|
Minivac 601
Minivac 601 Digital Computer Kit was an Electromechanics, electromechanical digital computer system created by information theory pioneer Claude Shannon as an educational toy using digital circuits.Advertisement: Minivac 601 Page 33, 1961-10, ''Popular Science'' Description In 1961, the system was sold by Scientific Development Corporation's "Consumer Products Division", which was soon renamed as the "Digital Equipment Division".Advertisement: Minivac 601Page 31, 1961-11, ''Popular Science'' The Minivac 601 was originally housed in a blue-painted wooden case. It used DPDT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Shannon
Claude Elwood Shannon (April 30, 1916 – February 24, 2001) was an American people, American mathematician, electrical engineering, electrical engineer, and cryptography, cryptographer known as a "father of information theory". As a 21-year-old master's degree student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), he wrote A Symbolic Analysis of Relay and Switching Circuits, his thesis demonstrating that electrical applications of Boolean algebra could construct any logical numerical relationship. Shannon contributed to the field of cryptanalysis for national defense of the United States during World War II, including his fundamental work on codebreaking and secure telecommunications. Biography Childhood The Shannon family lived in Gaylord, Michigan, and Claude was born in a hospital in nearby Petoskey, Michigan, Petoskey. His father, Claude Sr. (1862–1934), was a businessman and for a while, a judge of probate in Gaylord. His mother, Mabel Wolf Shannon (1890–1945), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock Signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') oscillates between a high and a low state and is used like a metronome to coordinate actions of digital circuits. A clock signal is produced by a clock generator. Although more complex arrangements are used, the most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle, usually with a fixed, constant frequency. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of sufficient complexity use a clock signal in order to synchronize different parts of the circuit, cycling at a rate slower than the worst-case internal propagation delays. In some cases, more than one clock cycle is required to perform a predictable action. As ICs become mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Electronics
Analogue electronics ( en-US, analog electronics) are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal. The word analogue is derived from the el, word ανάλογος (analogos) meaning "proportional". Analogue signals An analogue signal uses some attribute of the medium to convey the signal's information. For example, an aneroid barometer uses the angular position of a needle as the signal to convey the information of changes in atmospheric pressure. Electrical signals may represent information by changing their voltage, current, frequency, or total charge. Information is converted from some other physical form (such as sound, light, temperature, pressure, position) to an electrical signal by a transducer which converts one type of energy into another (e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A diode vacuum tube or thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to plate. A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also used. Among many uses, diodes are found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed to add capacitance to a circuit. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the ''condenser microphone''. The physical form and construction of practical capacitors vary widely and many types of capacitor are in common use. Most capacitors contain at least two electrical conductors often in the form of metallic plates or surfaces separated by a dielectric medium. A conductor may be a foil, thin film, sintered bead of metal, or an electrolyte. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
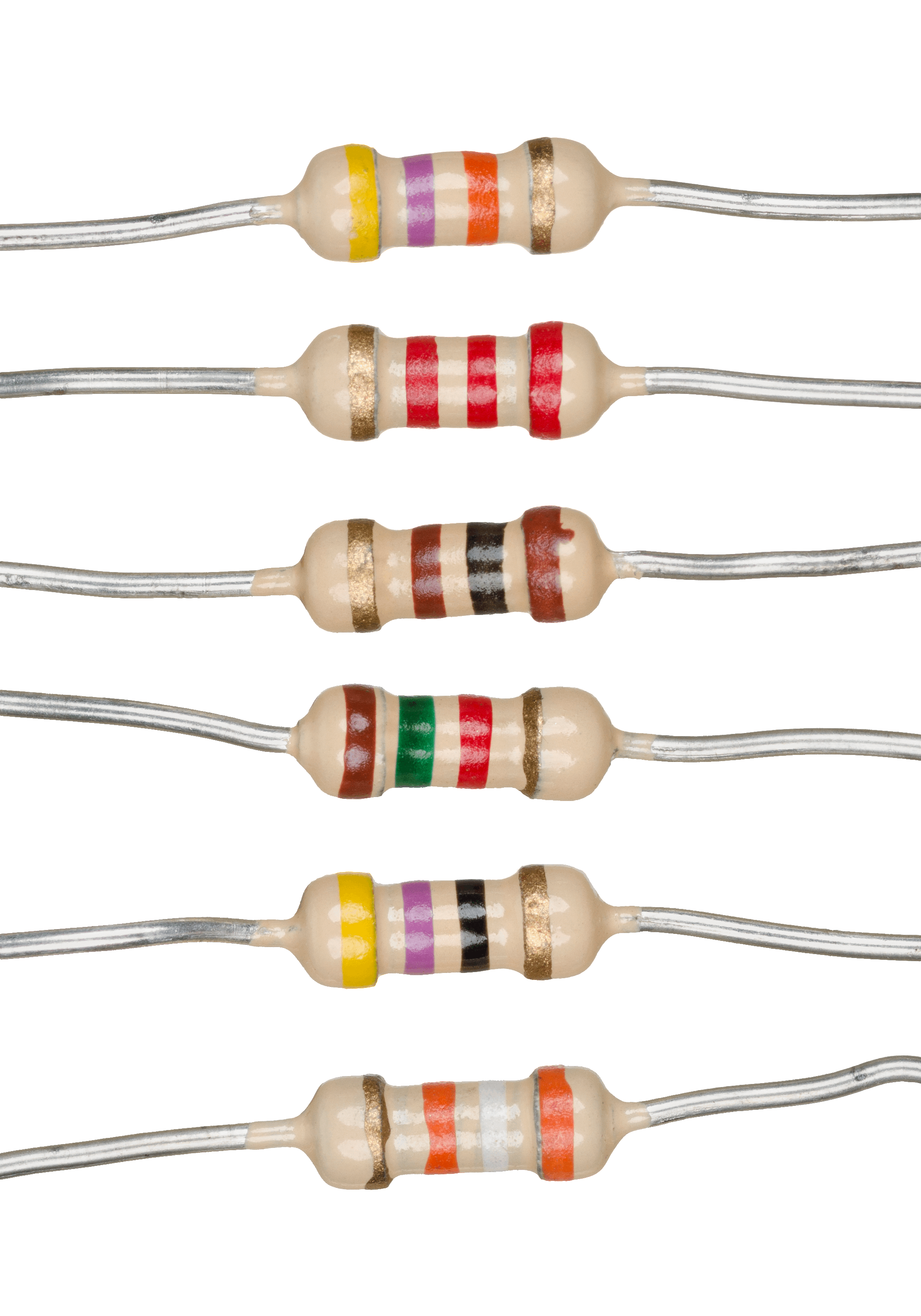
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevator
An elevator or lift is a wire rope, cable-assisted, hydraulic cylinder-assisted, or roller-track assisted machine that vertically transports people or freight between floors, levels, or deck (building), decks of a building, watercraft, vessel, or other structure. They are typically powered by electric motors that drive traction cables and counterweight systems such as a hoist (device), hoist, although some pump hydraulic fluid to raise a cylindrical piston like a hydraulic jack, jack. In agriculture and manufacturing, an elevator is any type of conveyor device used to lift materials in a continuous stream into bins or silos. Several types exist, such as the chain and bucket elevator, grain auger screw conveyor using the principle of Archimedes' screw, or the chain and paddles or forks of hay elevators. Languages other than English, such as Japanese, may refer to elevators by loanwords based on either ''elevator'' or ''lift''. Due to wheelchair access laws, elevators are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tic-Tac-Toe
Tic-tac-toe (American English), noughts and crosses (Commonwealth English), or Xs and Os (Canadian or Irish English) is a paper-and-pencil game for two players who take turns marking the spaces in a three-by-three grid with ''X'' or ''O''. The player who succeeds in placing three of their marks in a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal row is the winner. It is a solved game, with a forced draw assuming best play from both players. Gameplay Tic-tac-toe is played on a three-by-three grid by two players, who alternately place the marks X and O in one of the nine spaces in the grid. In the following example, the first player (''X'') wins the game in seven steps: There is no universally-agreed rule as to who plays first, but in this article the convention that X plays first is used. Players soon discover that the best play from both parties leads to a draw. Hence, tic-tac-toe is often played by young children who may not have discovered the optimal strategy. Because of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taper Pin
Taper may refer to: * Part of an object in the shape of a cone (conical) * Taper (transmission line), a transmission line gradually increasing or decreasing in size * Fishing rod taper, a measure of the flexibility of a fishing rod * Conically tapered joints, made of ground glass, commonly used in chemistry labs to mate two glassware components fitted with glass tubings * Luer Taper, a standardized fitting system used for making leak-free connections between slightly conical syringe tips and needles * Tapered thread, a conical screw thread made of a helicoidal ridge wrapped around a cone * Machine taper, in machinery and engineering * Mark Taper Forum, a theatre in the Los Angeles Music Center * A ratio used in aeronautics (see Chord (aeronautics)) * A thin candle * Philadelphia Tapers (also New York Tapers and Washington Tapers), a defunct professional basketball team * Taper (cymbal), the reduction in thickness of a cymbal from center to rim * Taper pin, used in manufact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jumper Wire
A jump wire (also known as jumper, jumper wire, DuPont wire) is an electrical wire, or group of them in a cable, with a connector or pin at each end (or sometimes without them – simply "tinned"), which is normally used to interconnect the components of a breadboard or other prototype or test circuit, internally or with other equipment or components, without soldering. Individual jump wires are fitted by inserting their "end connectors" into the slots provided in a breadboard, the header connector of a circuit board, or a piece of test equipment. Types There are different types of jumper wires. Some have the same type of electrical connector Components of an electrical circuit are electrically connected if an electric current can run between them through an electrical conductor. An electrical connector is an electromechanical device used to create an electrical connection between ... at both ends, while others have different connectors. Some common connectors a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexadecimal
In mathematics and computing, the hexadecimal (also base-16 or simply hex) numeral system is a positional numeral system that represents numbers using a radix (base) of 16. Unlike the decimal system representing numbers using 10 symbols, hexadecimal uses 16 distinct symbols, most often the symbols "0"–"9" to represent values 0 to 9, and "A"–"F" (or alternatively "a"–"f") to represent values from 10 to 15. Software developers and system designers widely use hexadecimal numbers because they provide a human-friendly representation of binary-coded values. Each hexadecimal digit represents four bits (binary digits), also known as a nibble (or nybble). For example, an 8-bit byte can have values ranging from 00000000 to 11111111 in binary form, which can be conveniently represented as 00 to FF in hexadecimal. In mathematics, a subscript is typically used to specify the base. For example, the decimal value would be expressed in hexadecimal as . In programming, a number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge, Massachusetts
Cambridge ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. As part of the Boston metropolitan area, the cities population of the 2020 U.S. census was 118,403, making it the fourth most populous city in the state, behind Boston, Worcester, and Springfield. It is one of two de jure county seats of Middlesex County, although the county's executive government was abolished in 1997. Situated directly north of Boston, across the Charles River, it was named in honor of the University of Cambridge in England, once also an important center of the Puritan theology embraced by the town's founders. Harvard University, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Lesley University, and Hult International Business School are in Cambridge, as was Radcliffe College before it merged with Harvard. Kendall Square in Cambridge has been called "the most innovative square mile on the planet" owing to the high concentration of successful startups that have emerged in the vicinity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)