|
Montauban Cathedral
Montauban Cathedral (French language, French: ''Cathédrale Notre-Dame-de-l'Assomption de Montauban'') is a Roman Catholic cathedral and a Monument historique, national monument of France located in the town of Montauban. It is the seat of the Bishopric of Montauban, created in 1317, abolished by the Concordat of 1801 and transferred to the Archdiocese of Toulouse, and restored in 1822. The cathedral of Montauban was Protestant from the start of the French Wars of Religion, Wars of Religion until Catholicism returned to Montauban in 1629. The construction of a new church, the present building, was agreed after the revocation of the Edict of Nantes in 1685. The cornerstone of the new cathedral was laid in 1692, and the church was consecrated in 1739. Initially, the architect François d'Orbay supervised the works. When he died in 1697, he was succeeded by Jules Hardouin-Mansart and Robert de Cotte. The towers frame the west façade, a pure product that applies all the conventions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montauban
Montauban (, ; oc, Montalban ) is a commune in the Tarn-et-Garonne department, region of Occitania, Southern France. It is the capital of the department and lies north of Toulouse. Montauban is the most populated town in Tarn-et-Garonne, and the sixth most populated of Occitanie behind Toulouse, Montpellier, Nîmes, Perpignan and Béziers. In 2019, there were 61,372 inhabitants, called ''Montalbanais''. The town has been classified ''Ville d’art et d’histoire'' (City of art and history) since 2015. The town, built mainly of a reddish brick, stands on the right bank of the Tarn at its confluence with the Tescou. History Montauban is the second oldest (after Mont-de-Marsan) of the ''bastides'' of southern France. Its foundation dates from 1144 when Count Alphonse Jourdain of Toulouse, granted it a liberal charter. The inhabitants were drawn chiefly from Montauriol, a village which had grown up around the neighbouring monastery of St Théodard. In the 13th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François D'Orbay
François d'Orbay (1634–1697) was a French draughtsman and architect who worked closely with Louis Le Vau and Jules Hardouin Mansart. Early training and career D'Orbay was born in Paris and likely received his early training as an architect from his father, who was a master mason and entrepreneur. In the late 1650s he became an assistant to the architect Louis Le Vau, when the latter was working on the Château de Vincennes.Berger 1998. In 1660 Le Vau sent d'Orbay to Rome for further study. While in Rome, d'Orbay created an ambitious but unexecuted design for a stair in front of the Trinità dei Monti, as well as three buildings adjacent to the church. He probably returned to Paris before the end of 1660. Commissioned by Anne of Austria, d'Orbay designed and built the entrance to the church of the convent of the Prémontrés de la Croix-Rouge in 1662. A friend, the sculptor Étienne Le Hongre, executed the patron's coat of arms and the bas-relief of the attic (''The Euchar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Vow Of Louis XIII
''The Vow of Louis XIII'' is an 1824 painting by Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres, now in Montauban Cathedral. The oil painting shows a vow to the Virgin Mary by Louis XIII of France. It was commissioned by France's Ministry of Interior in August 1820 for the cathedral of Notre-Dame in Montauban.Tinterow and Conisbee 1999, p. 548.Rosenblum 1986, p. 126. The subject of the painting was to be Louis XIII's vow in 1638 to consecrate his kingdom to the Virgin in Her Assumption.Arikha 1986, pp. 55–56. When Ingres accepted the commission, he was living in Florence. Although he had experienced success as a portrait painter, his ambition was to establish a reputation in the more prestigious genre of history painting. He went to work with his usual diligence, and spent four years bringing the large canvas to completion. He traveled to Paris with it in October 1824. It was a critical success at that year's Salon and later established Ingres' reputation as the main representative of classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
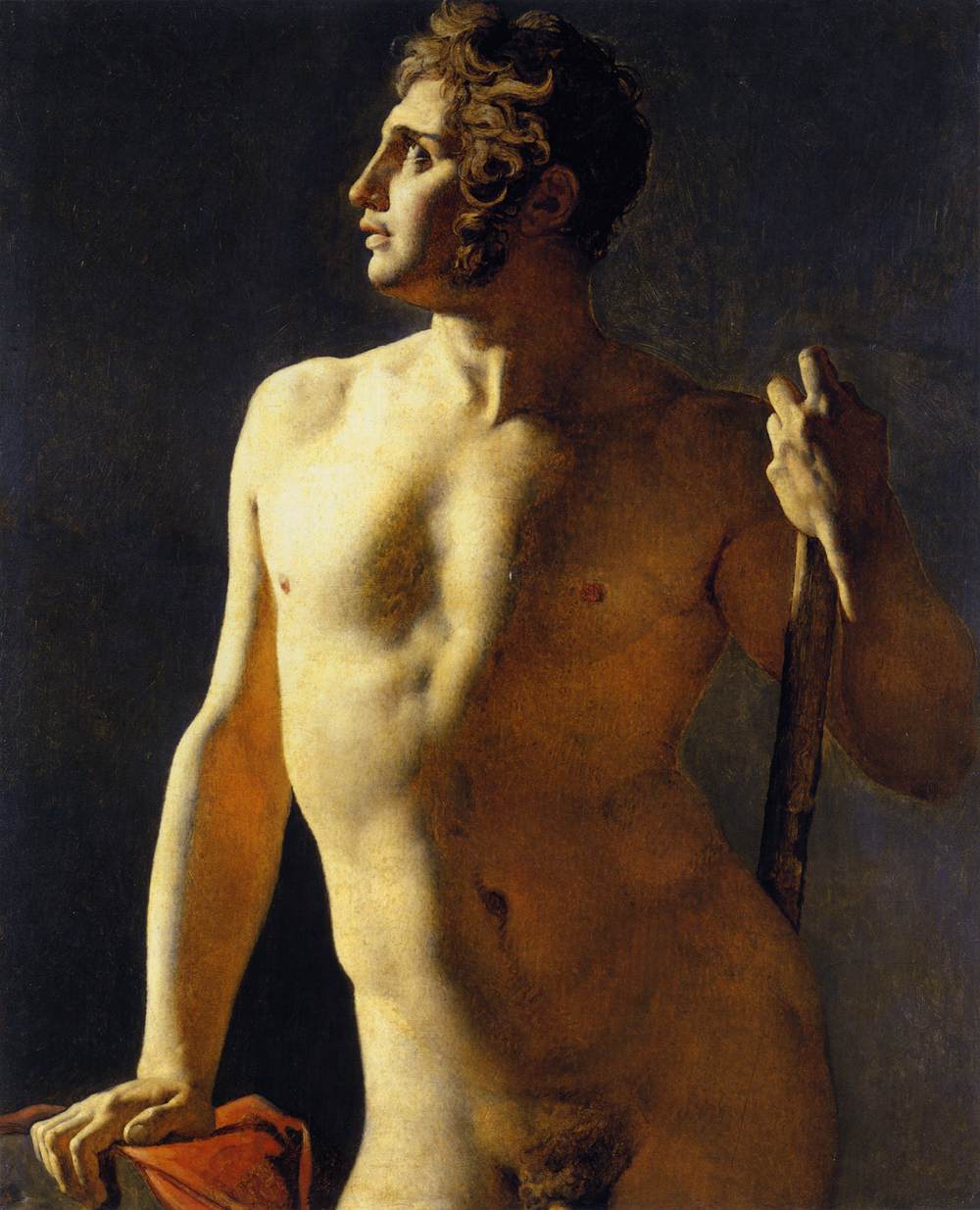
Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres
Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres ( , ; 29 August 1780 – 14 January 1867) was a French Neoclassical painter. Ingres was profoundly influenced by past artistic traditions and aspired to become the guardian of academic orthodoxy against the ascendant Romantic style. Although he considered himself a painter of history in the tradition of Nicolas Poussin and Jacques-Louis David, it is his portraits, both painted and drawn, that are recognized as his greatest legacy. His expressive distortions of form and space made him an important precursor of modern art, influencing Picasso, Matisse and other modernists. Born into a modest family in Montauban, he travelled to Paris to study in the studio of David. In 1802 he made his Salon debut, and won the Prix de Rome for his painting '' The Ambassadors of Agamemnon in the tent of Achilles''. By the time he departed in 1806 for his residency in Rome, his style—revealing his close study of Italian and Flemish Renaissance masters— ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Architecture
Classical architecture usually denotes architecture which is more or less consciously derived from the principles of Greek and Roman architecture of classical antiquity, or sometimes even more specifically, from the works of the Roman architect Vitruvius. Different styles of classical architecture have arguably existed since the Carolingian Renaissance, and prominently since the Italian Renaissance. Although classical styles of architecture can vary greatly, they can in general all be said to draw on a common "vocabulary" of decorative and constructive elements. In much of the Western world, different classical architectural styles have dominated the history of architecture from the Renaissance until the second world war, though it continues to inform many architects to this day. The term ''classical architecture'' also applies to any mode of architecture that has evolved to a highly refined state, such as classical Chinese architecture, or classical Mayan architecture. It can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
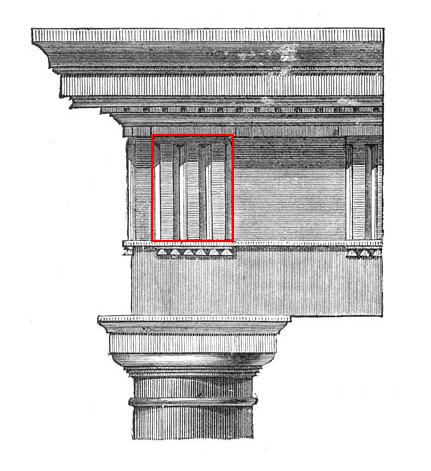
Triglyph
Triglyph is an architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze in classical architecture, so called because of the angular channels in them. The rectangular recessed spaces between the triglyphs on a Doric frieze are called metopes. The raised spaces between the channels themselves (within a triglyph) are called ''femur'' in Latin or ''meros'' in Greek. In the strict tradition of classical architecture, a set of guttae, the six triangular "pegs" below, always go with a triglyph above (and vice versa), and the pair of features are only found in entablatures of buildings using the Doric order. The absence of the pair effectively converts a building from being in the Doric order to being in the Tuscan order. The triglyph is largely thought to be a tectonic and skeuomorphic representation in stone of the wooden beam ends of the typical primitive hut, as described by Vitruvius and Renaissance writers. The wooden beams were notched in three separate plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metope (architecture)
In classical architecture, a metope (μετόπη) is a rectangular architectural element that fills the space between two triglyphs in a Doric order, Doric frieze, which is a decorative band of alternating triglyphs and metopes above the architrave of a building of the Doric order. Metopes often had painted or sculptural decoration; the most famous example are the 92 metopes of the Parthenon marbles some of which depict the battle between the Centaurs and the Lapiths. The painting on most metopes has been lost, but sufficient traces remain to allow a close idea of their original appearance. In terms of structure, metopes may be carved from a single block with a triglyph (or triglyphs), or they may be cut separately and slide into slots in the triglyph blocks as at the Temple of Aphaea. Sometimes the metopes and friezes were cut from different stone, so as to provide color contrast. Although they tend to be close to square in shape, some metopes are noticeably larger in heigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilaster
In classical architecture Classical architecture usually denotes architecture which is more or less consciously derived from the principles of Greek and Roman architecture of classical antiquity, or sometimes even more specifically, from the works of the Roman architect V ..., a pilaster is an :Architectural elements, architectural element used to give the appearance of a supporting column and to articulate an extent of wall, with only an ornamental function. It consists of a flat surface raised from the main wall surface, usually treated as though it were a column, with a Capital (architecture), capital at the top, plinth (base) at the bottom, and the various other column elements. In contrast to a pilaster, an engaged column or buttress can support the structure of a wall and roof above. In human anatomy, a pilaster is a ridge that extends vertically across the femur, which is unique to modern humans. Its structural function is unclear. Definition In discussing Leon Battis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
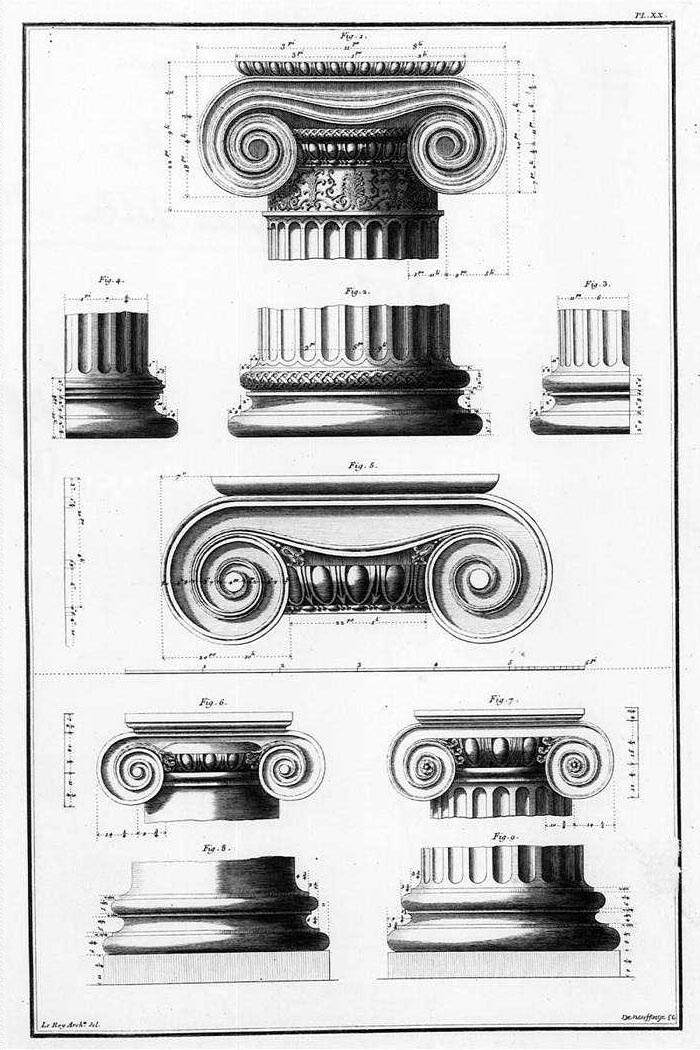
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
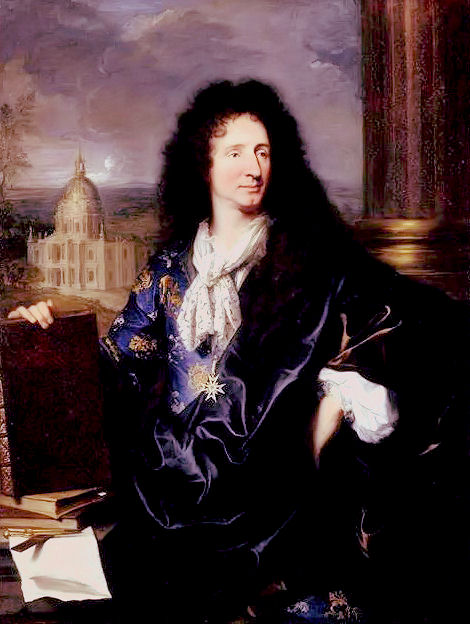
Robert De Cotte
Robert de Cotte (1656 – 15 July 1735) was a French architect-administrator, under whose design control of the royal buildings of France from 1699, the earliest notes presaging the Rococo style were introduced. First a pupil of Jules Hardouin-Mansart, he later became his brother-in-law and his collaborator. After Hardouin-Mansart's death, de Cotte completed his unfinished projects, notably the royal chapel at Versailles and the Grand Trianon. Biography Born in Paris, Robert de Cotte began his career as a contractor for masonry, working on important royal projects between 1682 and 1685, when he was made a member of the ''Académie royale d'architecture'' and architect of the Court, ranking third in importance after Mansart's seldom-credited assistant François Dorbay. On his return to France after a six-month sojourn in Italy (1689–1690), in the company of Jacques Gabriel, he became the director of the Manufacture des Gobelins, where not only the famous tapestries, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Hardouin-Mansart
Jules Hardouin-Mansart (; 16 April 1646 – 11 May 1708) was a French Baroque architect and builder whose major work included the Place des Victoires (1684–1690); Place Vendôme (1690); the domed chapel of Les Invalides (1690), and the Grand Trianon of the Palace of Versailles. His monumental work was designed to glorify the reign of Louis XIV of France. Biography Born Jules Hardouin in Paris in 1646, he studied under his renowned great-uncle François Mansart, one of the originators of the classical tradition in French architecture; Hardouin inherited Mansart's collection of plans and drawings and added Mansart's name to his own in 1668. He began his career as an entrepreneur in building construction, in partnership with his brother Michel, but then decided in 1672 to devote himself entirely to architecture. In 1674 he became one of the group of royal architects working for Louis XIV. His first important project was the Château de Clagny, built for the King's consort, Madame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
