|
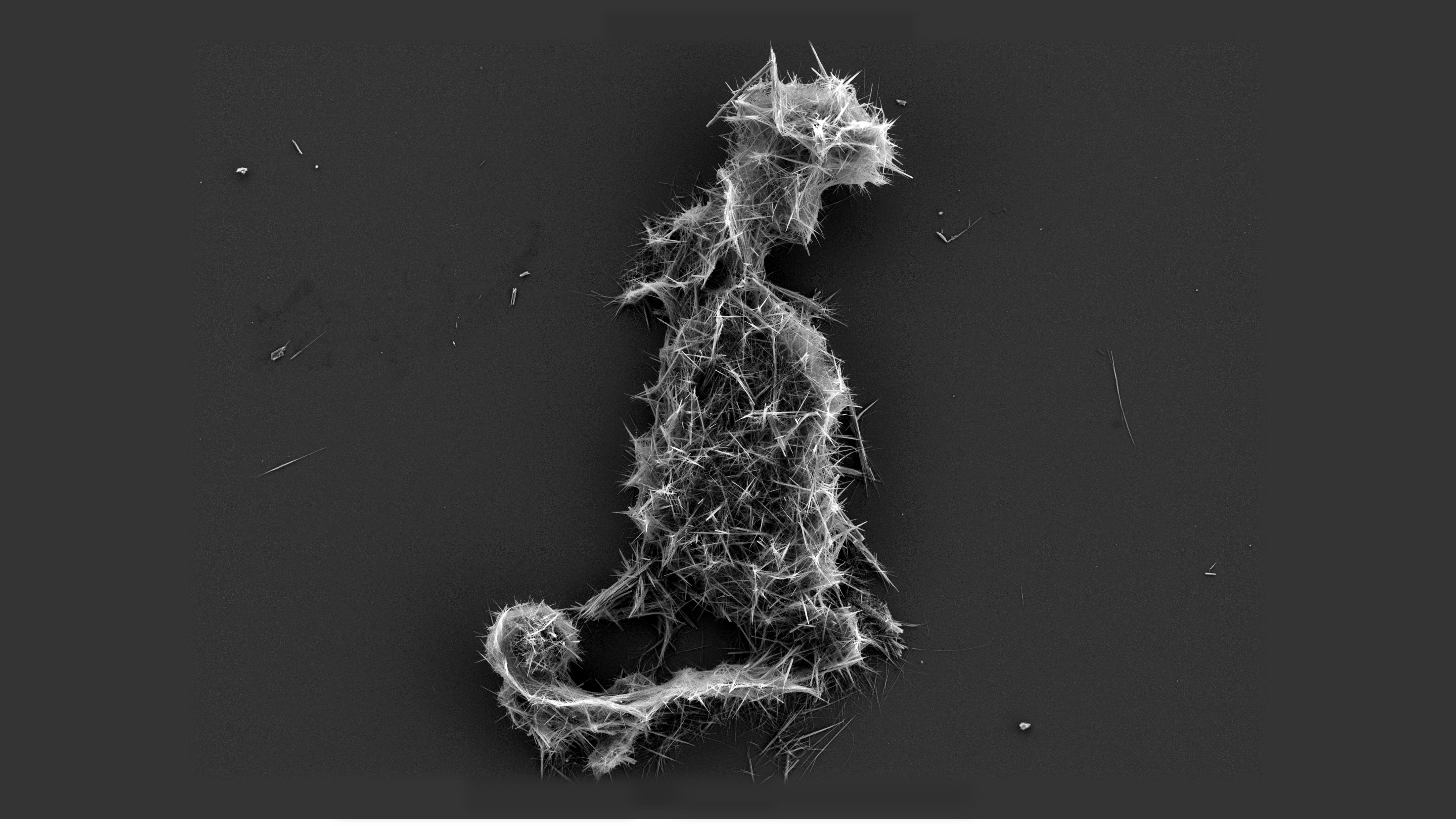
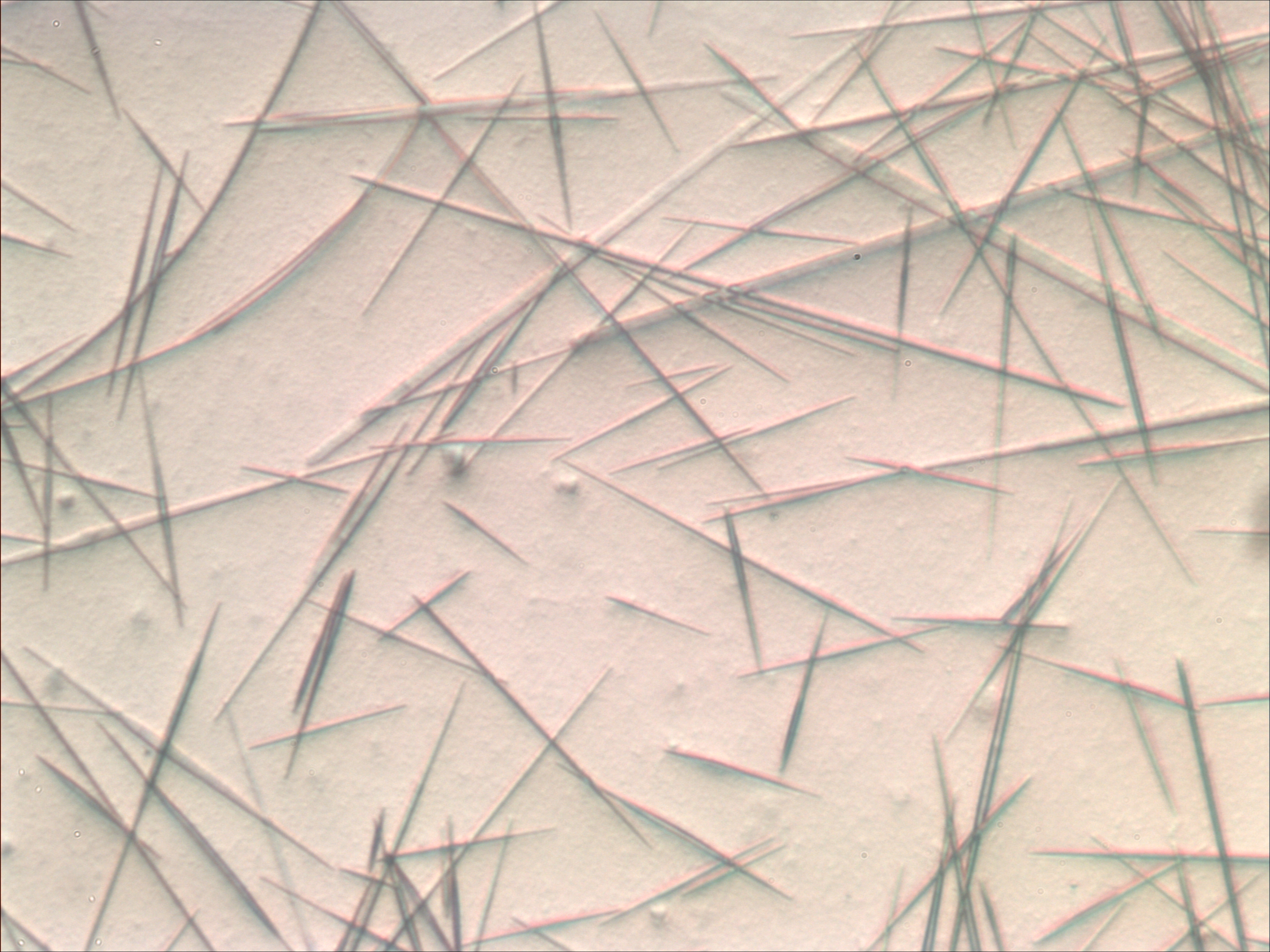
Molybdenum Blue
Molybdenum blue is a term applied to: *reduced heteropolymolybdate complexes, polyoxometalates containing Mo(V), Mo(VI), and a hetero atom such as phosphorus or silicon *reduced isopolymolybdate complexes, polyoxometalates containing Mo(V), Mo(VI) formed when solutions of Mo(VI) are reduced *a blue pigment containing molybdenum(VI) oxide The "heteropoly-molybdenum blues", are used extensively in analytical chemistry and as catalysts. The formation of "isopoly-molybdenum blues" which are intense blue has been used as a sensitive test for reducing reagents. They have recently been shown to contain very large anionic species based on the so-called "big wheel" containing 154 Mo atoms, with a formula o154O462H14(H2O)70sup>14−.''From Scheele and Berzelius to MÜller: polyoxometalates (POMs) revisited and the "missing link" between the bottom up and top down approaches'' P. Gouzerh, M. Che; ''L'Actualité Chimique'', 2006, 298, 9 The molybdenum blue pigment is historically documented' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
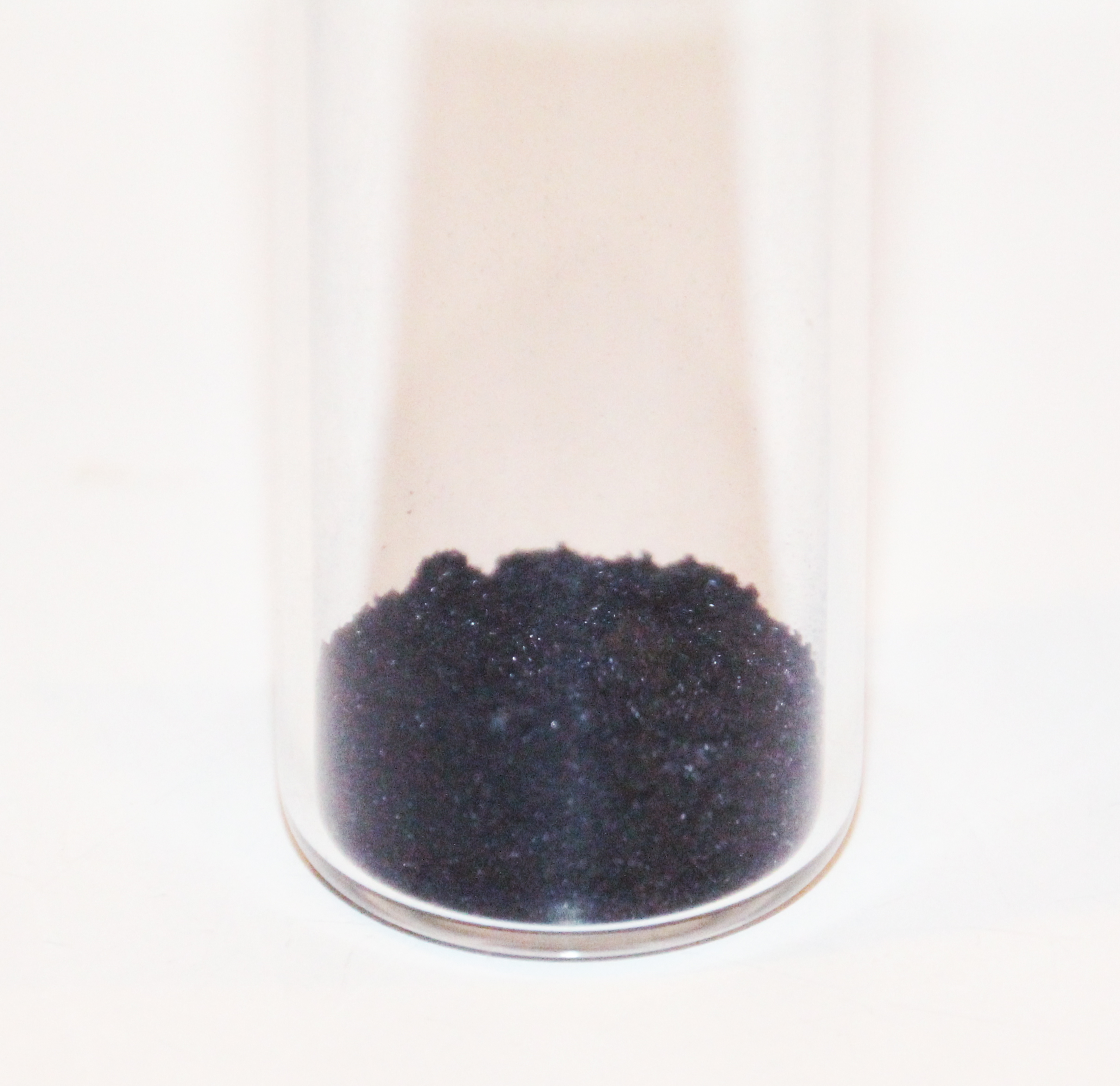
Sample Of Molybdenum Blue
Sample or samples may refer to: Base meaning * Sample (statistics), a subset of a population – complete data set * Sample (signal), a digital discrete sample of a continuous analog signal * Sample (material), a specimen or small quantity of something * Sample (graphics), an intersection of a color channel and a pixel * SAMPLE history, a mnemonic acronym for questions medical first responders should ask * Product sample, a sample of a consumer product that is given to the consumer so that he or she may try a product before committing to a purchase * Standard cross-cultural sample, a sample of 186 cultures, used by scholars engaged in cross-cultural studies People *Sample (surname) *Samples (surname) * Junior Samples (1926–1983), American comedian Places * Sample, Kentucky, unincorporated community, United States * Sampleville, Ohio, unincorporated community, United States * Hugh W. and Sarah Sample House, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Iowa, United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdenum(VI) Oxide
Molybdenum trioxide describes a family of inorganic compounds with the formula MoO3(H2O)n where n = 0, 1, 2. These compounds are produced on the largest scale of any molybdenum compound. The anhydrous oxide is a precursor to molybdenum metal, an important alloying agent. It is also an important industrial catalyst. It is a yellow solid, although impure samples can appear blue or green. Molybdenum trioxide occurs as the rare mineral molybdite. Structure In the gas phase, three oxygen atoms are bonded to the central molybdenum atom. In the solid state, anhydrous MoO3 is composed of layers of distorted MoO6 octahedra in an orthorhombic crystal. The octahedra share edges and form chains which are cross-linked by oxygen atoms to form layers. The octahedra have one short molybdenum-oxygen bond to a non-bridging oxygen. Also known is a metastable (β) form of MoO3 with a WO3-like structure. Preparation and principal reactions MoO3 is produced industrially by roasting molybd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluster Chemistry
In chemistry, an atom cluster (or simply cluster) is an ensemble of bound atoms or molecules that is intermediate in size between a simple molecule and a nanoparticle; that is, up to a few nanometers (nm) in diameter. The term ''microcluster'' may be used for ensembles with up to couple dozen atoms. Clusters with a definite number and type of atoms in a specific arrangement are often considered a specific chemical compound and are studied as such. For example, fullerene is a cluster of 60 carbon atoms arranged as the vertices of a truncated icosahedron, and decaborane is a cluster of 10 boron atoms forming an incomplete icosahedron, surrounded by 14 hydrogen atoms. The term is most commonly used for ensembles consisting of several atoms of the same element, or of a few different elements, bonded in a three-dimensional arrangement. Transition metals and main group elements form especially robust clusters. Indeed, in some contexts, the term may refer specifically to a metal cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdenum Compounds
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals have been known throughout history, but the element was discovered (in the sense of differentiating it as a new entity from the mineral salts of other metals) in 1778 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. The metal was first isolated in 1781 by Peter Jacob Hjelm. Molybdenum does not occur naturally as a free metal on Earth; it is found only in various oxidation states in minerals. The free element, a silvery metal with a grey cast, has the sixth-highest melting point of any element. It readily forms hard, stable carbides in alloys, and for this reason most of the world production of the element (about 80%) is used in steel alloys, including high-strength alloys and superalloys. Most molybdenum compounds have low solubilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Valence Compounds , a person who is of multiple races
*
*
{{disambiguation ...
Mixed is the past tense of ''mix''. Mixed may refer to: * Mixed (United Kingdom ethnicity category), an ethnicity category that has been used by the United Kingdom's Office for National Statistics since the 1991 Census * ''Mixed'' (album), a compilation album of two avant-garde jazz sessions featuring performances by the Cecil Taylor Unit and the Roswell Rudd Sextet See also * Mix (other) * Mixed breed, an animal whose parents are from different breeds or species * Mixed ethnicity Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-eth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions .... It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. History In the early tenth century, the Persian physician and alchemist Abu Bakr al-Razi ( 865–925, Latin: Rhazes) conducted experiments with sal ammoniac (ammonium chloride) and vitriol (hydrated sulfates of various metals), which he distilled together, thus producing the gas hydrogen chloride. In doing so, al-Razi may have stumbled upon a primitive method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Phosphate
The term calcium phosphate refers to a family of materials and minerals containing calcium ions (Ca2+) together with inorganic phosphate anions. Some so-called calcium phosphates contain oxide and hydroxide as well. Calcium phosphates are white solids of nutritious value and are found in many living organisms, e.g., bone mineral and tooth enamel. In milk, it exists in a colloidal form in micelles bound to casein protein with magnesium, zinc, and citrate–collectively referred to as colloidal calcium phosphate (CCP). Various calcium phosphate minerals are used in the production of phosphoric acid and fertilizers. Overuse of certain forms of calcium phosphate can lead to nutrient-containing surface runoff and subsequent adverse effects upon receiving waters such as algal blooms and eutrophication (over-enrichment with nutrients and minerals). Orthophosphates, di- and monohydrogen phosphates These materials contain Ca2+ combined with , , or : * Monocalcium phosphate, E341 (CAS# 775 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin Dioxide
Tin(IV) oxide, also known as stannic oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula SnO2. The mineral form of SnO2 is called cassiterite, and this is the main ore of tin. With many other names, this oxide of tin is an important material in tin chemistry. It is a colourless, diamagnetic, amphoteric solid. Structure Tin(IV) oxide crystallises with the rutile structure. As such the tin atoms are six coordinate and the oxygen atoms three coordinate. SnO2 is usually regarded as an oxygen-deficient n-type semiconductor. Hydrous forms of SnO2 have been described as stannic acid. Such materials appear to be hydrated particles of SnO2 where the composition reflects the particle size. Preparation Tin(IV) oxide occurs naturally. Synthetic tin(IV) oxide is produced by burning tin metal in air. Annual production is in the range of 10 kilotons. SnO2 is reduced industrially to the metal with carbon in a reverberatory furnace at 1200–1300 °C. Amphoterism Although SnO2 is insoluble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Scientist
''New Scientist'' is a magazine covering all aspects of science and technology. Based in London, it publishes weekly English-language editions in the United Kingdom, the United States and Australia. An editorially separate organisation publishes a monthly Dutch-language edition. First published on 22 November 1956, ''New Scientist'' has been available in online form since 1996. Sold in retail outlets (paper edition) and on subscription (paper and/or online), the magazine covers news, features, reviews and commentary on science, technology and their implications. ''New Scientist'' also publishes speculative articles, ranging from the technical to the philosophical. ''New Scientist'' was acquired by Daily Mail and General Trust (DMGT) in March 2021. History Ownership The magazine was founded in 1956 by Tom Margerison, Max Raison and Nicholas Harrison as ''The New Scientist'', with Issue 1 on 22 November 1956, priced at one shilling (a twentieth of a pound in pre-decimal UK cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achim Müller
Achim Müller (born 14 February 1938 in Detmold) is a German chemist. He is Professor Emeritus at the Faculty of Chemistry, University of Bielefeld. His research involves mainly the chemistry of transition metals, especially with relation to nanochemistry. Müller’s work on a new type of isopolyoxovanadates has provided some of the most instructive examples of host-guest inorganic chemistry, leading to the recognition that a polyoxometalate is a supramolecular species involving a negatively charged host cage and a negatively charged encapsulated guest, and hence opening a new era in polyoxometalate chemistry. The template self-organization of an ”electronically inverse host” around a negatively charged guest might seem somewhat puzzling: According to theoretical studies, this follows from the fact that electrostatic repulsion is overcome by maximizing the molecular electrostatic potential at the guest His current research relates mainly to the synthesis of spherical porous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrosyl
In organic chemistry, nitroso refers to a functional group in which the nitric oxide () group is attached to an organic moiety. As such, various nitroso groups can be categorized as ''C''-nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosoalkanes; ), ''S''-nitroso compounds ( nitrosothiols; ), ''N''-nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosamines, ), and ''O''-nitroso compounds (alkyl nitrites; ). Synthesis Nitroso compounds can be prepared by the reduction of nitro compounds or by the oxidation of hydroxylamines. Ortho-nitrosophenols may be produced by the Baudisch reaction. In the Fischer–Hepp rearrangement aromatic 4-nitrosoanilines are prepared from the corresponding nitrosamines. Properties Nitrosoarenes typically participate in a monomer–dimer equilibrium. The dimers, which are often pale yellow, are often favored in the solid state, whereas the deep-green monomers are favored in dilute solution or at higher temperatures. They exist as ''cis'' and ''trans'' isomers. Due to the stability o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentagonal Bipyramid Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, a pentagonal bipyramid is a molecular geometry with one atom at the centre with seven ligands at the corners of a pentagonal bipyramid. A perfect pentagonal bipyramid belongs to the molecular point group ''D5h''. The pentagonal bipyramid is a case where bond angles surrounding an atom are not identical (see also trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry). This is one of the three common shapes for heptacoordinate transition metal complexes, along with the capped octahedron and the capped trigonal prism. Pentagonal bipyramids are claimed to be promising coordination geometries for lanthanide-based Single-molecule magnets, since (a) they present no extradiagonal Crystal Field terms, therefore minimising spin mixing, and (b) all of their diagonal terms are in first approximation protected from low-energy vibrations, minimising vibronic coupling. Examples * Iodine heptafluoride (IF7) with 7 bonding groups * Peroxo chromium Chromium is a chemical element with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |