|
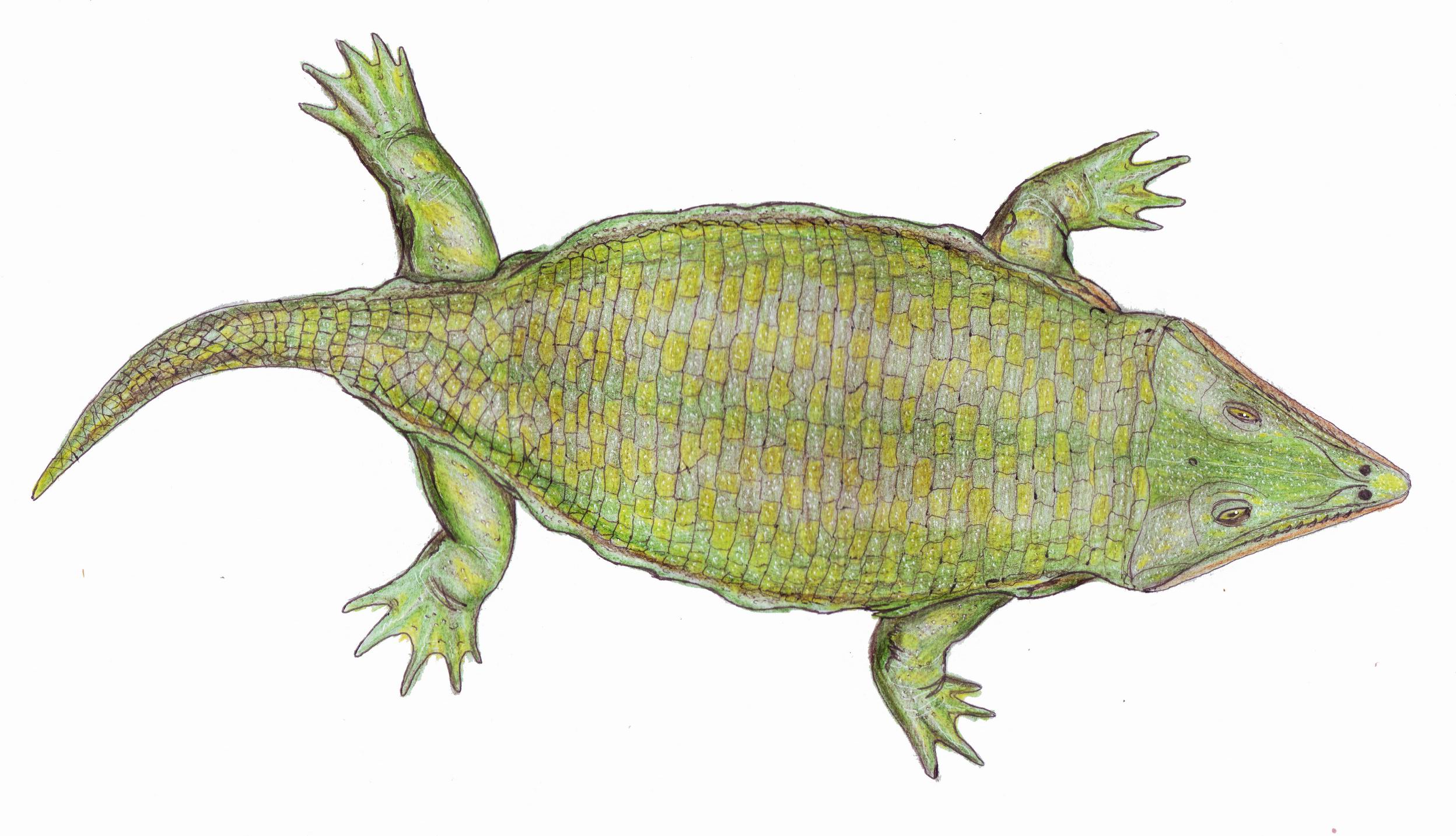
Mioproteus
''Mioproteus'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric salamanders from Neogene Europe. Its living relatives are the olm and the mudpuppies. The species ''M. caucasicus'' is from the Middle Miocene. The species ''M. wezei'' first appears in the fossil record during the Pliocene, then disappears during the Middle Pleistocene. See also * Prehistoric amphibian * List of prehistoric amphibians This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all Genus, genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accep ... References Quaternary amphibians of Europe Pliocene amphibians Miocene amphibians Miocene genus first appearances Pleistocene genus extinctions Pleistocene amphibians Neogene amphibians of Europe Cenozoic salamanders Fossil taxa described in 1978 Proteidae Prehistoric amphibian genera {{paleo-salamander-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteidae
The family Proteidae is a group of aquatic salamanders found today in the Balkan Peninsula and North America. The range of the genus ''Necturus'' (commonly known as waterdogs or mudpuppies) runs from southern central Canada, through the midwestern United States, east to North Carolina and south to Georgia and Mississippi. The range of the olm, the only extant member of the genus ''Proteus'', is limited to the Western Balkans. The fossil record of the family extends into the end of the Late Cretaceous, with ''Paranecturus'' being known from the Maastrichtian of North America. Taxonomy Proteidae, is divided into two extant genera, ''Necturus'' with five North American species, and ''Proteus'' with one extant European species, the olm. A number of extinct genera are known extending back to the end of the Late Cretaceous. Family Proteidae * Genus ''Necturus'' ** Alabama waterdog (''N. alabamensis'') **Western waterdog (''N. beyeri'') **Neuse River waterdog (''N. lewisi'') **Red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Amphibian
This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all Genus, genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomen dubium, nomina dubia''), or were not formally published (''nomen nudum, nomina nuda''), as well as synonym (zoology), junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered amphibians. Modern forms are excluded from this list. The list currently includes 454 names. Naming conventions and terminology Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Synonym (zoology), Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally designated and the type (zoology), type specimens are later assigned to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Prehistoric Amphibians
This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful ('' nomina dubia''), or were not formally published (''nomina nuda''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered amphibians. Modern forms are excluded from this list. The list currently includes 454 names. Naming conventions and terminology Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally designated and the type specimens are later assigned to the same genus, the first to be published (in chronological order) is the senior synon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene Amphibians
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1978
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the abso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenozoic Salamanders
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configuration of continents. It is the latest of three geological eras since complex life evolved, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. It started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor. The Cenozoic is also known as the Age of Mammals because the terrestrial animals that dominated both hemispheres were mammalsthe eutherians (placentals) in the northern hemisphere and the metatherians (marsupials, now mainly restricted to Australia) in the southern hemisphere. The extinction of many groups allowed mammals and birds to greatly diversify so that l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neogene Amphibians Of Europe
The Neogene ( ), informally Upper Tertiary or Late Tertiary, is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period Mya. The Neogene is sub-divided into two epochs, the earlier Miocene and the later Pliocene. Some geologists assert that the Neogene cannot be clearly delineated from the modern geological period, the Quaternary. The term "Neogene" was coined in 1853 by the Austrian palaeontologist Moritz Hörnes (1815–1868). During this period, mammals and birds continued to evolve into modern forms, while other groups of life remained relatively unchanged. The first humans (''Homo habilis'') appeared in Africa near the end of the period. Some continental movements took place, the most significant event being the connection of North and South America at the Isthmus of Panama, late in the Pliocene. This cut off the warm ocean currents from the Pacific to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Amphibians
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the two reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Genus Extinctions
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene Genus First Appearances
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene Amphibians
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Period in the . The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the |