|
Molly Schumer
Molly Schumer is an American scientist who studies evolution, hybridization, and population genetics. She is an assistant professor of biology at Stanford University. She is a member of Stanford Bio-X and a Hannah H. Grey Fellow at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. Education Schumer completed her Bachelor of Arts in 2009 at Reed College, earning Phi Beta Kappa. She went on to pursue her PhD in Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at Princeton University (jointly supervised by Peter Andolfatto and Gil Rosenthal), finishing in February 2016. After her PhD, Schumer worked as a postdoctoral researcher at Columbia University with Molly Przeworski before joining the Harvard Society of Fellows in July 2016, where she worked in the lab of David Reich. She became a Hanna H. Grey Fellow at HHMI in 2017, and was hired for her current assistant professorship at Stanford University in 2019. Research Schumer's lab investigates biological hybrids and population genetics. Model organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and it is not synonymous with environmentalism. Among other things, ecology is the study of: * The abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment * Life processes, antifragility, interactions, and adaptations * The movement of materials and energy through living communities * The successional development of ecosystems * Cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species * Patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes Ecology has practical applications in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource managemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. It is also defined as the study of the history of life forms on Earth. Evolution is based on the theory that all species are related and they gradually change over time. In a population, the genetic variations affect the physical characteristics i.e. phenotypes of an organism. These changes in the phenotypes will be an advantage to some organisms, which will then be passed onto their offspring. Some examples of evolution in species over many generations are the Peppered Moth and Flightless birds. In the 1930s, the discipline of evolutionary biology emerged through what Julian Huxley called the modern synthesis of understanding, from previously unrelated fields of biological research, such as genetics and ecology, systematics, and paleontology. The importance of studying Evolutionary biology is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
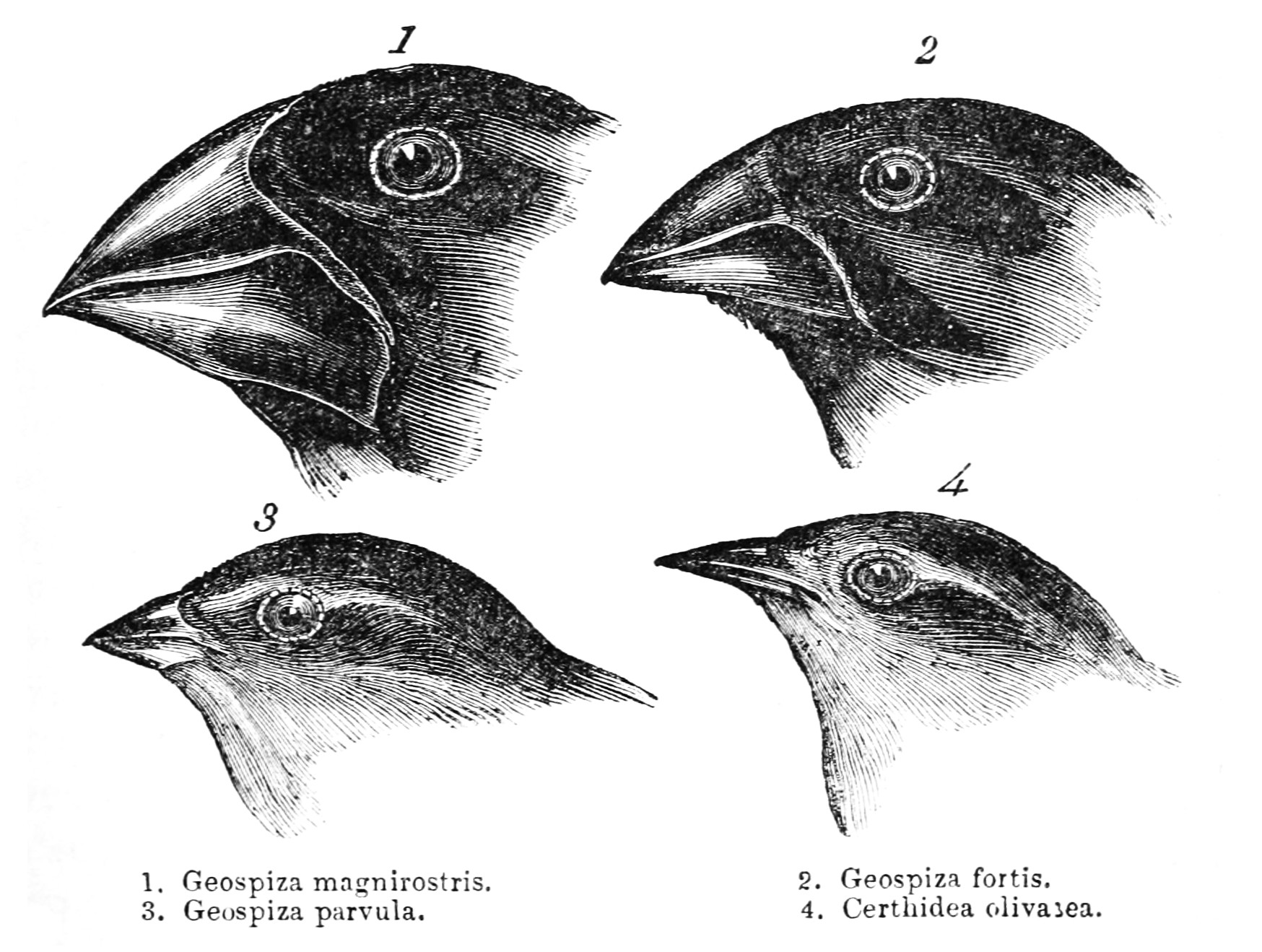
Parallel Evolution
Parallel evolution is the similar development of a trait in distinct species that are not closely related, but share a similar original trait in response to similar evolutionary pressure.Zhang, J. and Kumar, S. 1997Detection of convergent and parallel evolution at the amino acid sequence level. ''Mol. Biol. Evol.'' 14, 527-36. Parallel vs. convergent evolution Given a particular trait that occurs in each of two lineages descended from a specified ancestor, it is possible in theory to define parallel and convergent evolutionary trends strictly, and distinguish them clearly from one another. However the criteria for defining convergent as opposed to parallel evolution often are unclear in practice, so that arbitrary diagnosis is common in some cases. When two species are similar in a particular character, evolution is defined as parallel if the ancestors shared that similarity; if they did not, the evolution of that character in those species is defined as convergent. However, thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution (journal)
''Evolution: International Journal of Organic Evolution'', is a monthly scientific journal that publishes significant new results of empirical or theoretical investigations concerning facts, processes, mechanics, or concepts of evolutionary phenomena and events. ''Evolution'' is published by the Society for the Study of Evolution. Its current editor-in-chief is Tracey Chapman. Former editors-in-chief The journal was founded soon after the Second World War. Its first editor was the evolutionary geneticist Ernst Mayr. * Ruth Geyer Shaw, July 2013 – 2017 * Daphne Fairbairn Daphne (; ; el, Δάφνη, , ), a minor figure in Greek mythology, is a naiad, a variety of female nymph associated with fountains, wells, springs, streams, brooks and other bodies of freshwater. There are several versions of the myth in whi ..., 2010- June 2013 References External linksOfficial website Evolutionary biology journals Publications established in 1947 Academic journals published by l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Speciation
Hybrid speciation is a form of speciation where hybridization between two different species leads to a new species, reproductively isolated from the parent species. Previously, reproductive isolation between two species and their parents was thought to be particularly difficult to achieve, and thus hybrid species were thought to be very rare. With DNA analysis becoming more accessible in the 1990s, hybrid speciation has been shown to be a somewhat common phenomenon, particularly in plants. In botanical nomenclature, a hybrid species is also called a nothospecies. Hybrid species are by their nature polyphyletic. Ecology A hybrid may occasionally be better fitted to the local environment than the parental lineage, and as such, natural selection may favor these individuals. If reproductive isolation is subsequently achieved, a separate species may arise. Reproductive isolation may be genetic, ecological, behavioral, spatial, or a combination of these. If reproductive isolation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homoploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair, which chromosomes naturally exist as. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more chromosome sets. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an organism's life cycle. Half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julidochromis
''Julidochromis'' is a genus of cichlids in the subfamily Pseudocrenilabrinae. They are commonly called julies and are endemic to Lake Tanganyika in eastern Africa. This genus includes six formally described species, some with a number local variants of uncertain taxonomic status. Further taxonomic work is required to determine how many species exist; the closely related ''Chalinochromis'' with two more species is sometimes included here and this may be correct. Hybridization makes attempts to determine relationships with molecular phylogenetic methods difficult. These ray-finned fish are smallish to mid-sized (about ) and have a yellowish background colour with black lengthwise stripes or a checkerboard pattern. Species There are currently 6 formally described species in this genus: * ''Julidochromis dickfeldi'' Staeck, 1975 * ''Julidochromis marksmithi'' W. E. Burgess, 2014 Burgess, W.E. (2014): ''Julidochromis marksmithi'', A New Species of ''Julidochromis'' from the Tanzani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiphophorus
''Xiphophorus'' is a genus of euryhaline and freshwater fishes in the family Poeciliidae of order Cyprinodontiformes, native to Mexico and northern Central America. The many ''Xiphophorus'' species are all known as platyfish (or platies) and swordtails. Platyfish formerly were classified in another genus, ''Platypoecilia'', which is now obsolete. The type species is ''X. hellerii,'' the green swordtail. Like most other new world Poeciliids, platies and swordtails are live-bearers that use internal fertilization and give birth to live young instead of laying eggs like the bulk of the world's fishes. The name ''Xiphophorus'' derives from the Greek words ξίφος (dagger) and φόρος (bearer), referring to the gonopodium on the males. All are relatively small fishes, which reach a maximum length of depending on the exact species involved. Distribution and conservation status The various ''Xiphophorus'' species range from the southern Rio Grande basin in Mexico, through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gila Topminnow
The Gila topminnow or charalito (''Poeciliopsis occidentalis'') is a species of fish in the family Poeciliidae. It is found in Mexico and the United States. Description The Gila topminnow has an elongated curved body. Males are rarely over and they are smaller than females, which can sometimes be . The belly is often white with darker body above, has scales with dark outlines, and a lateral dark band on the side. Distribution Gila topminnow once occupied in the Gila River drainage in Arizona, New Mexico, and Mexico. Currently, they are known to be in Gila River drainage in Arizona and Mexico. Biology Gila topminnow was once the most common fish found in the Gila River drainage. They are fertilized internally; reproduction season usually is from April to November. The female gives birth from 10–15 young per brood. These young brood will reach maturity from a weeks to several months. Gila topminnow are omnivorous, and eat food such as detritus and amphipod crustaceans; but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution. Studying model organisms can be informative, but care must be taken when generalizing from one organism to another. In researching human disease, model organisms allow for better understanding the disease process without the added risk of harming an actual human. The species chosen will usually meet a determined taxonomic equivalency to humans, so as to react to disease or its treatment in a way that resembles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Reich (geneticist)
David Emil Reich (born July 14, 1974) is an American geneticist known for his research into the population genetics of ancient humans, including their migrations and the mixing of populations, discovered by analysis of genome-wide patterns of mutations. He is professor in the department of genetics at the Harvard Medical School, and an associate of the Broad Institute. Reich was highlighted as one of Nature's 10 for his contributions to science in 2015. He received the Dan David Prize in 2017, the NAS Award in Molecular Biology, the Wiley Prize, and the Darwin–Wallace Medal in 2019. In 2021 he was awarded the Massry Prize. Early life Reich grew up as part of a Jewish family in Washington, D.C. His parents are novelist Tova Reich (sister of Rabbi Avi Weiss) and Walter Reich, a professor at George Washington University, who served as the first director of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. David Reich started out as a sociology major as an undergraduate at Harvard Colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Society Of Fellows
The Society of Fellows is a group of scholars selected at the beginnings of their careers by Harvard University for their potential to advance academic wisdom, upon whom are bestowed distinctive opportunities to foster their individual and intellectual growth. Junior fellows are appointed by senior fellows based upon previous academic accomplishments and receive generous financial support for three years while they conduct independent research at Harvard University in any discipline, without being required to meet formal degree requirements or to be graded in any way. The only stipulation is that they maintain primary residence in Cambridge, Massachusetts, for the duration of their fellowship. Membership in the society is for life. The society has contributed numerous scholars to the Harvard faculty and thus significantly influenced the tenor of discourse at the university. Among its best-known members are philosopher Willard Van Orman Quine, W. V. O. Quine, Jf '36; behaviorist B. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)