|
Monsoon Regatta
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains. The major monsoon systems of the world consist of the West African, Asia–Australian, the North American, and South American monsoons. The term was first used in English in British India and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowing from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area. Etymology The etymology of the word monsoon is not wholly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon Clouds Near Nagercoil
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains. The major monsoon systems of the world consist of the West African, Asia–Australian, the North American, and South American monsoons. The term was first used in English in British India and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowing from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area. Etymology The etymology of the word monsoon is not wholly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
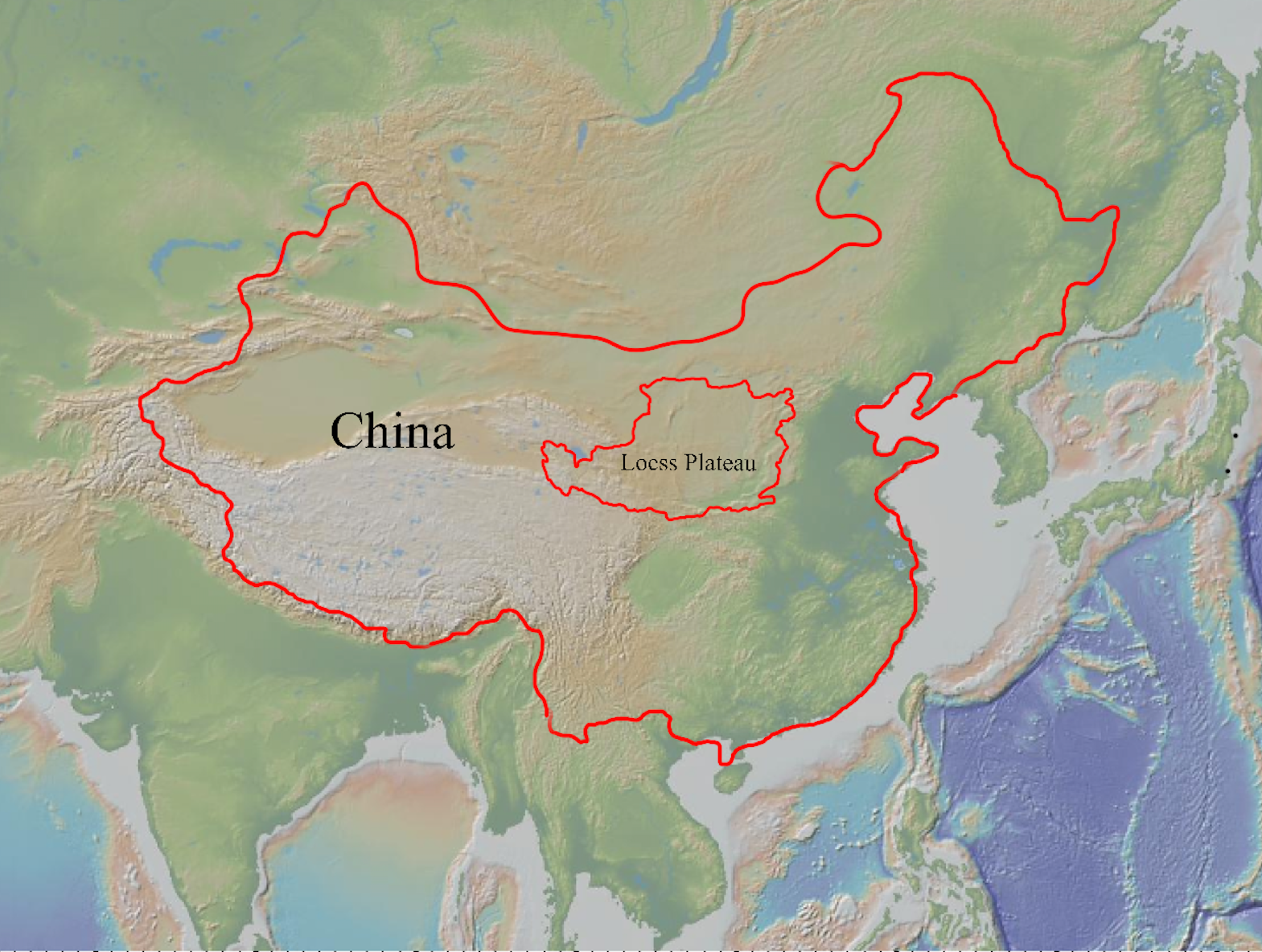
Loess Plateau
The Chinese Loess Plateau, or simply the Loess Plateau, is a plateau in north-central China formed of loess, a clastic silt-like sediment formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. It is located southeast of the Gobi Desert and is surrounded by the Yellow River. It includes parts of the Chinese provinces of Gansu, Shaanxi and Shanxi. The depositional setting of the Chinese Loess Plateau was shaped by the tectonic movement in the Neogene period, after which strong southeast winds caused by the East Asian Monsoon transported sediment to the plateau during the Quaternary period. The three main morphological types in the Loess Plateau are loess platforms, ridges and hills, formed by the deposition and erosion of loess. Most of the loess comes from the Gobi Desert and other nearby deserts. The sediments were transported to the Loess Plateau during interglacial periods by southeasterly prevailing winds and winter monsoon winds. After the deposition of sediments on the plateau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
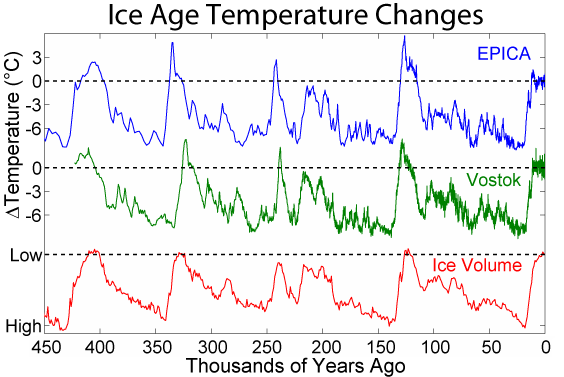
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent. Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Europe, and Asia and profoundly affected Earth's climate by causing drought, desertification, and a large drop in sea levels. Based on changes in position of ice sheet margins dated via terrestrial cosmogenic nuclides and radiocarbon dating, growth of ice sheets commenced 33,000 years ago and maximum coverage was between 26,500 years and 19–20,000 years ago, when deglaciation commenced in the Northern Hemisphere, causing an abrupt rise in sea level. Decline of the West Antarctica ice sheet occurred between 14,000 and 15,000 years ago, consistent with evidence for another abrupt rise in the sea level about 14,500 years ago. Glacier fluctuations around the Strait of Magellan suggest the peak in glacial surface area was constrained to betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Pliocene
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Early may refer to: History * The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.: ** Early Christianity ** Early modern Europe Places in the United States * Early, Iowa * Early, Texas * Early Branch, a stream in Missouri * Early County, Georgia Other uses * ''Early'' (Scritti Politti album), 2005 * ''Early'' (A Certain Ratio album), 2002 * Early (name) * Early effect, an effect in transistor physics * Early Records, a record label * the early part of the morning See also * Earley (other) Earley is a town in England. Earley may also refer to: * Earley (surname), a list of people with the surname Earley * Earley (given name), a variant of the given name Earlene * Earley Lake, a lake in Minnesota *Earley parser, an algorithm *Earley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Miocene
The Middle Miocene is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages: the Langhian and Serravallian stages. The Middle Miocene is preceded by the Early Miocene. The sub-epoch lasted from 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma to 11.608 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago). During this period, a sharp drop in global temperatures took place. This event is known as the Middle Miocene Climate Transition. For the purpose of establishing European Land Mammal Ages The European Land Mammal Mega Zones (abbreviation: ELMMZ, more commonly known as European land mammal ages or ELMA) are zones in rock layers that have a specific assemblage of fossils (biozones) based on occurrences of fossil assemblages of Europe ... this sub-epoch is equivalent to the Astaracian age. External links GeoWhen Database - Middle Miocene .02 02 * * {{geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial Period
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate between glacial periods. The Last Glacial Period ended about 15,000 years ago. The Holocene is the current interglacial. A time with no glaciers on Earth is considered a greenhouse climate state. Quaternary Period Within the Quaternary, which started about 2.6 million years before present, there have been a number of glacials and interglacials. At least eight glacial cycles have occurred in the last 740,000 years alone. Penultimate Glacial Period The Penultimate Glacial Period (PGP) is the glacial period that occurred before the Last Glacial Period. It began about 194,000 years ago and ended 135,000 years ago, with the beginning of the Eemian interglacial. Last Glacial Period The last glacial period was the most recent glacial period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
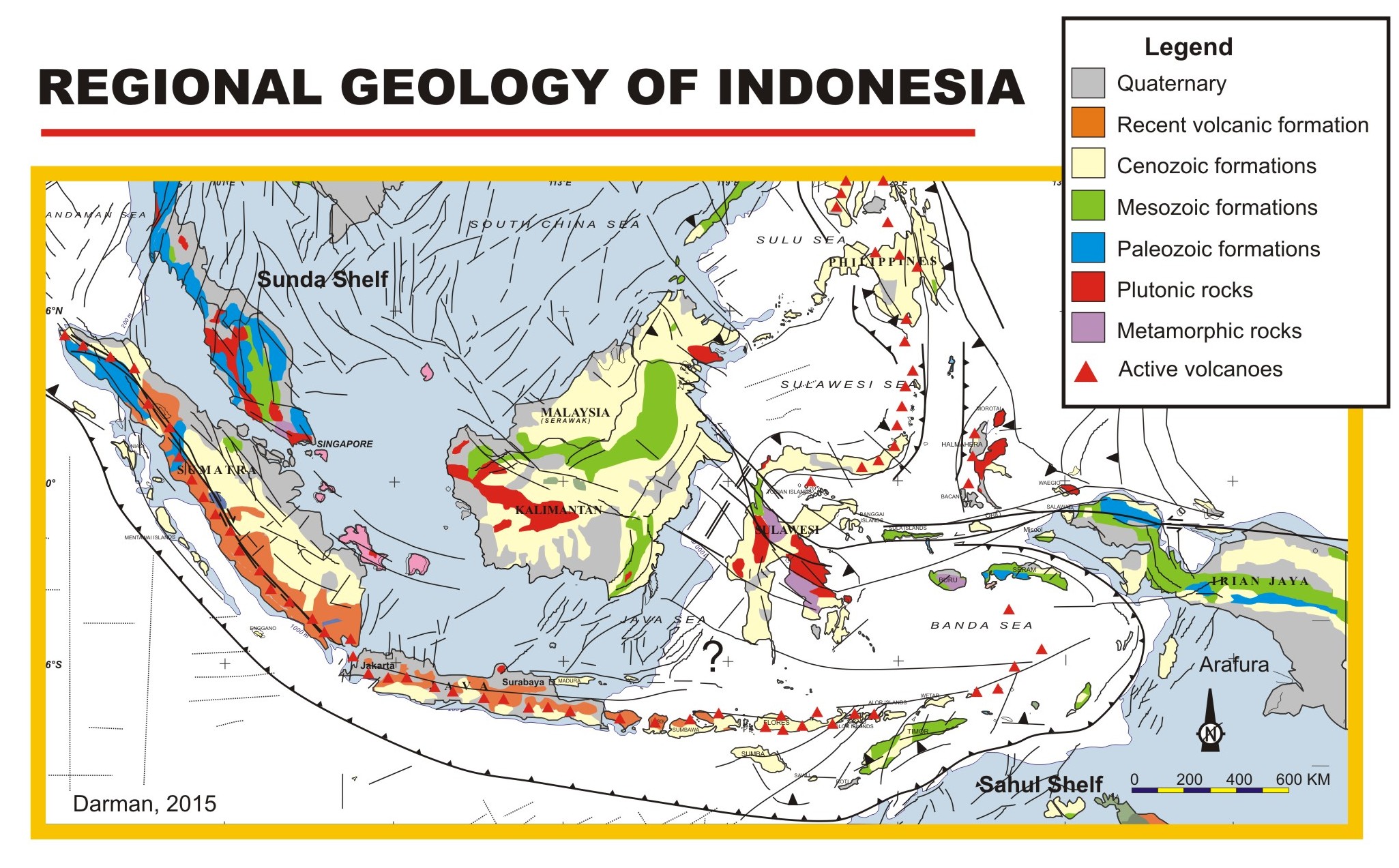
Geology Of Indonesia
This is a brief summary of the geology of Indonesia. Indonesia is located between two major tectonic plates, the Australian Plate and the Eurasian Plate. Tectonics The tectonics of Indonesia are very complex, as it is a meeting point of several tectonic plates. Indonesia is located between two continental plates: the Australian Plate (Sahul Shelf) and the Eurasian Plate (Sunda Shelf); and between two oceanic plates: the Pacific Plate and the Philippine Sea Plate. The subduction of the Indian Plate beneath the Eurasian Plate formed the volcanic arc in western Indonesia, one of the most seismically active areas on the planet with a long history of powerful eruptions and earthquakes. This chain of active volcanoes formed Sumatra, Java, Bali, and the Lesser Sunda Islands, most of which, particularly Java and Bali, emerged within the last 2–3 million years. The Pacific and Australian plate movements controlled the tectonics of the eastern portion of Indonesia. Structural g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology
''Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology'' ("''Palaeo3''") is a peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing multidisciplinary studies and comprehensive reviews in the field of palaeoenvironmental geology. The journal is edited by T. J. Algeo, H. Falcon-Lang, P. Hesse, I. Montanez, J. Pike and S. Xie. It was established in 1965 and is currently published by Elsevier. Indexing and abstracting ''Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology'' is indexed and abstracted in the following databases: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', ''Advance in Space Research'' has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 3.318. References External links * Biology journals Elsevier academic journals English-language journals Publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eemian
The Eemian (also called the last interglacial, Sangamonian, Sangamonian Stage, Ipswichian, Mikulin, Kaydaky, penultimate,NOAA - Penultimate Interglacial Period http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/global-warming/penultimate-interglacial-period Valdivia or Riss-Würm) was the interglacial period which began about 130,000 years ago at the end of the Penultimate Glacial Period and ended about 115,000 years ago at the beginning of the Last Glacial Period. It corresponds to Marine Isotope Stage 5e. Although sometimes referred to as the "last interglacial" (in the "most recent previous" sense of "last"), it was the second-to-latest interglacial period of the current Ice Age, the most recent being the Holocene which extends to the present day (having followed the last glacial period). The prevailing Eemian climate was, on average, around 1 to 2 degrees Celsius (1.8 to 3.6 Fahrenheit) warmer than that of the Holocene. During the Eemian, the proportion of in the atmosphere was about 280 parts per mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
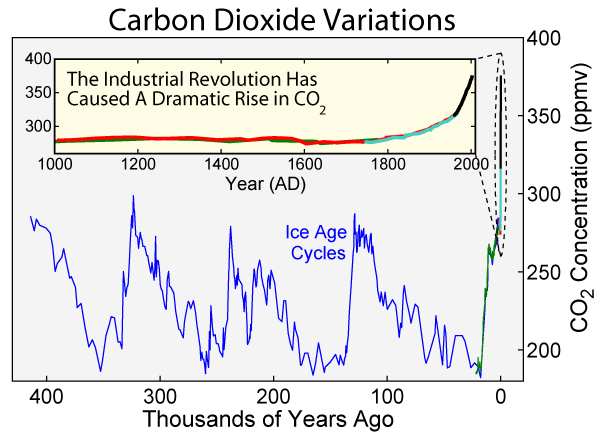
Climate Change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Due to climate change, deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Increased warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causing m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |