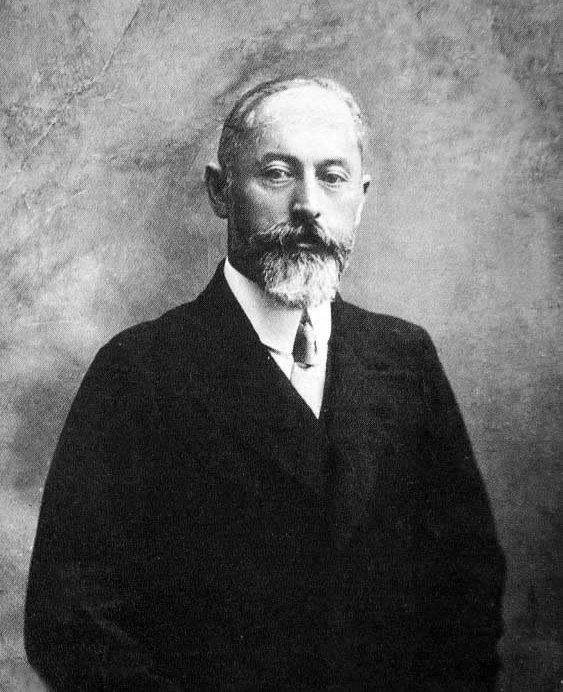|
Mirjaqip Dulatuli
Mirjaqyp Dulatuly ( kk, Міржақып Дулатұлы, ''Mırjaqyp Dulatūly''; Russian: Миржакып Дулатов (1885–1935), also known as Mir Yakub Dulatov, was a Kazakh poet, writer and one of leaders of Kazakh nationalist Alash Orda government. He also is known to have used the pen names ''Madiyar'' and ''Arghyn''. Early life Dulatuly was born on November 25, 1885 to a Muslim family in the village of Sarikopa, Kostanay Province. He was from Middle jüz, Argin tribe. He lost his mother, Demesh, at the age of two and his father, Dulat, at the age of 12. He received early education in the traditional village school. In 1897, Dulatuli enrolled in a Kazakh-Russian high school and graduated in 1902 as a village teacher. In 1904, he met Ahmet Baitursynuly and Älihan Bökeihan in Karkaraly. Under the influence of these two leaders of emerging Kazakh reformist nationalist movement, he developed an anti-colonial, anti-Russian view. He moved to St. Petersburg in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Democratic Party
) , newspaper = ''Rech'' , ideology = ConstitutionalismConstitutional monarchismLiberal democracyParliamentarism Political pluralismSocial liberalism , position = Centre to centre-left , international = , colours = Azure White , country = Russia The Constitutional Democratic Party (russian: Конституцио́нно-демократи́ческая па́ртия, translit=Konstitutsionno-demokraticheskaya partiya, K-D), also called Constitutional Democrats and formally the Party of People's Freedom (russian: links=no, Па́ртия Наро́дной Свобо́ды), was a centrist, liberal political party in the Russian Empire that promoted Western constitutional monarchy — among other policies — and attracted a base ranging from moderate conservatives to mild socialists. Party members were called Kadets (or Cadets) from the abbreviation K-D of the party name. Konstantin Kavelin's and Boris Chicherin's writings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
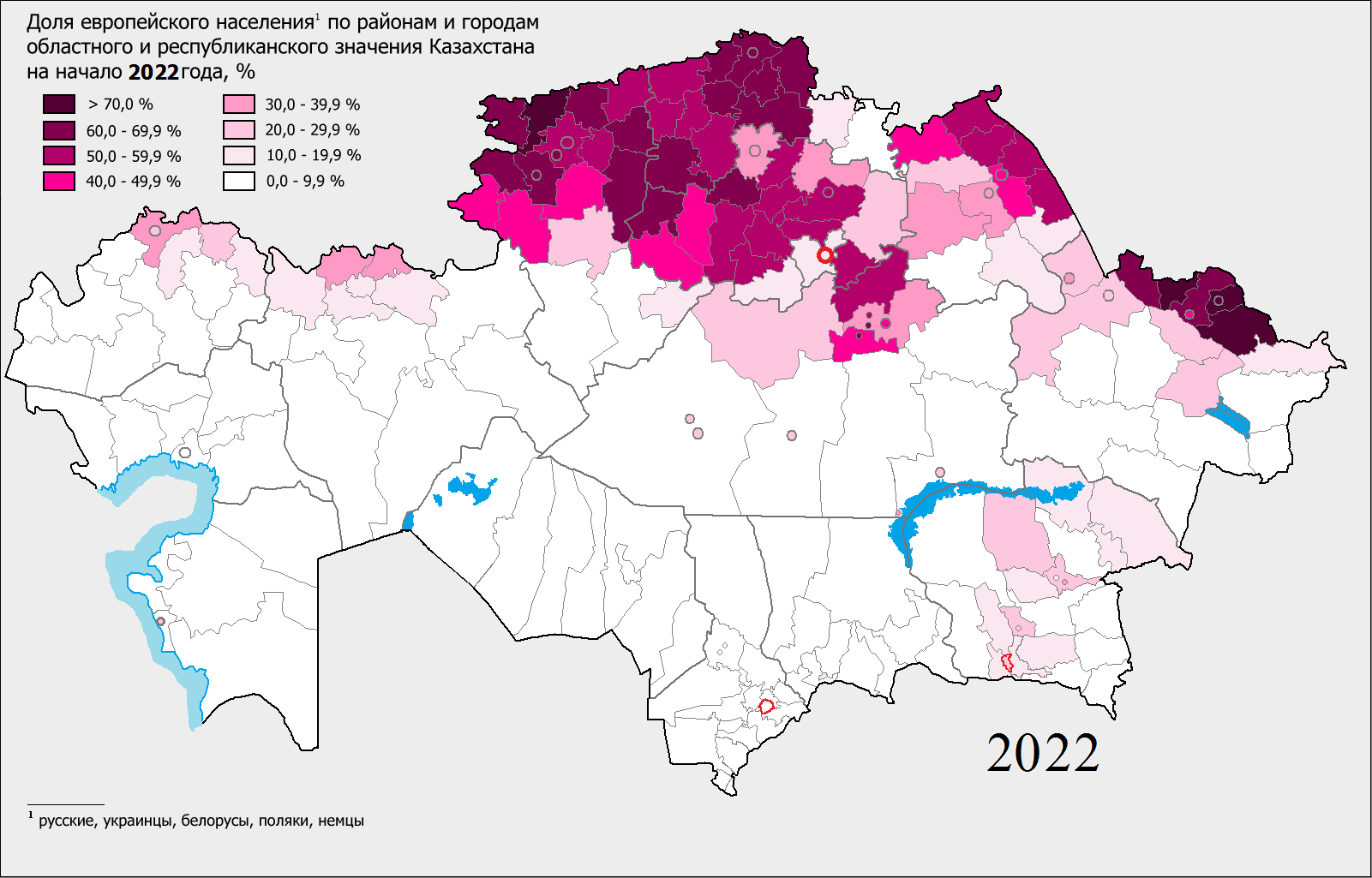
Kostanay Province
Kostanay Region ( kk, Қостанай облысы, translit=Qostanai oblysy; russian: Костанайская область, translit=Kostanayskaya oblast) is a region of Kazakhstan. Its administrative center is the city of Kostanay. The population of the region is 900,300. The population living in Kostanay is 207,000 which is equivalent to 23% of the region. Geography Kostanay Region is adjacent to the Russian federal subjects Orenburg Oblast, Chelyabinsk Oblast, Kurgan Oblast, and is near the Ural Mountains. It also touches four other Kazakh regions: Aktobe Region to the southwest, Karaganda Region to the south, Akmola Region to the southeast, and North Kazakhstan Region to the northeast. The Tobol (Tobyl) River, a tributary of the Irtysh River, starts in and flows through the region on its way to Russia. Kostanay Region's area is 197,000 square kilometers, making it the sixth largest of the Kazakh regions. Flora and fauna Resources of an animal and flora of Kostan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Return Of The Mir-Yakub
Return may refer to: In business, economics, and finance * Return on investment (ROI), the financial gain after an expense. * Rate of return, the financial term for the profit or loss derived from an investment * Tax return, a blank document or template supplied by a government for use in the reporting of tax information * Product return, the process of bringing back merchandise to a retailer for a refund or exchange * Returns (economics), the benefit distributed to the owner of a factor of production * Abnormal return, denoting the difference in behaviour between one stock and the overall stock market * Taxes, where tax returns are forms submitted to taxation authorities In technology * Return (architecture), the receding edge of a flat face * Carriage return, a key on an alphanumeric keyboard commonly equated with the "enter" key * Return statement, a computer programming statement that ends a subroutine and resumes execution where the subroutine was called * Return code, a meth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include oral literature, much of which has been transcribed. Literature is a method of recording, preserving, and transmitting knowledge and entertainment, and can also have a social, psychological, spiritual, or political role. Literature, as an art form, can also include works in various non-fiction genres, such as biography, diaries, memoir, letters, and the essay. Within its broad definition, literature includes non-fictional books, articles or other printed information on a particular subject.''OED'' Etymologically, the term derives from Latin ''literatura/litteratura'' "learning, a writing, grammar," originally "writing formed with letters," from ''litera/littera'' "letter". In spite of this, the term has also been applied to spoken or s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solovki Prison Camp
The Solovki special camp (later the Solovki special prison), was set up in 1923 on the Solovetsky Islands in the White Sea as a remote and inaccessible place of detention, primarily intended for socialist opponents of Soviet Russia's new Bolshevik regime. The first book on the Gulag, namely, '' In the Claws of the GPU'' (1934) by Francišak Aljachnovič, described the Solovki prison camp. At first, the Anarchists, Mensheviks and Socialist Revolutionaries enjoyed a special status there and were not made to work. Gradually, prisoners from the old regime (priests, gentry, and White Army officers) joined them and the guards and the ordinary criminals worked together to keep the "politicals" in order. This was the nucleus from which the entire Gulag grew, thanks to its proximity to the first great construction project of the Five-Year Plans, the White Sea–Baltic Canal. In one way, Solovki and the White Sea Canal broke a basic rule of the Gulag: they were both far too close to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English as the Bolshevists,. It signifies both Bolsheviks and adherents of Bolshevik policies. were a far-left, revolutionary Marxist faction founded by Vladimir Lenin that split with the Mensheviks from the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP), a revolutionary socialist political party formed in 1898, at its Second Party Congress in 1903. After forming their own party in 1912, the Bolsheviks took power during the October Revolution in the Russian Republic in November 1917, overthrowing the Provisional Government of Alexander Kerensky, and became the only ruling party in the subsequent Soviet Russia and later the Soviet Union. They considered themselves the leaders of the revolutionary proletariat of Russia. Their beli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menshevik
The Mensheviks (russian: меньшевики́, from меньшинство 'minority') were one of the three dominant factions in the Russian socialist movement, the others being the Bolsheviks and Socialist Revolutionaries. The factions emerged in 1903 following a dispute within the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) between Julius Martov and Vladimir Lenin. The dispute originated at the 2nd Congress of the RSDLP, ostensibly over minor issues of party organization. Martov's supporters, who were in the minority in a crucial vote on the question of party membership, came to be called ''Mensheviks'', derived from the Russian ('minority'), while Lenin's adherents were known as ''Bolsheviks'', from ('majority'). Despite the naming, neither side held a consistent majority over the course of the entire 2nd Congress, and indeed the numerical advantage fluctuated between both sides throughout the rest of the RSDLP's existence until the Russian Revolution. The split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alash Autonomy
The Alash Autonomy ( kk, Алаш Автономиясы; Alaş Avtonomiasy, italic=no, ; russian: Алашская автономия, italic=no, ) was a Kazakh provisional government, or proto-state, located mainly in Central Asia, and partly in Eastern Europe. It was part of the Russian Republic, and then Soviet Russia. The Alash Autonomy was founded in 1917 by Kazakh elites, and disestablished after the Bolsheviks banned the ruling Alash party. The goal of the party was to obtain autonomy within Russia, and to form a national, democratic state. The political entity bordered Russian territories to the north and west, the Turkestan Autonomy to the south, and China to the east. Ethnonym The use of the word Alash spreads a lot in Kazakh culture. Most commonly, Alash is the group of three juzes, territorial and tribal divisions of Kazakhs. It means that the name of autonomy can be used as a synonym to Kazakh. The ruling party wanted autonomy to unite all Turkic people from C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qazaq (journal)
''Qazaq'' ( kk, Қазақ, قازاق) was a Kazakh language weekly journal started by Akhmet Baitursynov (editor in chief), Alikhan Bukeikhanov and Mirjaqip Dulatuli. ''Qazaq'' was published from 1913 until March 1918, when it was shut down by the Soviet government. Influenced by other Jadid journals, ''Qazaq'' was considered to be a medium promoting the emerging Kazakh nationalism against Tsarist imperial policies. ''Qazaq'' published articles on the Kazakh culture, colonization of lands by Russian settlers, taxation issues, educational issues, pros and cons of Kazakh nomadic life and ongoing settlements etc. The founders of ''Qazaq'' newspaper wanted to introduce western style reforms to the Kazakh lands as a first step in the gradual progress of Kazakh people towards autonomy and independence. Influenced by Western scientific and cultural achievements, contributors to the ''Qazaq'' newspaper wanted to introduce similar reforms to the nomadic Kazakhs. They thought nomadic life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ay Qap
''Ay Qap'' (آی قاپ, ''Айқап, Aıqap'' in modern scripts) was a Kazakh journal of opinion and debate published in Troitsk from January 1911 until September 1915 under the editorship of Mūhammedjan Seralin. It brought together well-known nationalists and reformists, progressivist thinkers and scholars, educators and writers, such as Ahmed Baytursınulı, Älikhan Bökeikhanov, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alikhan Bukeikhanov
Alikhan Nurmukhameduly Bukeikhanov,, Arabic graphics: ٴالىيحان نۇرمۇحامەدۇلى بوكەيحان, romanized: ''Älihan Nūrmūhamedūly Bökeihan'', pronunciation: �ləj'χɑn no̙r'mo̙hɑmmjed'o̙ɫə bøkej'χɑn or Bökeihan (5 March 1866 – 27 September 1937) was a Kazakh politician and publisher who served as the Chairman (Prime Minister) of Provisional National Government of Alash Orda and one of the leaders of the Alash party from late 1917 to 1920. Early life Alikhan Bukeikhanov was born into a Kazakh Muslim family on 5 March 1866, in Tokyrauyn Volost, Russian Empire. He was the son of Nurmuhammed Bukeikhanov and as a great-grandson of Barak Sultan, former khan of the Orta zhuz, he was a direct descendant of Genghis Khan. Bukeikhanov graduated from the Russian-Kazakh School and Omsk Technical School in 1890. He later studied at the Saint Petersburg Forestry Institute, where he graduated from the Faculty of Economics in 1894. During Bukeikhan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akhmet Baitursynov
Ahmet Baitursynuly ( kk, Ахмет Байтұрсынұлы, , romanized: ''Ahmed Baitūrsynūly''; Russified: Ахмет Байтурсынов) ( 5 September 1872 — 8 December 1937) was a Kazakh intellectual who worked in the fields of politics, poetry, linguistics and education. Baitursynuly reformed the Kazakh alphabet. In 1912, he excluded all the purely Arabic letters not used in the Kazakh language and added letters specific to the Kazakh language. The new alphabet, named ''Tote jazu'' (meaning ''straight writing''), is still used by Kazakhs living in China, Afghanistan, and in Iran. Baitursynov also developed the basics of Kazakh and the scientific terminology for the definition of Kazakh grammar. In 1937, he was executed by a firing squad during the Great Purge. Early life, education Ahmet Baitursynuly was born to a Muslim Kazakh family in what is today Kostanay Region, Kazakhstan and was educated at the Orenburg Teachers' School. After graduating in 1895, Baitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |