|
Miozoa
Myzozoa is a grouping of specific phyla within Alveolata, that either feed through myzocytosis, or were ancestrally capable of feeding through myzocytosis. Many protozoan orders are included within Myzozoa. It is sometimes described as a phylum, containing the major subphyla Dinozoa and Apicomplexa, plus minor subphyla. The term Myzozoa superseded the previous term "Miozoa", by the same authority, and gave a slightly altered meaning. Phyla Within Myzozoa, there are around four phyla: *Apicomplexa – parasitic protozoa that lack axonemal locomotive structures except in gametes *Dinoflagellates – mostly marine flagellates many of which have chloroplasts *Chromerida – a marine phylum of photosynthetic protozoa *Perkinsozoa The term/group Myzozoa was not considered in a resolution of protist groups by Adl et al. 2012. Strict taxonomy only considers common traits possessed by all organisms of the group. Some organisms within each of the component groups of Myzozoa have lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicomplexa
The Apicomplexa (also called Apicomplexia) are a large phylum of parasitic alveolates. Most of them possess a unique form of organelle that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid called an apicoplast, and an apical complex structure. The organelle is an adaptation that the apicomplexan applies in penetration of a host cell. The Apicomplexa are unicellular and spore-forming. All species are obligate endoparasites of animals, except '' Nephromyces'', a symbiont in marine animals, originally classified as a chytrid fungus. Motile structures such as flagella or pseudopods are present only in certain gamete stages. The Apicomplexa are a diverse group that includes organisms such as the coccidia, gregarines, piroplasms, haemogregarines, and plasmodia. Diseases caused by Apicomplexa include: * Babesiosis ('' Babesia'') * Malaria (''Plasmodium'') * Cryptosporidiosis ('' Cryptosporidium parvum'') * Cyclosporiasis ('' Cyclospora cayetanensis'') * Cystoisosporiasis ('' Cys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellate
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their means of motion. The term presently does not imply any specific relationship or classification of the organisms that possess flagella. However, the term "flagellate" is included in other terms (such as " dinoflagellate" and " choanoflagellata") which are more formally characterized. Form and behavior Flagella in eukaryotes are supported by microtubules in a characteristic arrangement, with nine fused pairs surrounding two central singlets. These arise from a basal body. In some flagellates, flagella direct food into a cytostome or mouth, where food is ingested. Flagella often support hairs, called mastigonemes, or contain rods. Their ultrastructure plays an important role in classifying eukaryotes. Among protoctists and micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes in turn are wrapped into 30-nanometer fibers that form tightly packed chromatin. Histones prevent DNA from becoming tangled and protect it from DNA damage. In addition, histones play important roles in gene regulation and DNA replication. Without histones, unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long. For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA if completely stretched out; however, when wound about histones, this length is reduced to about 90 micrometers (0.09 mm) of 30 nm diameter chromatin fibers. There are five families of histones which are designated H1/H5 (linker histones), H2, H3, and H4 (core histones). The nucleosome core is formed of two H2A-H2B dimers and a H3-H4 tetramer. The tight wrapping of DNA around his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perkinsus Marinus
''Perkinsus marinus'' is a species of alveolates belonging to the phylum Perkinsozoa.Joseph, S., et al. (2010)The alveolate ''Perkinsus marinus'': biological insights from EST gene discovery.''BMC Genomics'' 11(1), 228. It is similar to a dinoflagellate. It is known as a prevalent pathogen of oysters, causing massive mortality in oyster populations. The disease it causes is known as dermo or perkinsosis, and is characterized by the degradation of oyster tissues.Bower, S. MSynopsis of infectious diseases and parasites of commercially exploited shellfish: ''Perkinsus marinus'' ("dermo" disease) of oysters.Fisheries and Oceans Canada. 2011. The genome of this species has been sequenced. The species originally was named ''Dermocystidium marinum''. Taxonomy ''P. marinus'' is a protozoan of the protist superphylum Alveolata, the alveolates. Its phylum, Perkinsozoa, is a relatively new taxon positioned between the dinoflagellates and the Apicomplexa, and is probably more closel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
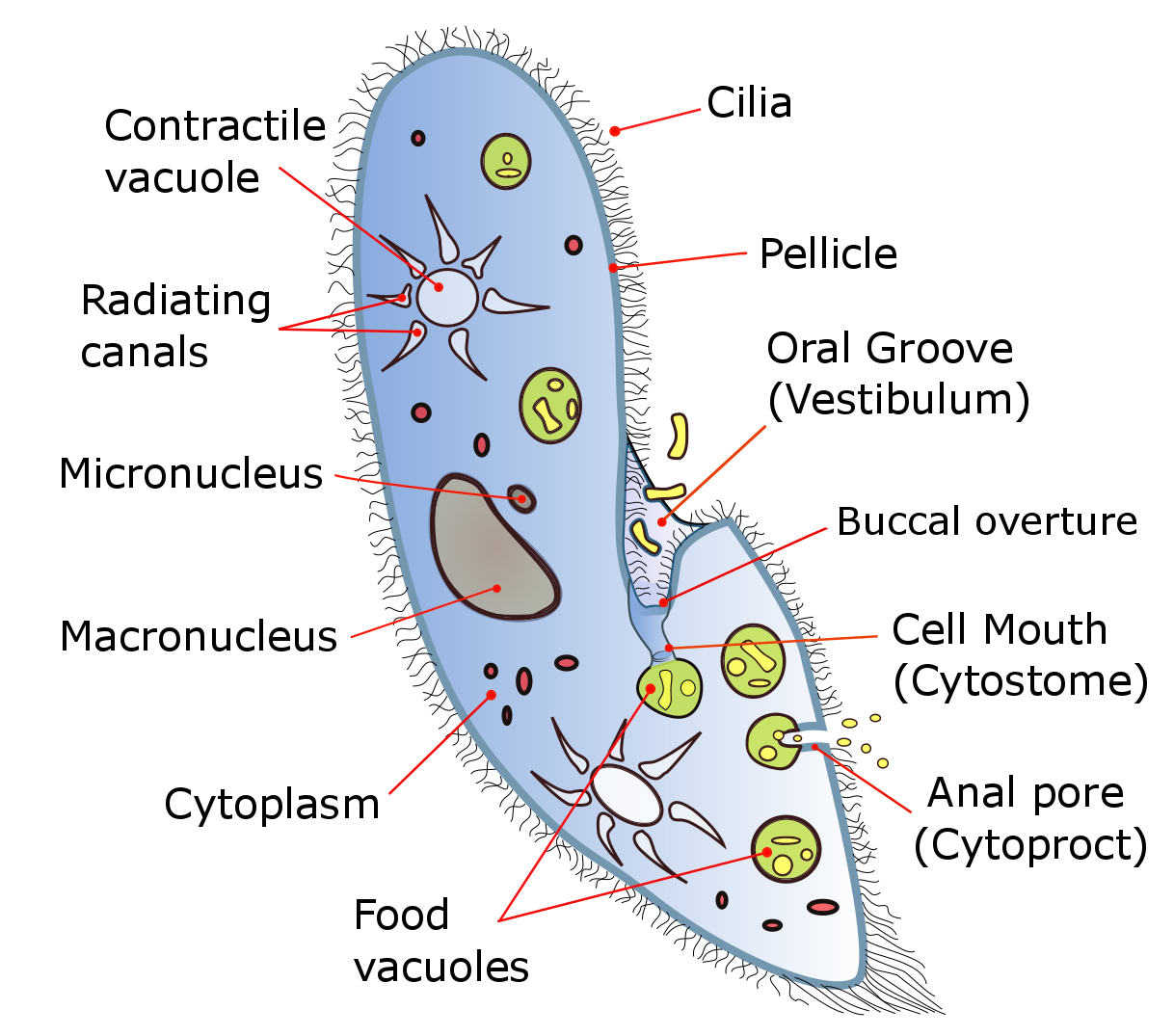
Ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some obligate and opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species range in size from as little as 10 µm in some colpodeans to as much as 4 mm in length in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colpodella
''Colpodella'' is a genus of alveolates comprising 5 species, and two further possible species: They share all the synapomorphies of apicomplexans, but are free-living, rather than parasitic. Many members of this genus were previously assigned to a different genus - '' Spiromonas''. The type species is ''Colpodella pugnax'' Cienkowski 1865. Description These are small ('Dingensia angusta'' (Dujardin 1841) Patterson & Zoelffel 1991 Species transferred to other genera: * ''Colpodella gonderi'' (Foissner & Foissner 1984) Simpson & Patterson 1996 as ''Microvorax gonderi'' (Foissner & Foissner 1984) Cavalier-Smith 2017 * ''Colpodella perforans'' (Hollande 1938) Patterson & Zölffel 1991 as ''Chilovora perforans'' (Hollande 1938) Cavalier-Smith & Chao 2004 * ''Colpodella pontica'' Mylnikov 2000 as ''Voromonas pontica'' (Mylnikov 2000) Cavalier-Smith & Chao 2004 * ''Colpodella pugnax'' Simpson & Patterson 1996 non Cienkowsky 1865 as '' Algovora pugnax'' (Simpson & Patterson 1996) Cava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voromonas
''Voromonas'' is a genus of predatory alveolates. The genus and species were described by Mylnikov in 2000. It was originally described as ''Colpodella pontica'' but was later renamed by Cavalier-Smith and Chao in 2004. Taxonomy There is one species known in this genus. A DNA based analysis suggests that this species may be related to the ''Colpodella''. Feeding At the anterior end of the protozoan, this organism manifests a rostrum which contains a microtubular structure (the pseudoconoid) The pseudoconoid forms an open cone and which is located adjacent to microtubular bands, micronemes and rhoptries. The pseudoconoid begins near the kinetosomes of the flagella and passes along the flagellate pocket into the rostrum. While feeding on prey organisms the rostrum is inserted into the body of the prey and the cytoplasm is sucked out. Known prey organisms include bodonids, chrysomonads, percolomonads. Known non prey organisms include naked amoebas, ciliates, cryptomonads an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like '' Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce two morphologically distinct types of gametes, and in which each individual produces only one type, a female is any individual that produces the larger type of gamete—called an ovum— and a male produces the smaller type—called a sperm. Sperm cells or spermatozoa are small and motile due to the flagellum, a tail-shaped structure that allows the cell to propel and move. In contrast, each egg cell or ovum is relatively large and non-motile. In short a gamete is an egg cell (female gamete) or a sperm (male gamete). In animals, ova mature in the ovaries of females and sperm develop in the testes of males. During fertilization, a spermatozoon and ovum unite to form a new diploid organism. Gametes carry half the genetic information of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey ( phagotrophy and myzocytosis). In terms of number of species, dinoflagellates are one of the largest groups of marine eukaryotes, although substantially smaller than diatoms. Some species are endosymbionts of marine animals and play an important part in the biology of coral reefs. Other dinoflagellates are unpigmented predators on other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic (for example, '' Oodinium'' and '' Pfiesteria''). Some dinoflagell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axoneme
An axoneme, also called an axial filament is the microtubule-based cytoskeletal structure that forms the core of a cilium or flagellum. Cilia and flagella are found on many cells, organisms, and microorganisms, to provide motility. The axoneme serves as the "skeleton" of these organelles, both giving support to the structure and, in some cases, the ability to bend. Though distinctions of function and length may be made between cilia and flagella, the internal structure of the axoneme is common to both. Structure Inside a cilium and a flagellum is a microtubule-based cytoskeleton called the axoneme. The axoneme of a primary cilium typically has a ring of nine outer microtubule doublets (called a 9+0 axoneme), and the axoneme of a motile cilium has two central microtubules in addition to the nine outer doublets (called a 9+2 axoneme). The axonemal cytoskeleton acts as a scaffolding for various protein complexes and provides binding sites for molecular motor proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |