|
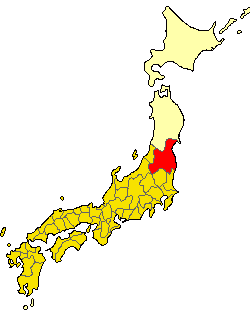
Mishima, Fukushima
is a town located in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 1,590 in 755 households, and a population density of . The total area of the town was . In 2017, Mishima was selected as one of The Most Beautiful Villages in Japan. Geography Mishima is located in the western portion of the Aizu region of Fukushima Prefecture. Most of the town is covered with forests. Traffic is concentrated along the Tadami River in the northern part of the town, and the main functions of the town such as government offices and hospitals are located in the Miyashita area. Miyashita Dam is located slightly upstream, and there is a hydroelectric power plant using the dam. The town has a number of hot springs. *Mountains: Mount Takamori *Rivers: Tadami River *Lakes: Miyashita Dam Neighboring municipalities Fukushima Prefecture * Kaneyama * Shōwa * Yanaizu Climate Mishima has a humid continental climate/oceanic climate (Köppen ''Dfb''/''Cfb'') characterized by warm sum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towns Of Japan
A town (町; ''chō'' or ''machi'') is a local administrative unit in Japan. It is a local public body along with prefecture (''ken'' or other equivalents), city (''shi''), and village (''mura''). Geographically, a town is contained within a district. Note that the same word (町; ''machi'' or ''chō'') is also used in names of smaller regions, usually a part of a ward in a city. This is a legacy of when smaller towns were formed on the outskirts of a city, only to eventually merge into it. Towns See also * Municipalities of Japan * Japanese addressing system The Japanese addressing system is used to identify a specific location in Japan. When written in Japanese characters, addresses start with the largest geographical entity and proceed to the most specific one. When written in Latin characters, ad ... References {{reflist External links "Large_City_System_of_Japan";_graphic_shows_towns_compared_with_other_Japanese_city_types_at_p._1_[PDF_7_of_40/nowiki>">DF_7_of_4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ruling emperors before the Meiji Restoration, the events restored practical abilities and consolidated the political system under the Emperor of Japan. The goals of the restored government were expressed by the new emperor in the Charter Oath. The Restoration led to enormous changes in Japan's political and social structure and spanned both the late Edo period (often called the Bakumatsu) and the beginning of the Meiji era, during which time Japan rapidly Industrialisation, industrialized and adopted Western culture, Western ideas and production methods. Foreign influence The Japanese knew they were behind the Western powers when US Commodore (United States), Commodore Matthew C. Perry came to Japan in 1853 in Black Ships, large warshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by economic growth, strict social order, isolationist foreign policies, a stable population, perpetual peace, and popular enjoyment of arts and culture. The period derives its name from Edo (now Tokyo), where on March 24, 1603, the shogunate was officially established by Tokugawa Ieyasu. The period came to an end with the Meiji Restoration and the Boshin War, which restored imperial rule to Japan. Consolidation of the shogunate The Edo period or Tokugawa period is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's regional '' daimyo''. A revolution took place from the time of the Kamakura shogunate, which existed with the Tennō's court, to the Tok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aizu Domain
was a domain of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan during the Edo period from 1601 to 1871.Ravina, Mark. (1998) ''Land and Lordship in Early Modern Japan,'' p. 222 The Aizu Domain was based at Tsuruga Castle in Mutsu Province, the core of the modern city of Aizuwakamatsu, located in the Tōhoku region of the island of Honshu. The Aizu Domain was ruled for most of its existence by the '' shinpan'' ''daimyō'' of the Aizu-Matsudaira clan, a local cadet branch of the ruling Tokugawa clan, but was briefly ruled by the '' tozama'' ''daimyō'' of the Gamō and Katō clans. The Aizu Domain was assessed under the '' Kokudaka'' system with a peak value of 919,000 '' koku'', but this was reduced to 230,000 ''koku''. The Aizu Domain was dissolved in the abolition of the ''han'' system in 1871 by the Meiji government and its territory was absorbed into Fukushima Prefecture, covering much of the traditional region of Aizu. History Pre-Edo period The area of Kurokawa, later called "Waka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutsu Province
was an old province of Japan in the area of Fukushima, Miyagi, Iwate and Aomori Prefectures and the municipalities of Kazuno and Kosaka in Akita Prefecture. Mutsu Province is also known as or . The term is often used to refer to the combined area of Mutsu and the neighboring province Dewa, which together make up the entire Tōhoku region. History Invasion by the Kinai government Mutsu, on northern Honshū, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Emishi, and became the largest as it expanded northward. The ancient regional capital of the Kinai government was Tagajō in present-day Miyagi Prefecture. * 709 ('' Wadō 2, 3rd month''), an uprising against governmental authority took place in Mutsu and in nearby Echigo Province. Troops were dispatched to subdue the revolt. * 712 (''Wadō 5''), Mutsu was separated from Dewa Province. Empress Genmei's ''Daijō-kan'' made cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters (for their latitude), with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 45 and 63 latitude, most notably in northwestern Europe, northwestern America, as well as New Zealand. Precipitation Locations with oceanic climates tend to feature frequent cloudy conditions with precipitation, low hanging clouds, and frequent fronts and storms. Thunderstorms are normally few, since strong daytime heating and hot and cold air masses meet infrequently in the region. In most areas with an oceanic climate, precipitation comes in the form of rain for the majority of the year. However, some areas with this climate see some snowfall annually during winter. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humid Continental Climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing cold (sometimes severely cold in the northern areas) winters. Precipitation is usually distributed throughout the year but often do have dry seasons. The definition of this climate regarding temperature is as follows: the mean temperature of the coldest month must be below or depending on the isotherm, and there must be at least four months whose mean temperatures are at or above . In addition, the location in question must not be semi-arid or arid. The cooler ''Dfb'', ''Dwb'', and ''Dsb'' subtypes are also known as hemiboreal climates. Humid continental climates are generally found between latitudes 30° N and 60° N, within the central and northeastern portions of North America, Europe, and Asia. They are rare and isolat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yanaizu, Fukushima
Enzō-ji is a town located in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 3,304 in 1,269 households, and a population density of 19 persons per km². The total area of the town was . Geography Yanaizu is located in the northern portion of the Aizu region of Fukushima Prefecture.The Takitani River flows north and south through the town and joins the Tadami River, which crosses the northern part of the town. The southern part of the town is mountainous. *Mountains : Mount Hakase *Rivers : Tadami River, Takitani River Neighboring municipalities Fukushima Prefecture * Nishiaizu *Aizubange *Aizumisato * Shōwa *Mishima * Kaneyama Climate Yanaizu has a Humid continental climate (Köppen ''Dfb'') characterized by warm summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Yanaizu is 11.7 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1428 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shōwa, Fukushima
Shōwa Village Hall is a village located in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. , the village had an estimated population of 1,236 in 658 households, and a population density of 5.9 persons per km2. The total area of the village was . Geography Shōwa is located in the western portion of the Aizu region of Fukushima Prefecture, and consists of scattered hamlets along the Nojiri River. *Mountains: *Rivers: Nojiri River Neighboring municipalities *Fukushima Prefecture ** Kaneyama **Mishima **Aizumisato ** Yanaizu ** Shimogō **Minamiaizu ** Tadami Climate Shōwa has a humid continental climate (Köppen ''Dfb'') characterized by warm summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Shōwa is 9.1 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1615 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 22.4 °C, and lowest in January, at around -3.3 °C. Demographics Per Japanese census data, the popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaneyama, Fukushima
is a town located in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 1972, in 1037 households and a population density of 6.7 persons per km². The total area is . Kaneyama is noted for its spectacular scenery. Geography Kaneyama is located in mountainous northwest of the Aizu region of Fukushima Prefecture, bordered Niigata Prefecture to the west. Kaneyama has no town center, but is an artificial construct made up of a number of small villages scattered alongside the Tadami River. Kaneyama has many hot springs. *Mountains : Mount Mikagura (1386.5 m), Mount Takamori *Rivers : Tadami River *Lakes: Lake Numazawa Climate Kaneyama has a humid continental climate (Köppen ''Dfa'') characterized by warm summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Kaneyama is 9.1 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1615 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 23.5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miyashita Dam
Miyashita Dam is a gravity dam on the Tadami River upstream of Mishima in the Fukushima Prefecture of Japan. It was constructed between 1941 and 1946 for the purpose of hydroelectric power generation. It supplies a 94 MW power station with water. See also *Yanaizu Dam Yanaizu Dam is a gravity dam on the Tadami River upstream of Yanaizu in the Fukushima Prefecture of Japan. It was constructed between December 1952 and August 1953 for the purpose of hydroelectric power generation. It supplies a 75 MW power ... – located downstream * Uwada Dam – located upstream References Dams in Fukushima Prefecture Hydroelectric power stations in Japan Dams completed in 1946 Energy infrastructure completed in 1946 Dams on the Tadami River Gravity dams 1946 establishments in Japan {{Japan-powerstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |