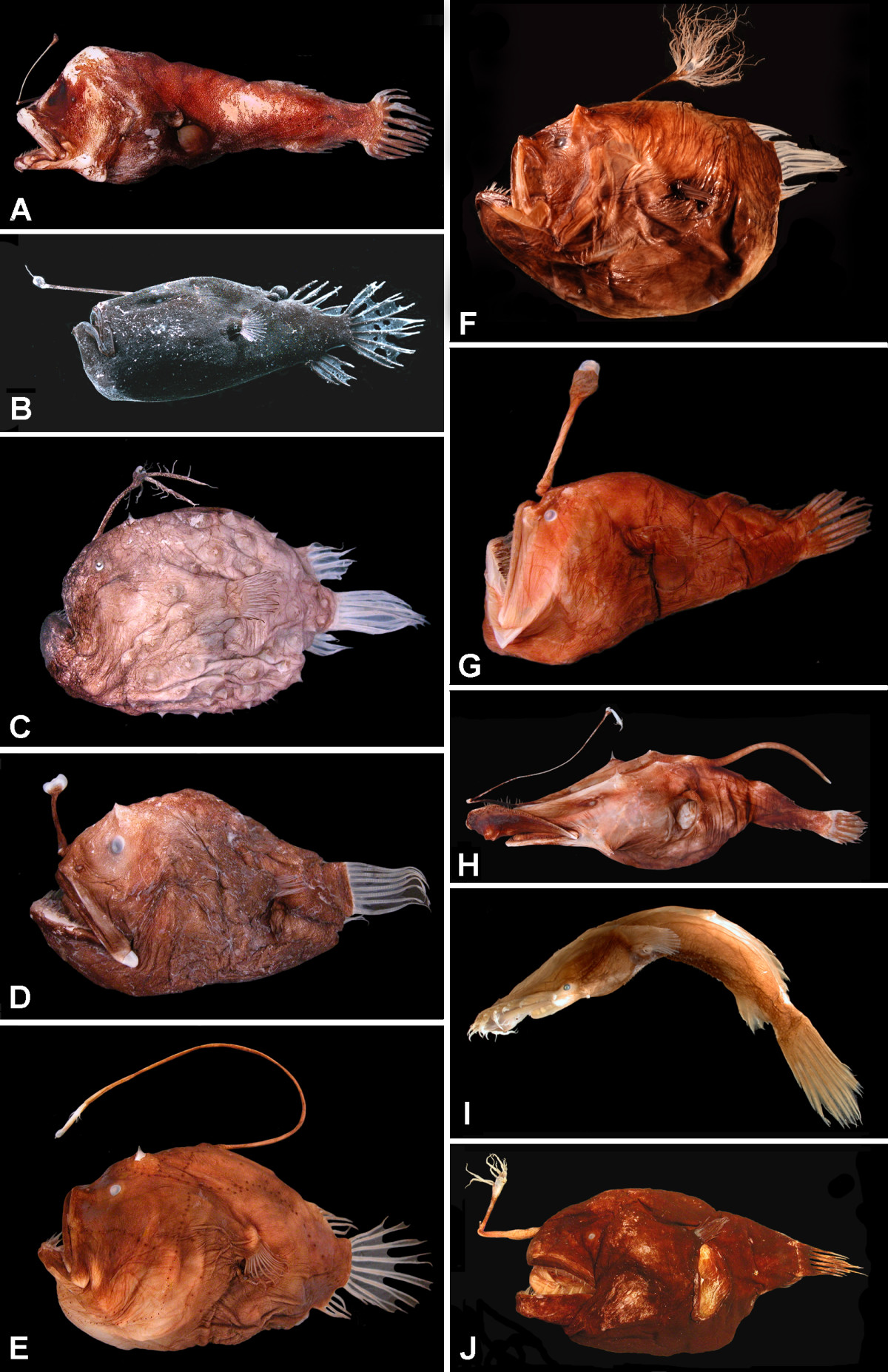
Anglerfish
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence comes from symbiotic bacteria, which are thought to be acquired from seawater, that dwell in and around the sea. Some anglerfish are notable for extreme sexual dimorphism and sexual symbiosis of the small male with the much larger female, seen in the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep sea anglerfish. In these species, males may be several orders of magnitude smaller than females. Anglerfish occur worldwide. Some are pelagic (dwelling away from the sea floor), while others are benthic (dwelling close to the sea floor). Some live in the deep sea (such as the Ceratiidae), while others on the continental shelf, such as the frogfishes and the Lophiidae (monkfish or goosefish). Pelagic forms are most often laterally compressed, whereas the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophius Brachysomus
''Lophius brachysomus'' is an extinct species of anglerfish in the family Lophiidae. It was described by Louis Agassiz in 1835 from the Monte Bolca locality. It became extinct during the middle Eocene (lowermost Lutetian). Species known from three or four individuals. Habitat of this species described as place in a tropical or subtropical, moderately deep basin like a coastal lagoon in inner continental shelf regions of the central Tethys Sea, with reduced hydrodynamic energy and episodic anoxic conditions, with soft mud or sand bottoms, much like extant members of the family. Together with '' Sharfia mirabilis'' this species is one of the oldest member of the family Lophiidae known to date. It was stated to have large triangular opercles, a facial support structure and protective covering for the gills of many bony fish, with concave anterior and anteroventral margins and a peculiar cancellous texture on its medial surface, as seen through its fossilized remains. Type spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile Perch
The Nile perch (''Lates niloticus''), also known as the African snook, Goliath perch, African barramundi , Goliath barramundi, Giant lates or the Victoria perch, is a species of freshwater fish in family Latidae of order Perciformes. It is widespread throughout much of the Afrotropical realm, being native to the Congo, Nile, Senegal, Niger and Lake Chad, Volta, Lake Turkana, and other river basins. It also occurs in the brackish waters of Lake Maryut in Egypt. The Nile perch is a fish of substantial economic and food-security importance in East Africa. Originally described as ''Labrus niloticus,'' among the marine wrasses, the species has also been referred to as ''Centropomus niloticus''. Common names include African snook, Victoria perch (a misleading trade name, as the species is not native to Lake Victoria, though they have been introduced there), and many local names in various African languages, such as the Luo name ''mbuta'' or ''mputa''. In Tanzania, it is called '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lates
''Lates'' is a genus of freshwater and euryhaline lates perches belonging to the family Latidae. The generic name is also used as a common name, lates, for many of the species. All species are predatory, and the Nile perch (''L. niloticus''), in particular, has become infamous as an invasive species introduced into the East African Lake Victoria, where many native Haplochromines were driven extinct. In contrast to the widespread Barramundi and Nile perch (though the fish does face threats from human activity), several members of the genus ''Lates'' with relatively restricted African or Asian distributions are themselves considered threatened. Etymology The generic name ''Lates'' derives from the Latin ''latēre'' (to be hidden). Description These fishes range in size from less than in maximum overall length, the largest species reaching weights up to . They all have the characteristic centropomid shape, with the two-part dorsal fin and general percoid form. All species are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuna
A tuna is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae (mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bullet tuna (max length: , weight: ) up to the Atlantic bluefin tuna (max length: , weight: ), which averages and is believed to live up to 50 years. Tuna, opah and mackerel sharks are the only species of fish that can maintain a body temperature higher than that of the surrounding water. An active and agile predator, the tuna has a sleek, streamlined body, and is among the fastest-swimming pelagic fish – the yellowfin tuna, for example, is capable of speeds of up to . Greatly inflated speeds can be found in early scientific reports and are still widely reported in the popular literature. Found in warm seas, the tuna is commercially fished extensively as a food fish, and is popular as a bluewater game fish. As a result of overfishing, some tuna species, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spadefish
Ephippidae is a family containing the spadefishes, with about eight genera and a total of 20 marine species. Well-known species include the Atlantic spadefish (''Chaetodipterus faber'') and the reef-dwelling genus ''Platax'', the batfishes, which are kept as aquarium fish. They are spade-shaped and laterally compressed, and have very symmetrical, triangular dorsal and anal fins. They are shiny silver with areas of yellow and vertical brown or black banding. The eyes are often located in one of the vertical bands as a method of camouflage. Scuba divers sometimes mistake them for angelfish, which are similar in shape, but not closely related. Other genera in the family are characterized by long, trailing, pointed dorsal and anal fins. Most species feed primarily on algae and small invertebrates. Some spadefishes are popular sport fishing catches. The Atlantic spadefish (''Chaetodipterus faber''), for example, is a black and white striped fish common just offshore in the southeaster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exellia Velifer
''Exellia'' is a genus of extinct spadefish that lived in the Tethys Ocean during the early Paleogene. The adult form is shaped akin to a large spadefish or a short dolphinfish, with very large pelvic fins, and a long dorsal fin starting from in front of the eyes to near the base of the caudal peduncle. The juvenile form resembles a juvenile drumfish, with the dorsal fin forming a long crest on top of the head. The earlier species, ''E. proxima'', is known from the Danata Formation Lagerstätten from the Late Paleocene of Turkmenistan. The latter-occurring species, ''E. velifer'', is the better studied species, and is known from numerous adult and juvenile specimens from the Middle Eocene Monte Bolca Lagerstätten. Most researchers regard ''Exellia'' as a spadefish, though, some remove this genus, and the related ''Eoluvarus'' to a separate family Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |