|
Mir-203 MicroRNA
In molecular biology miR-203 is a short non-coding RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms, such as translational repression and Argonaute-catalyzed messenger RNA cleavage. miR-203 has been identified as a skin-specific microRNA, and it forms an expression gradient that defines the boundary between proliferative epidermal basal progenitors and terminally differentiating suprabasal cells. It has also been found upregulated in psoriasis and differentially expressed in some types of cancer. Introduction MicroRNAs are short (20-22nt), non-coding RNA molecules involved in the regulation of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) by pairing with their 3' UTR and affecting their stability or directing their silencing or degradation. MicroRNAs are likely to play roles in most cellular processes, including proliferation, development, differentiation and apoptosis. They are located in intergenic and intragenic regions, and are transcribed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MicroRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miRNAs base-pair to complementary sequences in mRNA molecules, then gene silence said mRNA molecules by one or more of the following processes: (1) cleavage of mRNA strand into two pieces, (2) destabilization of mRNA by shortening its poly(A) tail, or (3) translation of mRNA into proteins. This last method of gene silencing is the least efficient of the three, and requires the aid of ribosomes. miRNAs resemble the small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, except miRNAs derive from regions of RNA transcripts that fold back on themselves to form short hairpins, whereas siRNAs derive from longer regions of double-stranded RNA. The human genome may encode over 1900 miRNAs, although more recent analysis suggests that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosha
Drosha is a Class 2 ribonuclease III enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''DROSHA'' (formerly ''RNASEN'') gene. It is the primary nuclease that executes the initiation step of miRNA processing in the nucleus. It works closely with DGCR8 and in correlation with Dicer. It has been found significant in clinical knowledge for cancer prognosisSlack FJ, Weidhaas JB (December 2008). "MicroRNA in cancer prognosis". ''The New England Journal of Medicine.'' 359 (25): 2720-2. and HIV-1 replication.Swaminathan, G., Navas-Martín, S., & Martín-García, J. (2014). MicroRNAs and HIV-1 infection: antiviral activities and beyond. ''Journal of molecular biology'', ''426''(6), 1178-1197. History Human Drosha was cloned in 2000 when it was identified as a nuclear dsRNA ribonuclease involved in the processing of ribosomal RNA precursors. The other two human enzymes that participate in the processing and activity of miRNA are the Dicer and Argonaute proteins. Recently, proteins like Drosha h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
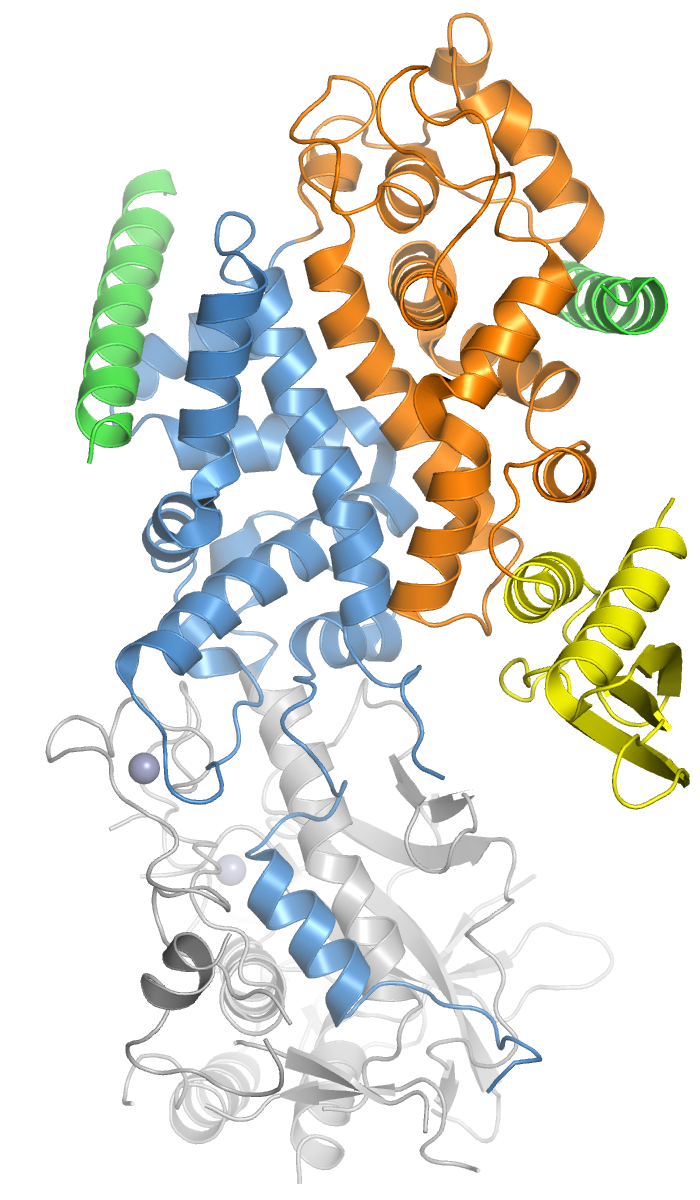
Protein Kinase C
In cell biology, Protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine amino acid residues on these proteins, or a member of this family. PKC enzymes in turn are activated by signals such as increases in the concentration of diacylglycerol (DAG) or calcium ions (Ca2+). Hence PKC enzymes play important roles in several signal transduction cascades. In biochemistry, the PKC family consists of fifteen isozymes in humans. They are divided into three subfamilies, based on their second messenger requirements: conventional (or classical), novel, and atypical. Conventional (c)PKCs contain the isoforms α, βI, βII, and γ. These require Ca2+, DAG, and a phospholipid such as phosphatidylserine for activation. Novel (n)PKCs include the δ, ε, η, and θ isoforms, and require DAG, but do not require Ca2+ for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnormal cell division. Cell division is a physiological process that occurs in almost all tissues and under a variety of circumstances. Normally, the balance between proliferation and programmed cell death, in the form of apoptosis, is maintained to ensure the integrity of tissues and organs. According to the prevailing accepted theory of carcinogenesis, the somatic mutation theory, mutations in DNA and epimutations that lead to cancer disrupt these orderly processes by interfering with the programming regulating the processes, upsetting the normal balance between proliferation and cell death. This results in uncontrolled cell division and the evolution of those cells by natural selection in the body. Only certain mutations lead to cancer w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves and blood. This may result in a low red blood cell count, inflammation around the lungs, and inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves the body's immune system attacking the joints. This results in inflammation and thickening of the joint capsule. It also affects the underlying bone and cartilage. The diagnosis is made mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abl Gene
Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 also known as ABL1 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''ABL1'' gene (previous symbol ''ABL'') located on chromosome 9. c-Abl is sometimes used to refer to the version of the gene found within the mammalian genome, while v-Abl refers to the viral gene, which was initially isolated from the Abelson murine leukemia virus. Function The ''ABL1'' proto-oncogene encodes a cytoplasmic and nuclear protein tyrosine kinase that has been implicated in processes of cell differentiation, cell division, cell adhesion, and stress response such as DNA repair. Activity of ABL1 protein is negatively regulated by its SH3 domain, and deletion of the SH3 domain turns ABL1 into an oncogene. The t(9;22) translocation results in the head-to-tail fusion of the '' BCR'' and ''ABL1'' genes, leading to a fusion gene present in many cases of chronic myelogenous leukemia. The DNA-binding activity of the ubiquitously expressed ABL1 tyrosine kinase is regulated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOCS3
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3 or SOCS-3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SOCS3'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the STAT-induced STAT inhibitor (SSI), also known as suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS), family. SSI family members are cytokine-inducible negative regulators of cytokine signaling. SOCS3 is a conserved gene, found in across the animal kingdom, including Drosophila, chickens, and crocodiles. Function The expression of SOCS3 gene is induced by various cytokines, including IL6, IL10, and interferon (IFN)-gamma. For signaling of IL-6, Epo, GCSF and Leptin, binding of SOCS3 to the respective cytokine receptor has been found to be crucial for the inhibitory function of SOCS3. Overexpression of SOCS3 inhibits insulin signaling in adipose tissue and the liver, but not in muscle. But deletion of SOCS3 in the skeletal muscle of mice protects against obesity-related insulin resistance. SOCS3 contributes to both leptin resistance and insu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type. In mammals, roughly 50–150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. ''In vivo'', they eventually differentiate into all of the body's cell types (making them pluripotent). This process starts with the differentiation into the three germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm – at the gastrulation stage. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TP63
Tumor protein p63, typically referred to as p63, also known as transformation-related protein 63 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TP63'' (also known as the '' p63'') gene. The ''TP63'' gene was discovered 20 years after the discovery of the ''p53'' tumor suppressor gene and along with '' p73'' constitutes the ''p53'' gene family based on their structural similarity. Despite being discovered significantly later than ''p53'', phylogenetic analysis of ''p53'', ''p63'' and ''p73'', suggest that ''p63'' was the original member of the family from which ''p53'' and ''p73'' evolved. Function Tumor protein p63 is a member of the p53 family of transcription factors. p63 -/- mice have several developmental defects which include the lack of limbs and other tissues, such as teeth and mammary glands, which develop as a result of interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium. TP63 encodes for two main isoforms by alternative promoters (TAp63 and ΔNp63). ΔNp63 is involved i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell-cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm, chromosomes and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division. In cells with nuclei ( eukaryotes, i.e., animal, plant, fungal, and protist cells), the cell cycle is divided into two main stages: interphase and the mitotic (M) phase (including mitosis and cytokinesis). During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, and replicates its DNA and some of its organelles. During the mitotic phase, the replicated chromosomes, organelles, and cytoplasm separate into two new daughter cells. To ensure the proper replication of cellular components and division, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints after each of the key steps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratinocyte
Keratinocytes are the primary type of Cell (biology), cell found in the epidermis (skin), epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. In humans, they constitute 90% of epidermal skin cells. Basal cells in the stratum basale, basal layer (''stratum basale'') of the skin are sometimes referred to as basal keratinocytes. Keratinocytes form a barrier against environmental damage by heat, UV radiation, Dehydration, water loss, pathogenic bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses. A number of structural proteins, enzymes, lipids, and antimicrobial peptides contribute to maintain the important barrier function of the skin. Keratinocytes differentiate from epidermal stem cells in the lower part of the epidermis and migrate towards the surface, finally becoming corneocytes and eventually be shed off, which happens every 40 to 56 days in humans. Function The primary function of keratinocytes is the formation of a barrier against environmental damage by heat, UV radiation, Dehydration, wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA-induced Silencing Complex
The RNA-induced silencing complex, or RISC, is a multiprotein complex, specifically a ribonucleoprotein, which functions in gene silencing via a variety of pathways at the transcriptional and translational levels. Using single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) fragments, such as microRNA (miRNA), or double-stranded small interfering RNA (siRNA), the complex functions as a key tool in gene regulation. The single strand of RNA acts as a template for RISC to recognize complementary messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript. Once found, one of the proteins in RISC, Argonaute, activates and cleaves the mRNA. This process is called RNA interference (RNAi) and it is found in many eukaryotes; it is a key process in defense against viral infections, as it is triggered by the presence of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). Discovery The biochemical identification of RISC was conducted by Gregory Hannon and his colleagues at the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. This was only a couple of years after the discovery of RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)