|
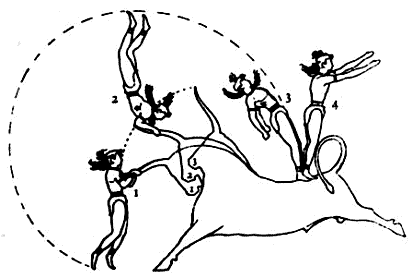
Minoan Bull-leaper
The Minoan bull leaper is a bronze group of a bull and leaper in the British Museum. It is the only known largely complete three-dimensional sculpture depicting Minoan bull-leaping. Although bull leaping certainly took place in Crete at this time, the leap depicted is practically impossible and it has therefore been speculated that the sculpture may be an exaggerated depiction. This speculation has been backed up by the testaments of modern-day bull leapers from France and Spain. Description The group was cast in a single mould using the lost-wax casting technique. The group's homogeneity was demonstrated by analysing the composition of the bronze of bull and leaper: both contain about 96% copper and 1.5% tin, with 1% zinc. The low proportion of tin in the alloy would have made it difficult for the bronze to fill the mould, resulting in the missing lower legs of the leaper, and probably the arms. Stylistically, the group is coherent, since the arched back of the leaper mirrors the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Sculpture Showing An Acrobat Leaping Over A Bulls Head, Crete, Minoan, About 1700-1450 BC, British Museum (8207269149) (cropped)
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as strength, ductility, or machinability. The archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in modern times. Because historical artworks wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A History Of The World In 100 Objects
''A History of the World in 100 Objects'' was a joint project of BBC Radio 4 and the British Museum, consisting of a 100-part radio series written and presented by British Museum director Neil MacGregor. In 15-minute presentations broadcast on weekdays on Radio 4, MacGregor used objects of ancient art, industry, technology and arms, all of which are in the British Museum's collections, as an introduction to parts of human history. The series, four years in planning, began on 18 January 2010 and was broadcast over 20 weeks. * * * * A book to accompany the series, ''A History of the World in 100 Objects'' by Neil MacGregor, was published by Allen Lane on 28 October 2010. The entire series is also available for download along with an audio version of the book for purchase. The British Museum won the 2011 Art Fund Prize for its role in hosting the project. In 2016, a touring exhibition of several items depicted on the radio programme, also titled ''A History of the World in 100 Obj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Sculpture
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sculptural processes originally used carving (the removal of material) and modelling (the addition of material, as clay), in stone, metal, ceramics, wood and other materials but, since Modernism, there has been an almost complete freedom of materials and process. A wide variety of materials may be worked by removal such as carving, assembled by welding or modelling, or moulded or cast. Sculpture in stone survives far better than works of art in perishable materials, and often represents the majority of the surviving works (other than pottery) from ancient cultures, though conversely traditions of sculpture in wood may have vanished almost entirely. However, most ancient sculpture was brightly painted, and this has been lost. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minoan Art
Minoan art is the art produced by the Bronze Age Aegean Minoan civilization from about 3000 to 1100 BC, though the most extensive and finest survivals come from approximately 2300 to 1400 BC. It forms part of the wider grouping of Aegean art, and in later periods came for a time to have a dominant influence over Cycladic art. Since wood and textiles have decomposed, the best-preserved (and most instructive) surviving examples of Minoan art are its pottery, palace architecture (with frescos which include "the earliest pure landscapes anywhere"), small sculptures in various materials, jewellery, metal vessels, and intricately-carved seals. It was influenced by the neighbouring cultures of Ancient Egypt and the ancient Near East, which had produced sophisticated urban art for much longer, but the character of the small but wealthy mercantile Minoan cities was very different, with little evidence of large temple-based religion, monarchs, or warfare, and "all the imaginative powe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minoan Archaeological Artifacts
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, whose earliest beginnings were from 3500BC, with the complex urban civilization beginning around 2000BC, and then declining from 1450BC until it ended around 1100BC, during the early Greek Dark Ages, part of a wider bronze age collapse around the Mediterranean. It represents the first advanced civilization in Europe, leaving behind a number of massive building complexes, Minoan art, sophisticated art, and writing systems. Its economy benefited from a network of trade around much of the Mediterranean. The civilization was rediscovered at the beginning of the 20th century through the work of British archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans. The name "Minoan" derives from the mythical Minos, King Minos and was coined by Evans, who identified the site at Knossos with the labyrinth of the Minotaur. The Minoan civilization has been described as the earliest of its kind in Europe, and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Sculptures In The United Kingdom
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as strength, ductility, or machinability. The archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in modern times. Because historical artworks were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattle In Art
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult males are referred to as bulls. Cattle are commonly raised as livestock for meat (beef or veal, see beef cattle), for milk (see dairy cattle), and for hides, which are used to make leather. They are used as riding animals and draft animals ( oxen or bullocks, which pull carts, plows and other implements). Another product of cattle is their dung, which can be used to create manure or fuel. In some regions, such as parts of India, cattle have significant religious significance. Cattle, mostly small breeds such as the Miniature Zebu, are also kept as pets. Different types of cattle are common to different geographic areas. Taurine cattle are found primarily in Europe and temperate areas of Asia, the Americas, and Australia. Zebus (al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bull-leaping
Bull-leaping ( grc, ταυροκαθάψια, ) is a term for various types of non-violent bull fighting. Some are based on an ancient ritual from the Minoan civilization involving an acrobat leaping over the back of a charging bull (or cow). As a sport it survives in modern France, usually with cows rather than bulls, as ; in Spain, with bulls, as and in Tamil Nadu, India with bulls as Jallikattu. Ritual leaping over bulls is a motif in Middle Bronze Age figurative art, especially in Minoan art, and what are probably Minoan objects found in Mycenaean Greece, but it is also sometimes found in Hittite Anatolia, the Levant, Bactria and the Indus Valley. It is often interpreted as a depiction of a rite performed in connection with bull worship. Iconography Younger (1995) classifies bull-leaping depictions in Bronze Age Aegean art as follows: * Type I: the acrobat approaches the bull from the front, grabs the horns, and somersaults backwards * Type II: the acrobat approaches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Metalwork
Ancient Greek art stands out among that of other ancient cultures for its development of naturalistic but idealized depictions of the human body, in which largely nude male figures were generally the focus of innovation. The rate of stylistic development between about 750 and 300 BC was remarkable by ancient standards, and in surviving works is best seen in sculpture. There were important innovations in painting, which have to be essentially reconstructed due to the lack of original survivals of quality, other than the distinct field of painted pottery. Greek architecture, technically very simple, established a harmonious style with numerous detailed conventions that were largely adopted by Roman architecture and are still followed in some modern buildings. It used a vocabulary of ornament that was shared with pottery, metalwork and other media, and had an enormous influence on Eurasian art, especially after Buddhism carried it beyond the expanded Greek world created by Alexand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek And Roman Sculptures In The British Museum
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century BC Works
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 ( MDCI), to December 31, 1700 ( MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal court could be more easily ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bull-Leaping Fresco
The bull-leaping fresco is the most completely restored of several stucco panels originally sited on the upper-story portion of the east wall of the palace at Knossos in Crete. It shows a bull-leaping scene. Although they were frescos, they were painted on stucco relief scenes. They were difficult to produce. The artist had to manage not only the altitude of the panel but also the simultaneous molding and painting of fresh stucco. The panels, therefore, do not represent the formative stages of the technique. In Minoan chronology, their polychrome hues – white, pale red, dark red, blue, black – exclude them from the Early Minoan (EM) and early Middle Minoan (MM) Periods. They are, in other words, instances of the "mature art" created no earlier than MM III. The flakes of the destroyed panels fell to the ground from the upper story during the destruction of the palace, probably by earthquake, in Late Minoan (LM) II. By that time the east stairwell, near which they fell, was disu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)