|
Mont Lozère
Mont Lozère ( oc, Mont Losera) is the highest peak in the Cévennes, a subrange of the Massif Central in France. It is above sea level and lies within the Cévennes National Park. Mont Lozère is commonly used for skiing during the winter months. It is also a popular destination for student groups during the summer months. It offers some stunning natural scenery and is covered by coniferous plantations and 'broom' scrub moorland. Mount Lozere is the source of the River Tarn, and also the highest point on the Robert Louis Stevenson Trail (GR 70), a popular long-distance path following approximately the route travelled by Robert Louis Stevenson in 1878 and described in his book ''Travels with a Donkey in the Cévennes''. The GR70 follows a ''draille'' (drove road A drovers' road, drove ''roador droveway is a route for droving livestock on foot from one place to another, such as to market or between summer and winter pasture (see transhumance). Many drovers' roads were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cévennes
The Cévennes ( , ; oc, Cevenas) is a cultural region and range of mountains in south-central France, on the south-east edge of the Massif Central. It covers parts of the ''départements'' of Ardèche, Gard, Hérault and Lozère. Rich in geographical, natural, and cultural significance, portions of the region are protected within the Cévennes National Park, the Cévennes Biosphere Reserve (UNESCO), as well as a UNESCO World Heritage Site: Causses and the Cévennes, Mediterranean agro-pastoral Cultural Landscape. The area has been inhabited since 400,000 BCE and has numerous megaliths which were erected beginning around 2500 BCE. As an agriculturally-rich area, but not a suitable location for cities, the Cévennes developed a wide diversity of pastoral systems, including transhumance. The irrigation and road networks put in place in the early Middle Ages for these pastoral systems are still in use today. The name ''Cévennes'' comes from the Gaulish ''Cebenna.'' As of 1999, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lozère
Lozère (; oc, Losera ) is a landlocked department in the region of Occitanie in Southern France, located near the Massif Central, bounded to the northeast by Haute-Loire, to the east by Ardèche, to the south by Gard, to the west by Aveyron, and the northwest by Cantal. It is named after Mont Lozère. With 76,604 inhabitants as of 2019,Populations légales 2019: 48 Lozère INSEE Lozère is the least populous French department. History Lozère was created in 1790 during the , when the whole of was divided int ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin. Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massif Central
The (; oc, Massís Central, ; literally ''"Central Massif"'') is a highland region in south-central France, consisting of mountains and plateaus. It covers about 15% of mainland France. Subject to volcanism that has subsided in the last 10,000 years, these central mountains are separated from the Alps by a deep north–south cleft created by the Rhône river and known in French as the ' (literally "Rhône furrow"). The region was a barrier to transport within France until the opening of the A75 motorway, which not only made north–south travel easier, but also opened access to the massif itself. Geography and geology The is an old massif, formed during the Variscan orogeny, consisting mostly of granitic and metamorphic rocks. It was powerfully raised and made to look geologically younger in the eastern section by the uplift of the Alps during the Paleogene period and in the southern section by the uplift of the Pyrenees. The massif thus presents a strongly asymm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cévennes National Park
Cévennes National Park (french: Parc national des Cévennes) is a French national park located in Southern France, in the mountainous area of Cévennes. Created in 1970, the park has its administrative seat in Florac at Florac Castle. It is located mainly in the departments of Lozère and Gard; it also covers some parts of Ardèche and Aveyron, therefore stretching across a record number of departments for a national park. The Aven Armand cave is located in the park. In 2011, the Park was made a part of The Causses and the Cévennes, Mediterranean agro-pastoral Cultural Landscape UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography frameless, Map of the Cévennes National Park, showing in red the central protected zone and, in green, the area encompassed by the park., 400px The park includes several mountains and plateaus, including: Mont Lozère, Mont Aigoual, Causse Méjean, France. Mont Lozère is the highest peak in the area, reaching 1,699 metres. History The Cévennes countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skiing
Skiing is the use of skis to glide on snow. Variations of purpose include basic transport, a recreational activity, or a competitive winter sport. Many types of competitive skiing events are recognized by the International Olympic Committee (IOC), and the International Ski Federation (FIS). History Skiing has a history of almost five millennia. Although modern skiing has evolved from beginnings in Scandinavia, it may have been practiced more than 100 centuries ago in what is now China, according to an interpretation of ancient paintings. However, this continues to be debated. The word "ski" comes from the Old Norse word "skíð" which means to "split piece of wood or firewood". Asymmetrical skis were used in northern Finland and Sweden until at least the late 19th century. On one foot, the skier wore a long straight non-arching ski for sliding, and a shorter ski was worn on the other foot for kicking. The underside of the short ski was either plain or covered with ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coniferous
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extant conifers are perennial woody plants with secondary growth. The great majority are trees, though a few are shrubs. Examples include cedars, Douglas-firs, cypresses, firs, junipers, kauri, larches, pines, hemlocks, redwoods, spruces, and yews.Campbell, Reece, "Phylum Coniferophyta". Biology. 7th. 2005. Print. P. 595 As of 1998, the division Pinophyta was estimated to contain eight families, 68 genera, and 629 living species. Although the total number of species is relatively small, conifers are ecologically important. They are the dominant plants over large areas of land, most notably the taiga of the Northern Hemisphere, but also in similar cool climates in mountains further south. Boreal conifers have many wintertime ada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarn (river)
The Tarn (; oc, Tarn, la, Tarnis, possibly meaning 'rapid' or 'walled in') is a long river in the administrative region of Occitania in southern France. It is a right tributary of the Garonne. The Tarn runs in a roughly westerly direction, from its source at an elevation of on Mont Lozère in the Cévennes mountains (part of the Massif Central), through the deep gorges and canyons of the Gorges du Tarn that cuts through the Causse du Larzac, to Moissac in Tarn-et-Garonne, where it joins the Garonne, downstream from the centre of town. Its basin covers approximately , and it has a mean flow of approximately . The Millau Viaduct spans the valley of the Tarn near Millau, and is now one of the area's most popular attractions. Main tributaries The tributaries of the Tarn include: * Agout (in Saint-Sulpice) * Alrance * Aveyron (near Montauban) * Cernon * Dourbie (in Millau) * Dourdou de Camarès * Jonte (in Le Rozier) * Lemboulas * Lumensonesque * Muze * Rance ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
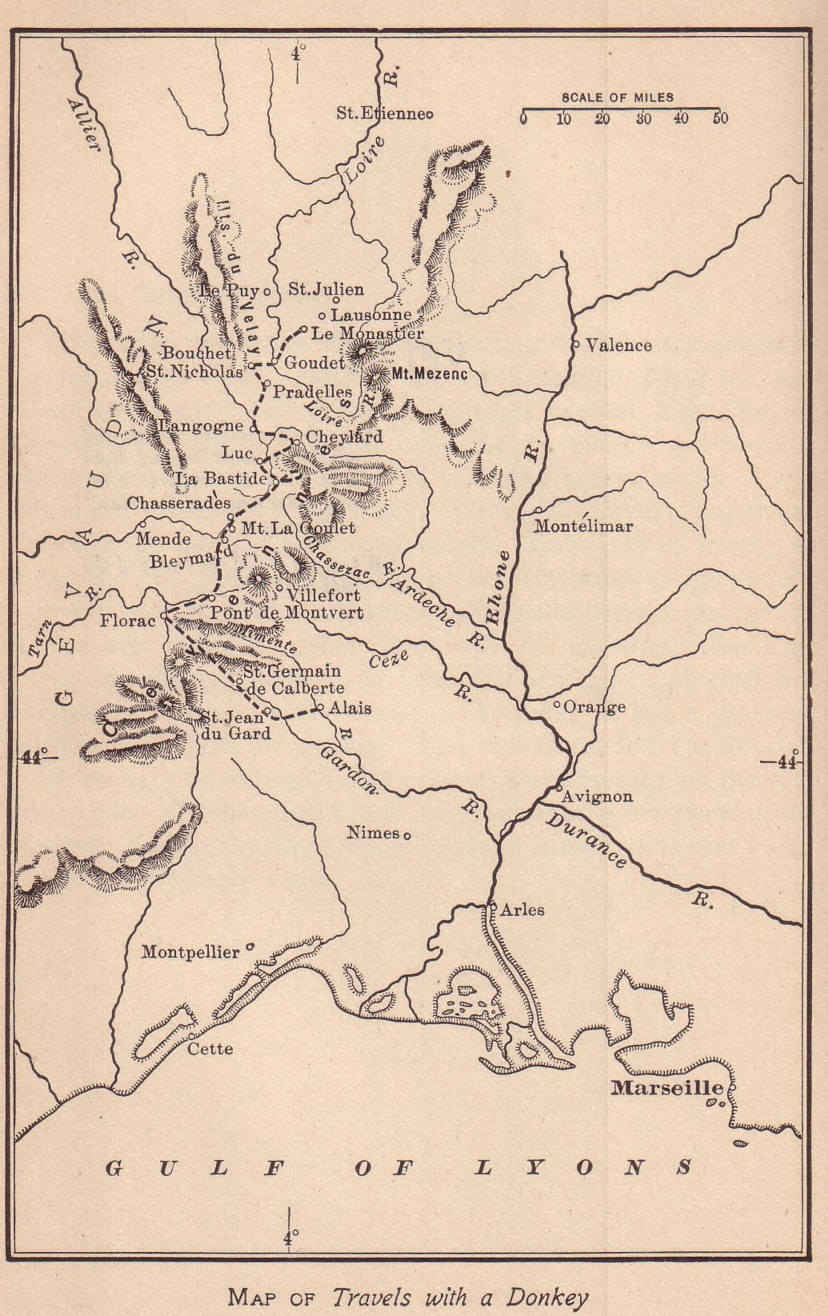
GR 70
The GR 70, also known as the Chemin de Stevenson or the Robert Louis Stevenson Trail, is a Grande Randonnée (long-distance footpath) that runs for approximately through the French departments of Haute-Loire, Lozère and Gard in a generally north–south direction from Le Monastier-sur-Gazeille to Saint-Jean-du-Gard. It follows approximately the route taken by Robert Louis Stevenson in 1878, a journey described in his book '' Travels with a Donkey in the Cévennes''. Although it is not on the formal route, many hikers begin at Le-Puy-en-Velay and walk to Le Monastier-sur-Gazeille via a section of the GR 430. Similarly, many walkers continue beyond the official end-point of Saint-Jean-du-Gard to Alès Alès (; oc, Alès) is a commune in the Gard department in the Occitanie region in southern France. It is one of the sub-prefectures of the department. It was formerly known as ''Alais''. Geography Alès lies north-northwest of Nîmes, on t ... via sections of the GR 61 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Louis Stevenson
Robert Louis Stevenson (born Robert Lewis Balfour Stevenson; 13 November 1850 – 3 December 1894) was a Scottish novelist, essayist, poet and travel writer. He is best known for works such as '' Treasure Island'', '' Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde'', ''Kidnapped'' and '' A Child's Garden of Verses''. Born and educated in Edinburgh, Stevenson suffered from serious bronchial trouble for much of his life, but continued to write prolifically and travel widely in defiance of his poor health. As a young man, he mixed in London literary circles, receiving encouragement from Andrew Lang, Edmund Gosse, Leslie Stephen and W. E. Henley, the last of whom may have provided the model for Long John Silver in ''Treasure Island''. In 1890, he settled in Samoa where, alarmed at increasing European and American influence in the South Sea islands, his writing turned away from romance and adventure fiction toward a darker realism. He died of a stroke in his island home in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Travels With A Donkey In The Cévennes
''Travels with a Donkey in the Cévennes'' (1879) is one of Robert Louis Stevenson's earliest published works and is considered a pioneering classic of outdoor literature. Background Stevenson was in his late 20s and still dependent on his parents for support. His journey was designed to provide material for publication while allowing him to distance himself from a love affair with an American woman of which his friends and families did not approve and who had returned to her husband in California. ''Travels'' recounts Stevenson's 12-day, solo hiking journey through the sparsely populated and impoverished areas of the Cévennes mountains in south-central France in 1878. The terrain, with its barren rocky heather-filled hillsides, he often compared to parts of Scotland. The other principal character is Modestine, a stubborn, manipulative donkey he could never quite master. It is one of the earliest accounts to present hiking and camping outdoors as a recreational activity. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drovers' Road
A drovers' road, drove ''roador droveway is a route for droving livestock on foot from one place to another, such as to market or between summer and winter pasture (see transhumance). Many drovers' roads were ancient routes of unknown age; others are known to date back to medieval or more recent times. Description Drovers' roads are often wider than other roads, able to accommodate large herds or flocks. Packhorse ways were quite narrow as the horses moved in single file, whereas drove roads were at least and up to wide.Addison (1980), Pp. 70-78. In the United Kingdom, where many original drovers' roads have been converted into single carriageway metalled roads, unusually wide verges often give an indication of the road's origin. In Wales, the start of many droveways, drovers' roads are often recognisable by being deeply set into the countryside, with high earth walls or hedges. The most characteristic feature of these roads is the occasional sharp turn in the road, which p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |