|
Modern Hebrew Verb Conjugation
In Hebrew, verbs, which take the form of derived stems, are conjugated to reflect their tense and mood, as well as to agree with their subjects in gender, number, and person. Each verb has an inherent voice, though a verb in one voice typically has counterparts in other voices. This article deals mostly with Modern Hebrew, but to some extent, the information shown here applies to Biblical Hebrew as well. Verb classification Roots Verbs in Hebrew, like nouns, adjectives, and adverbs, are formed and declined by altering a (usually) three letter stem. Vowels are added between or before these three consonants in a pattern to form a related meaning between different roots. For instance, ''(שמר)'' "(he) kept / guarded" and ''(כתב)'' "(he) wrote" both add the vowel "a" in between the first and second consonants and second and third consonants to indicate the past tense "he" form. A similar formation can be found in English strong verbs with write-wrote-written and drive-d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved throughout history as the main liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. Hebrew is the only Canaanite language still spoken today, and serves as the only truly successful example of a dead language that has been revived. It is also one of only two Northwest Semitic languages still in use, with the other being Aramaic. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' Lashon Hakodesh'' (, ) since an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with many elements taken from Hebrew (notably Mishnaic) and to some extent Aramaic. Most varieties of Yiddish include elements of Slavic languages and the vocabulary contains traces of Romance languages.Aram Yardumian"A Tale of Two Hypotheses: Genetics and the Ethnogenesis of Ashkenazi Jewry".University of Pennsylvania. 2013. Yiddish is primarily written in the Hebrew alphabet. Prior to World War II, its worldwide peak was 11 million, with the number of speakers in the United States and Canada then totaling 150,000. Eighty-five percent of the approximately six million Jews who were murdered in the Holocaust were Yiddish speakers,Solomon Birnbaum, ''Grammatik der jiddischen Sprache'' (4., erg. Aufl., Hambu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
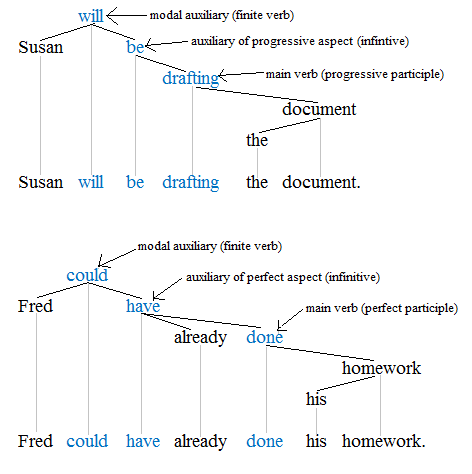
Modal Verb
A modal verb is a type of verb that contextually indicates a modality such as a ''likelihood'', ''ability'', ''permission'', ''request'', ''capacity'', ''suggestion'', ''order'', ''obligation'', or ''advice''. Modal verbs generally accompany the base (infinitive) form of another verb having semantic content. In English, the modal verbs commonly used are ''can'', ''could'', ''may'', ''might'', ''shall'', ''should'', ''will'', ''would'', ''ought to'', ''used to'', ''dare'' and ''must.'' Function A modal auxiliary verb gives information about the function of the main verb that it governs. Modals have a wide variety of communicative functions, but these functions can generally be related to a scale ranging from possibility ("may") to necessity ("must"), in terms of one of the following types of modality: *epistemic modality, concerned with the theoretical ''possibility of propositions being true or not true'' (including likelihood and certainty) *deontic modality, concerned with ''p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitual Aspect
In linguistics, the aspect of a verb is a grammatical category that defines the temporal flow (or lack thereof) in a given action, event, or state. As its name suggests, the habitual aspect (abbreviated ), not to be confused with iterative aspect or frequentative aspect, specifies an action as occurring habitually: the subject performs the action usually, ordinarily, or customarily. As such, the habitual aspect provides structural information on the nature of the subject referent, "John smokes" being interpretable as "John is a smoker", "Enjoh habitually gets up early in the morning" as "Enjoh is an early bird". The habitual aspect is a type of imperfective aspect, which does not depict an event as a single entity viewed only as a whole but instead specifies something about its internal temporal structure. Östen Dahl found that the habitual past, the most common tense context for the habitual, occurred in only seven of 60 languages sampled, including English. Especially in Turki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditional Mood
The conditional mood (abbreviated ) is a grammatical mood used in conditional sentences to express a proposition whose validity is dependent on some condition, possibly counterfactual. It may refer to a distinct verb form that expresses the conditional set of circumstances proper in the dependent clause or ''protasis'' (e.g. in Turkish or Azerbaijani), or which expresses the hypothetical state of affairs or uncertain event contingent to it in the independent clause or '' apodosis'', or both (e.g. in Hungarian or Finnish). Some languages distinguish more than one conditional mood; the East African language Hadza, for example, has a ''potential'' conditional expressing possibility, and a ''veridical'' conditional expressing certainty. Other languages do not have a conditional mood at all . In some informal contexts, such as language teaching, it may be called the "conditional tense". Some languages have verb forms called "conditional" although their use is not exclusive to cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliary Verb
An auxiliary verb (abbreviated ) is a verb that adds functional or grammatical meaning to the clause in which it occurs, so as to express tense, aspect, modality, voice, emphasis, etc. Auxiliary verbs usually accompany an infinitive verb or a participle, which respectively provide the main semantic content of the clause. An example is the verb ''have'' in the sentence ''I have finished my lunch.'' Here, the auxiliary ''have'' helps to express the perfect aspect along with the participle, ''finished''. Some sentences contain a chain of two or more auxiliary verbs. Auxiliary verbs are also called helping verbs, helper verbs, or (verbal) auxiliaries. Research has been conducted into split inflection in auxiliary verbs. Basic examples Below are some sentences that contain representative auxiliary verbs from English, Spanish, German and French, with the auxiliary verb marked in bold: ::a. Do you want tea? – ''do'' is an auxiliary accompanying the infinitive, ''want'', used here t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefixes In Hebrew
There are several prefixes in the Hebrew language which are appended to regular words to introduce a new meaning. In Hebrew, the letters that form those prefixes are called "formative letters" (Hebrew: אוֹתִיּוֹת הַשִּׁמּוּשׁ, ''Otiyot HaShimush''). Eleven of the twenty-two letters of the Hebrew alphabet are considered ''Otiyot HaShimush''. These letters are Aleph (א), Bet (ב), He (ה), Vav (ו), Yud (י), Kaf (כ), Lamed (ל), Mem (מ), Nun (נ), Shin (ש), and Tav (ת). A mnemonic to remember these letters is איתן משה וכלב (''Eitan, Moshe, v'Kalev''), which translates to " Ethan, Moses, and Caleb." Otiyot HaShimush Prefixes in Hebrew serve multiple purposes. A prefix can serve as a conjunction, preposition, definite article, or interrogative. Prefixes are also used when conjugating verbs in the future tense and for various other purposes. Conjunctions Inseparable prepositions Other prepositions Definite article Interro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infinitive
Infinitive (abbreviated ) is a linguistics term for certain verb forms existing in many languages, most often used as non-finite verbs. As with many linguistic concepts, there is not a single definition applicable to all languages. The word is derived from Late Latin ''odusinfinitivus'', a derivative of ''infinitus'' meaning "unlimited". In traditional descriptions of English, the infinitive is the basic dictionary form of a verb when used non-finitely, with or without the particle ''to''. Thus ''to go'' is an infinitive, as is ''go'' in a sentence like "I must go there" (but not in "I go there", where it is a finite verb). The form without ''to'' is called the bare infinitive, and the form with ''to'' is called the full infinitive or to-infinitive. In many other languages the infinitive is a distinct single word, often with a characteristic inflective ending, like ''morir'' (" odie") in Spanish, ''manger'' (" oeat") in French, ''portare'' (" ocarry") in Latin and Italian, ''lieb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jussive Mood
The jussive (abbreviated ) is a grammatical mood of verbs for issuing orders, commanding, or exhorting (within a subjunctive framework). English verbs are not marked for this mood. The mood is similar to the ''cohortative'' mood, which typically applies to the first person by appeal to the object's duties and obligations, and the '' imperative'', which applies to the second person (by command). The ''jussive'' however typically covers the first and third persons. It can also apply to orders by their author's wish in the ''mandative subjunctive'', as in the English, "The bank insists that she repay her debt." Examples German In the German language, the jussive mood is expressed using the present subjunctive (named or in German). It is typical of formal documents or religious texts, such as the Bible. Because it was more common in past centuries, it has often survived in proverbs: It is still common that recipes are written in jussive mood: Apart from that, jussive mood is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hortative
In linguistics, hortative modalities (; abbreviated ) are verbal expressions used by the speaker to encourage or discourage an action. Different hortatives can be used to express greater or lesser intensity, or the speaker's attitude, for or against it. Hortative modalities signal the speaker's encouragement or discouragement toward the addressee's bringing about the action of an utterance. Etymology The term hortative dates to 1576, from Late Latin ''hortatorius'' "encouraging, cheering", from ''hortatus'', past participle of ''hortari'' "exhort, encourage", intensive of ''horiri'' "urge, incite, encourage". When encouraging others it becomes ''exhortative'' while when including the speaker it becomes ''cohortative''. Ambiguity Hortative modalities share semantic and lexical similarities with other modalities, which can lead to confusion between them. Also, hortative constructions rarely have forms that are uniquely their own. The English expression Let's, a contraction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Arabic
Egyptian Arabic, locally known as Colloquial Egyptian ( ar, العامية المصرية, ), or simply Masri (also Masry) (), is the most widely spoken vernacular Arabic dialect in Egypt. It is part of the Afro-Asiatic language family, and originated in the Nile Delta in Lower Egypt. The ca. 100 million Egyptians speak a continuum of dialects, among which Cairene is the most prominent. It is also understood across most of the Arabic-speaking countries due to broad Egyptian influence in the region, including through Egyptian cinema and Egyptian music. These factors help to make it the most widely spoken and by far the most widely studied variety of Arabic. While it is primarily a spoken language, the written form is used in novels, plays and poems (vernacular literature), as well as in comics, advertising, some newspapers and transcriptions of popular songs. In most other written media and in radio and television news reporting, literary Arabic is used. Literary Arabic is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramaic Language
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in the ancient region of Syria. For over three thousand years, It is a sub-group of the Semitic languages. Aramaic varieties served as a language of public life and administration of ancient kingdoms and empires and also as a language of divine worship and religious study. Several modern varieties, namely the Neo-Aramaic languages, are still spoken in the present-day. The Aramaic languages belong to the Northwest group of the Semitic language family, which also includes the Canaanite languages such as Hebrew, Edomite, Moabite, and Phoenician, as well as Amorite and Ugaritic. Aramaic languages are written in the Aramaic alphabet, a descendant of the Phoenician alphabet, and the most prominent alphabet variant is the Syriac alphabet. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |