|
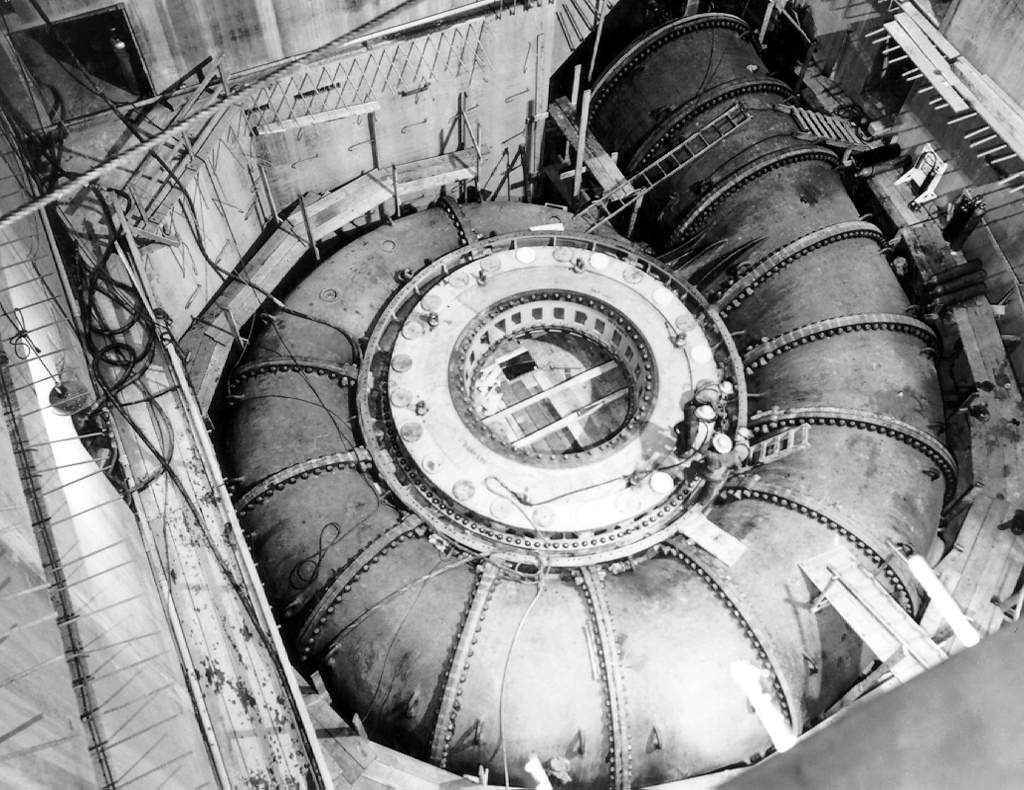
Monción Dam
The Monción Dam is an earth-fill embankment dam on the Mao River near Monción in Santiago Rodríguez Province of the Dominican Republic. At tall, it is the highest dam in the country and the Caribbean. The purpose of the dam is to produce hydroelectric power and supply water for irrigation. The dam's power station is located downstream and contains two 26 MW Francis turbine-generators for an installed capacity of 52 MW. The dam was completed and began filling its reservoir on 22 September 2001. Its power station was commissioned on 27 April 2002. See also *List of dams and reservoirs in Dominican Republic There are numerous dams and reservoirs in the Dominican Republic, which is composed of rivers, lakes, streams, and numerous waterfalls. The main rivers in the Dominican Republic are the Yaque del Norte, which is the longest in the country at 201& ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Moncion Dam Dams in the Dominican Republic Hydroelectric power stations in the Dominican Repu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monción
Monción is one of the 3 municipalities of the province in Santiago Rodríguez Province, Santiago Rodriguez, Dominican Republic. Previously it was called Guaraguanó, a name from the Taíno, but in 1898, the President of the Republic at that time, Ulises Heureaux, assigned the name of Monción, in honor of the hero of the Dominican Restoration War, General Benito Monción. In 1907, Monción became the official municipality of the Monte Cristi Province. Then in 1948, when the Province of Santiago Rodríguez Province, Santiago Rodríguez was created, it became its municipality. It is located specifically in the southwest part of the province. Its main economic source is the production of Cassava, being this municipality, the largest producer of this product in the country, for this reason it is known as the capital of Cassava. Limits South: Cordillera Central, Dominican Republic North: Mao, Dominican Republic East: San José de las Matas West: Sabaneta, Dominican Republic Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santiago Rodríguez Province
Santiago Rodríguez () is a province in the northwest region of the Dominican Republic. It was split from Monte Cristi in 1948. The Santiago Rodríguez province has the Monte Cristi and Valverde provinces to the north, the Santiago province to the east, the San Juan and Elías Piña provinces to the south and the Dajabón province to the west. Geography The province of Santiago Rodríguez presents a rugged relief with characteristics such as mountains, forests, hills, savannas and valleys all around. To the north, and separating it from the great Cibao valley, a formation composed of xerophilous vegetation known as the "Sierra Zamba" is observed. Wide canyons formed by the two rivers that drain the area, the Cana and the Gurabo, have formed and shaped a landscape composed of narrow gorges and ravines that embellish the topography of the region. In the south, the Central Mountain Range rises imposing itself on the Northeast landscape. Climate The province of Santiago Rodr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mao River
The Mao River is a river of the Dominican Republic. It is impounded by the Monción Dam The Monción Dam is an earth-fill embankment dam on the Mao River near Monción in Santiago Rodríguez Province of the Dominican Republic. At tall, it is the highest dam in the country and the Caribbean. The purpose of the dam is to produce hydro .... See also * List of rivers of the Dominican Republic References * The Columbia Gazetteer of North America. 2000. GEOnet Names Server Rivers of the Dominican Republic {{DominicanRepublic-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own steam engine in 1776. Watt's invention was fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one metre per second against a constant opposing force of one newton, the rate at which work is done is one watt. : \mathrm In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the volt-ampere (the latter unit, however, is used for a different quantity from the real power of an electrical circuit). : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis-type
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine for diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embankment Dam
An embankment dam is a large artificial dam. It is typically created by the placement and compaction of a complex semi-plastic mound of various compositions of soil or rock. It has a semi-pervious waterproof natural covering for its surface and a dense, impervious core. This makes the dam impervious to surface or seepage erosion. Such a dam is composed of fragmented independent material particles. The friction and interaction of particles binds the particles together into a stable mass rather than by the use of a cementing substance. Types Embankment dams come in two types: the earth-filled dam (also called an earthen dam or terrain dam) made of compacted earth, and the rock-filled dam. A cross-section of an embankment dam shows a shape like a bank, or hill. Most have a central section or core composed of an impermeable material to stop water from seeping through the dam. The core can be of clay, concrete, or asphalt concrete. This type of dam is a good choice for sites wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with Haiti, making Hispaniola one of only two Caribbean islands, along with Saint Martin, that is shared by two sovereign states. The Dominican Republic is the second-largest nation in the Antilles by area (after Cuba) at , and third-largest by population, with approximately 10.7 million people (2022 est.), down from 10.8 million in 2020, of whom approximately 3.3 million live in the metropolitan area of Santo Domingo, the capital city. The official language of the country is Spanish. The native Taíno people had inhabited Hispaniola before the arrival of Europeans, dividing it into five chiefdoms. They had constructed an advanced farming and hunting society, and were in the process of becoming an organized civilization. The Taínos also in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine for d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Dams And Reservoirs In Dominican Republic
There are numerous dams and reservoirs in the Dominican Republic, which is composed of rivers, lakes, streams, and numerous waterfalls. The main rivers in the Dominican Republic are the Yaque del Norte, which is the longest in the country at 201 km in length. The second largest and the strongest river is the Yuna River which is 138 km in length and the third largest is the Yaque del Sur which is 136 km in length. ''Note:'' * *Actual capacity might vary * **Some rivers have the same name as dams or hydro-electric plants. See also *Electricity sector in the Dominican Republic * Geography of the Dominican Republic *List of dams and reservoirs {{Dams and Reservoirs Economy of the Dominican Republic Hydroelectric power stations in the Dominican Republic Dams in the Dominican Republic Dominican Republic The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams In The Dominican Republic
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees (also known as dikes) are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. The earliest known dam is the Jawa Dam in Jordan, dating to 3,000 BC. The word ''dam'' can be traced back to Middle English, and before that, from Middle Dutch, as seen in the names of many old cities, such as Amsterdam and Rotterdam. History Ancient dams Early dam building took place in Mesopotamia and the Middle East. Dams were used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectric Power Stations In The Dominican Republic
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |