|
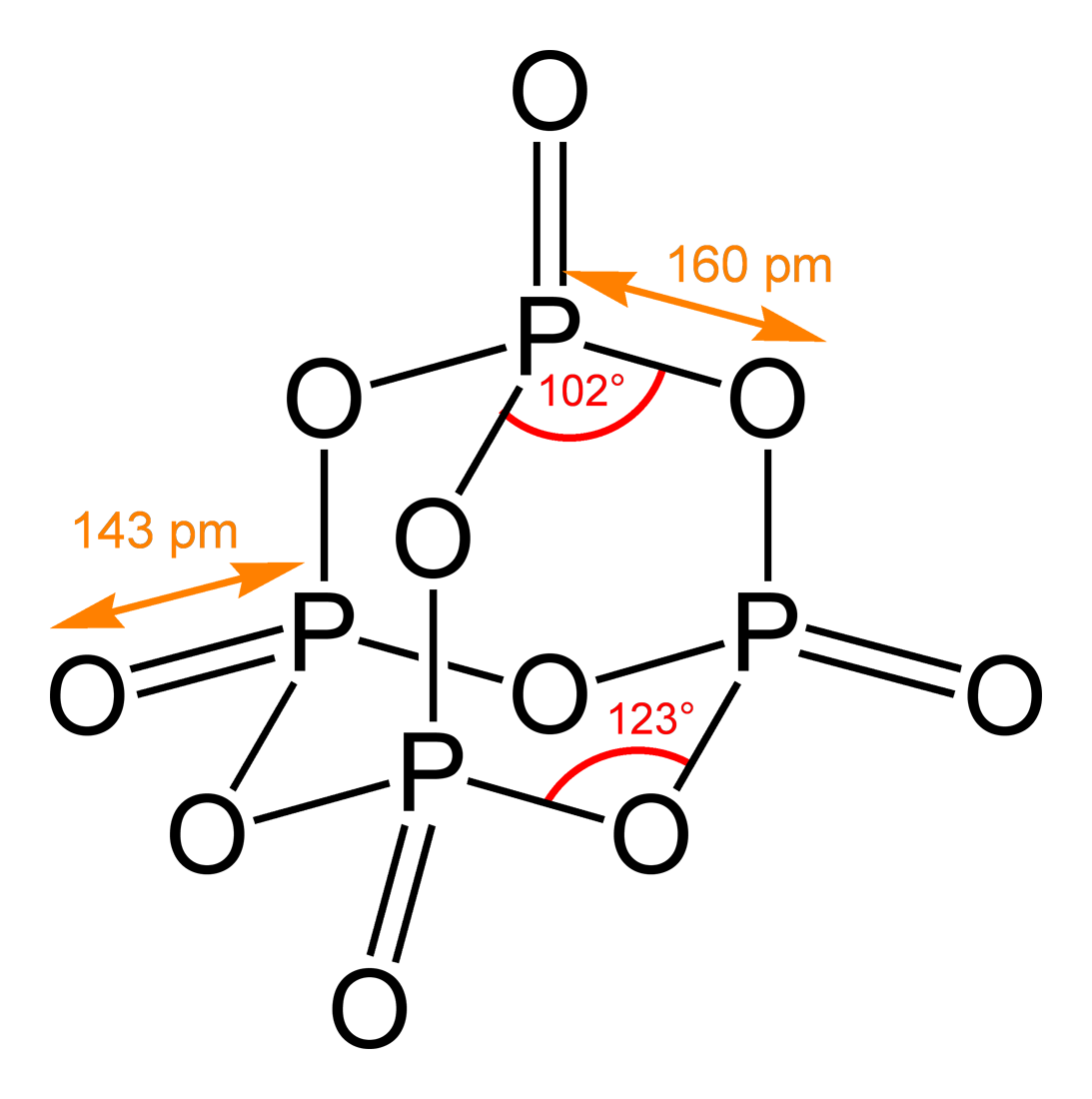
Molecular Conformation
A chemical structure determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together, and can be represented using structural formulae and by molecular models; complete electronic structure descriptions include specifying the occupation of a molecule's molecular orbitals. Structure determination can be applied to a range of targets from very simple molecules (e.g., diatomic oxygen or nitrogen), to very complex ones (e.g., such as protein or DNA). Background Theories of chemical structure were first developed by August Kekulé, Archibald Scott Couper, and Aleksandr Butlerov, among others, from about 1858. These theories were first to state that chemical compounds are not a random cluster of atoms and functional groups, but rather had a definite order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valency (chemistry)
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules. Description The combining capacity, or affinity of an atom of a given element is determined by the number of hydrogen atoms that it combines with. In methane, carbon has a valence of 4; in ammonia, nitrogen has a valence of 3; in water, oxygen has a valence of 2; and in hydrogen chloride, chlorine has a valence of 1. Chlorine, as it has a valence of one, can be substituted for hydrogen. Phosphorus has a valence of 5 in phosphorus pentachloride, . Valence diagrams of a compound represent the connectivity of the elements, with lines drawn between two elements, sometimes called bonds, representing a saturated valency for each element. The two tables below show some examples of different compounds, their valence diagrams, and the valences for each element of the compound. Modern definitions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Voltammetry
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is a type of potentiodynamic electrochemical measurement. In a cyclic voltammetry experiment, the working electrode potential is ramped linearly versus time. Unlike in linear sweep voltammetry, after the set potential is reached in a CV experiment, the working electrode's potential is ramped in the opposite direction to return to the initial potential. These cycles of ramps in potential may be repeated as many times as needed. The current at the working electrode is plotted versus the applied voltage (that is, the working electrode's potential) to give the cyclic voltammogram trace. Cyclic voltammetry is generally used to study the electrochemical properties of an analyte in solution or of a molecule that is adsorbed onto the electrode. Experimental method In cyclic voltammetry (CV), the electrode potential ramps linearly versus time in cyclical phases (Figure 2). The rate of voltage change over time during each of these phases is known as the experiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after Indian physicist C. V. Raman) is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. Raman spectroscopy relies upon inelastic scattering of photons, known as Raman scattering. A source of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range is used, although X-rays can also be used. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, phonons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Infrared spectroscopy typically yields similar yet complementary information. Typically, a sample is illuminated with a laser beam. Electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functional groups in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms. It can be used to characterize new materials or identify and verify known and unknown samples. The method or technique of infrared spectroscopy is conducted with an instrument called an infrared spectrometer (or spectrophotometer) which produces an infrared spectrum. An IR spectrum can be visualized in a graph of infrared light absorbance (or transmittance) on the vertical axis vs. frequency, wavenumber or wavelength on the horizontal axis. Typical units of wavenumber used in IR spectra are reciprocal centimeters, with the symbol cm−1. Units of IR wavelength are commonly given in micrometers (formerly called "microns"), symbol μm, which are related to the wavenumber in a reciprocal way. A com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrational Spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functional groups in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms. It can be used to characterize new materials or identify and verify known and unknown samples. The method or technique of infrared spectroscopy is conducted with an instrument called an infrared spectrometer (or spectrophotometer) which produces an infrared spectrum. An IR spectrum can be visualized in a graph of infrared light absorbance (or transmittance) on the vertical axis vs. frequency, wavenumber or wavelength on the horizontal axis. Typical units of wavenumber used in IR spectra are reciprocal centimeters, with the symbol cm−1. Units of IR wavelength are commonly given in micrometers (formerly called "microns"), symbol μm, which are related to the wavenumber in a reciprocal way. A com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption Spectroscopy
Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, from the radiating field. The intensity of the absorption varies as a function of frequency, and this variation is the absorption spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is performed across the electromagnetic spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is employed as an analytical chemistry tool to determine the presence of a particular substance in a sample and, in many cases, to quantify the amount of the substance present. Infrared and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy are particularly common in analytical applications. Absorption spectroscopy is also employed in studies of molecular and atomic physics, astronomical spectroscopy and remote sensing. There is a wide range of experimental approaches for measuring absorption spectra. The most common arrangement is to direct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon-13 NMR
Carbon-13 (C13) nuclear magnetic resonance (most commonly known as carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy or 13C NMR spectroscopy or sometimes simply referred to as carbon NMR) is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to carbon. It is analogous to proton NMR ( NMR) and allows the identification of carbon atoms in an organic molecule just as proton NMR identifies hydrogen atoms. 13C NMR detects only the isotope. The main carbon isotope, is not detected. Although much less sensitive than 1H NMR spectroscopy, 13C NMR spectroscopy is widely used for characterizing organic and organometallic compounds. Chemical shifts 13C NMR chemical shifts follow the same principles as those of 1H, although the typical range of chemical shifts is much larger than for 1H (by a factor of about 20). The chemical shift reference standard for 13C is the carbons in tetramethylsilane (TMS), whose chemical shift is considered to be 0.0 ppm. ImageSize = width:540 height:440 AlignBar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton NMR
Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (proton NMR, hydrogen-1 NMR, or 1H NMR) is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance in NMR spectroscopy with respect to hydrogen-1 nuclei within the molecules of a substance, in order to determine the structure of its molecules. In samples where natural hydrogen (H) is used, practically all the hydrogen consists of the isotope 1H (hydrogen-1; i.e. having a proton for a nucleus). Simple NMR spectra are recorded in solution, and solvent protons must not be allowed to interfere. Deuterated (deuterium = 2H, often symbolized as D) solvents especially for use in NMR are preferred, e.g. deuterated water, D2O, deuterated acetone, (CD3)2CO, deuterated methanol, CD3OD, deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide, (CD3)2SO, and deuterated chloroform, CDCl3. However, a solvent without hydrogen, such as carbon tetrachloride, CCl4 or carbon disulfide, CS2, may also be used. Historically, deuterated solvents were supplied with a small amount (typically 0.1%) of tet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are perturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a frequency characteristic of the magnetic field at the nucleus. This process occurs near resonance, when the oscillation frequency matches the intrinsic frequency of the nuclei, which depends on the strength of the static magnetic field, the chemical environment, and the magnetic properties of the isotope involved; in practical applications with static magnetic fields up to ca. 20 tesla, the frequency is similar to VHF and UHF television broadcasts (60–1000 MHz). NMR results from specific magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is widely used to determine the structure of organic molecules in solution and study molecular physics and crystals as well as non-crystalline materials. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associated with a spectral signature in the context of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) In simpler terms, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

