|
Mokrani Revolt
The Mokrani Revolt ( ar, مقاومة الشيخ المقراني, lit=Resistance of Cheikh El-Mokrani; ber, Unfaq urrumi, lit=French insurrection) was the most important local uprising against France in Algeria since the conquest in 1830. The revolt broke out on March 16, 1871, with the uprising of more than 250 tribes, around a third of the population of the country. It was led by the Kabyles of the Biban mountains commanded by Cheikh Mokrani and his brother , as well as , head of the Rahmaniyya Sufi order. Background Cheikh Mokrani presentation Cheikh Mokrani (full name el-Hadj-Mohamed el-Mokrani) and his brother Boumezrag (full name Ahmed Bou-Mezrag) came from a noble family - the Ait Abbas dynasty (a branch of the Hafsids of Béjaïa), the ''Amokrane'', rulers, since the sixteenth century of the Kalâa of Ait Abbas in the Bibans and of the Medjana region. In the 1830s, their father el-Hadj-Ahmed el-Mokrani (d. 1853), had chosen to form an alliance with the French : he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Conquest Of Algeria
The French invasion of Algeria (; ) took place between 1830 and 1903. In 1827, an argument between Hussein Dey, the ruler of the Deylik of Algiers, and the French consul escalated into a blockade, following which the July Monarchy of France invaded and quickly seized Algiers in 1830, and seized other coastal communities. Amid internal political strife in France, decisions were repeatedly taken to retain control of the territory, and additional military forces were brought in over the following years to quell resistance in the interior of the country. Algerian resistance forces were divided between forces under Ahmed Bey ben Mohamed Chérif at Constantine, primarily in the east, and nationalist forces in the Kabylia and the west. Treaties with the nationalists under Emir Abdelkader enabled the French to first focus on the elimination of the remnants of the Deylik, achieved with the 1837 Siege of Constantine. Abd Al-Qādir continued to give stiff resistance in the west. Fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphis Léon Lallemand
Orphis Léon Lallemand (27 September 181720 December 1893) was a French officer. Career Conquest of Algeria He arrived in Algeria in May 1842 as a lieutenant of General staff to serve in North Africa during the French conquest of Algeria. He served successively with the ''53rd infantry regiment'', the ''9th regiment of hunters on horseback'' and the ''4th African Hunter Regiment'', from 1842 to 1846. He took part in the expeditions of the Troupes coloniales to which these regiments were then called in the provinces of Algiers and Oran. He was then attached to the General staff of the Oran division under Generals Louis Juchault de Lamoricière, Aimable Pélissier and Pierre Bosquet. Mokrani Revolt He participated in Algeria in the repression of the Mokrani revolt from April 1871. He presided over the Battle of Alma and Battle of the Col des Beni Aïcha on 19 April 1871, with colonel Alexandre Fourchault, through which he countered the Algerian rebels. Return to France On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agha (title)
Agha ( tr, ağa; ota, آغا; fa, آقا, āghā; "chief, master, lord") is an honorific title for a civilian or officer, or often part of such title. In the Ottoman times, some court functionaries and leaders of organizations like bazaar or the janissary units were entitled to the ''agha'' title. In rural communities, this term is used for people who own considerable lands and are influential in their community. Regardless of a rural community, this title is also used for any male that is influential or respected. Etymology The word ''agha'' entered English from Turkish, and the Turkish word comes from the Old Turkic ''aqa'', meaning "elder brother". It is an equivalent of Mongolian word ''aqa'' or ''aka''. Other uses "Agha" is nowadays used as a common Persian honorific title for men, the equivalent of "mister" in English.Khani, S., and R. Yousefi. "The study of address terms and their translation from Persian to English." (2014). The corresponding honorific term for w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Gates (Algeria)
The Iron Gates ( ar, البيبان, known in French as ''Défilé des Bibans'' or ''Porte de Fer'') are a mountain pass in the Bibans in Algeria. They gave their name to the Biban Range. History An 1839 French expedition under the duc d'Orléans disregarded the clauses of the 1837 Treaty of Tafna The Treaty of Tafna was signed by both Abd-el-Kader and General Thomas Robert Bugeaud on 30 May 1837. This agreement was developed after French imperial forces sustained heavy losses and military reversals in Algeria. The terms of the treaty ent ... with emir Abd el-Kader by passing through them, reigniting the war between them. References {{Reflist Mountain passes of Algeria Atlas Mountains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medjana
Medjana is a town and commune (municipality) in Bordj Bou Arréridj Province, Algeria. It is the (approximative) location the Ancient city and bishopric Vardimissa, which remains a Latin Catholic titular see. According to the 1998 census it has a population of 16,112. History Vardimissa (also spelled B- as n Greek) was important enough in the Roman province of Mauretania Caesariensis to become one of its many suffragan dioceses, but like most destined to fade completely, probably at the 7th century advent of Islam. Two of its bishops are historically documented : * Victor, participant at the Council of Carthage in 411, among the Catholic bishops confronted with Donatist heretical counterparts, without such for his see. * Burcus, intervening Catholic participant at the Council of Carthage in 484 called by king Huneric of the Vandal Kingdom hence presumably exiled or executed afterward.''Notitia provinciarum et civitatem Africae'', p. 45. Titular see The diocese was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
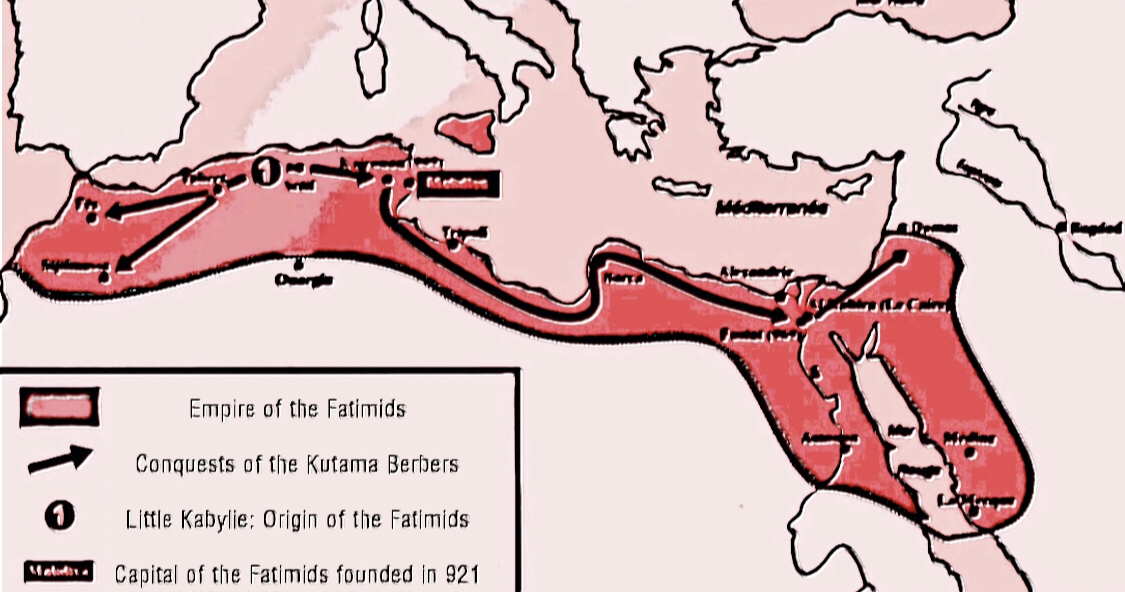
Kalâa Of Ait Abbas
The Kalâa of the Aït Abbas or Kalâa of the Beni Abbes ( Berber: ⵇⴰⵍⵄⴰ ⵍⴰⵉⵜ ⵄⴰⴱⴰⵙ alεa nāt εabbas ar, قلعة بني عباس), sometimes spelled Qal'a or Guelaa, was a citadel and the capital of the kingdom of Ait Abbas, which was founded in the sixteenth century in the Bibans and almost totally destroyed during the revolt of Cheikh Mokrani in 1871. Location The Kalâa of Aït Abbas is an important village of Kabylia in Algeria. As evidenced by the many ruins, it was an ancient fortress and capital of the local kingdom from the sixteenth to the nineteenth century. It is part of the current Algerian '' commune'' of Ighil Ali (''wilaya'' of Béjaïa). The site is located southeast of Ighil Ali, north of Teniet En Nasr, about northwest of Bordj Bou Arreridj and about southwest of Bejaia.Djamel AlilatDécouverte d'un canon du 16e siècle : Béjaïa, Qalaâ des Beni Abbès ''El Watan'', 21 April 2006. The Kalâa, following the heart-shaped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Béjaïa
Béjaïa (; ; ar, بجاية, Latn, ar, Bijāya, ; kab, Bgayet, Vgayet), formerly Bougie and Bugia, is a Mediterranean port city and commune on the Gulf of Béjaïa in Algeria; it is the capital of Béjaïa Province, Kabylia. Béjaïa is the largest principally Kabyle-speaking city in the region of Kabylia, Algeria. Geography The town is overlooked by the mountain ', whose profile is said to resemble a sleeping woman. Other nearby scenic spots include the ''Aiguades'' beach and the '' Pic des Singes'' (Peak of the Monkeys); the latter site is a habitat for the endangered Barbary macaque, which prehistorically had a much broader distribution than at present. All three of these geographic features are located in the Gouraya National Park. The Soummam river runs past the town. Under French rule, it was known under various European names, such as Budschaja in German, Bugia in Italian, and Bougie in French. The French and Italian versions, due to the town's wax trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hafsid Dynasty
The Hafsids ( ar, الحفصيون ) were a Sunni Muslim dynasty of Berber descentC. Magbaily Fyle, ''Introduction to the History of African Civilization: Precolonial Africa'', (University Press of America, 1999), 84. who ruled Ifriqiya (western Libya, Tunisia, and eastern Algeria) from 1229 to 1574. History Almohad Ifriqiya The Hafsids were of Berber descent, although to further legitimize their rule, they claimed Arab ancestry from the second Rashidun Caliph Omar. The ancestor of the dynasty and from whom their name is derived was Abu Hafs Umar ibn Yahya al-Hintati, a Berber from the Hintata tribal confederation, which belonged to the greater Masmuda confederation of Morocco. He was a member of the council of ten and a close companion of Ibn Tumart. His original Berber name was "Faskat u-Mzal Inti", which later was changed to "Abu Hafs Umar ibn Yahya al-Hintati" (also known as "Umar Inti") since it was a tradition of Ibn Tumart to rename his close companions once they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bou Mezrag
Bou () is a commune in the Loiret department in north-central France. The village is situated in the greater Orléans area, in a meander of the river Loire, 14 km east of Orléans and 9 km west of the town of Jargeau. Bou is separated by fields from the villages of Mardié and Chécy, which lie to the north. The village of Bou was traditionally an agricultural area, producing cereal crops and vegetables and a local wine known as Gris-meunier. The inhabitants of Bou are known as Boumiens. Population See also * Communes of the Loiret department The following is the list of the 325 communes of the Loiret department of France France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territori ... References Communes of Loiret {{Loiret-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rahmaniyya
The Raḥmâniyya (Arabic: الرحمانية) is an Algerian Sufi order (tariqa or brotherhood) founded by Kabyle religious scholar Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd al-Raḥman al-Azhari Bu Qabrayn in the 1770s. It was initially a branch of the Khalwatîya (Arabic: الخلوتية) established in Kabylia region. However, its membership grew unwaveringly elsewhere in Algeria and in North Africa. Founder Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Rahman al-Azharî (Arabic: محمد بن عبد الرحمن الأزهري), more commonly known as Bû Qabrayn (Arabic: بوقبرين, "the man with two tombs"), was an 18th-century Algerian Islamic scholar, saint and a Sufi mystic. He was born in 1715-29 into the Berber Ait Ismâ'îl tribe of the Qashtula, in Kabylia. He studied first in a nearby zawiya in his hometown of Jurjura. Then, he went on studying at the Great Mosque in Algiers before undertaking his journey to Mašriq in 1739–40 to perform the hajj. Following his stay in the Hijaz, Bu Qubrayn se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibans
The Bibans or Biban Range ( ar, البيبان, Kabylian: ''Tiggoura'', french: Chaîne des Bibans or ''Les Bibans'') are a chain of mountains in northern Algeria, bordering the south of Kabylie. Geography The highest summits are 1862 m high Mansoura () and 1832 m high Choukchout (). Located to the east of the Blidean Atlas and to the west of the Hodna Mountains, the Bibans are a subrange of the Tell Atlas, part of the Atlas Mountain System. The strategic Iron Gates mountain passes are located in the range and gave their name to the Biban Mountains. The main gorge is the deep Bab al-Kabir (Big Door), cut by the Ouadi Chebba, through which the railway line between Algiers and Constantine passes. The Bab al-Saghir (Little Door) of the Oadi Buktun is located 3.5 km to the east. Some authors claim that the range was known as ''El Ouennougha'' before the French colonization of Algeria. Traditionally these mountains have been populated by Kabyle people. In present days the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabylie
Kabylia ('' Kabyle: Tamurt n Leqbayel'' or ''Iqbayliyen'', meaning "Land of Kabyles", '','' meaning "Land of the Tribes") is a cultural, natural and historical region in northern Algeria and the homeland of the Kabyle people. It is part of the Tell Atlas mountain range and is located at the edge of the Mediterranean Sea. Kabylia covers two provinces of Algeria: Tizi Ouzou and Bejaia. Gouraya National Park and Djurdjura National Park are also located in Kabylia. History Antiquity Kabylia was a part of the Kingdom of Numidia (202 BC – 46 BC). List of Empires/Dynasties created by the Kabyle people * Zirid Dynasty * Hammadid Dynasty * Fatimid Caliphate * Taifa of Alpuente * Taifa of Granada * Kingdom of Beni Abbes * Kingdom of Kuku Middle Ages The history of Kabylie started to appear in the classical books during the fourth century AD with the revolt of the commander Firmus and his brother Guildon against the empire. The Vandals, a Germanic people, established a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |