|
Ministry Of War (imperial China)
The Ministry of War was one of Six Ministries under the Department of State Affairs in imperial China. Name The Ministry of War is also commonly translated as the Ministry or . Function During the Ming Dynasty, the Ministry of War had control over appointments, promotions, and demotions of military officers; the maintenance of military installations, equipment, and weapons; and administration over the imperial Chinese post or courier network. Courier network Workers found jobs at Relay Stations or Post Offices during the Ming dynasty in multiple ways. Some were directly appointed by the Emperor. In some cases, local indigenous leaders received these appointments. The subordinate positions were filled by members of the leader's entourage, including cooks, stable hands and innkeepers. Thereafter the Stationmaster became an inherited position, in some cases for over 100 years. At more isolated frontier stations, exiles, ex-criminals and prisoners of war filled the positions. Former ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Chinese Army
The recorded military history of China extends from about 2200 BC to the present day. Chinese pioneered the use of crossbows, advanced metallurgical standardization for arms and armor, early gunpowder weapons, and other advanced weapons, but also adopted nomadic cavalry and Western world, Western military technology.Frederic E. Wakeman: ''The Great Enterprise: The Manchu Reconstruction of Imperial Order in Seventeenth-century China'', Vol. 1 (1985), , p. 77 China's armies also benefited from an advanced logistics system as well as a rich strategic tradition, beginning with Sun Tzu's ''The Art of War'', that deeply influenced military thought. History of military organization The military history of China stretches from roughly 2200 BC to the present day. Chinese armies were advanced and powerful, especially after the Warring States period. These armies were tasked with the twofold goal of defending China and her subject peoples from foreign intruders, and with expanding China's t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of China Before 1911
The recorded military history of China extends from about 2200 BC to the present day. Chinese pioneered the use of crossbows, advanced metallurgical standardization for arms and armor, early gunpowder weapons, and other advanced weapons, but also adopted nomadic cavalry and Western military technology.Frederic E. Wakeman: ''The Great Enterprise: The Manchu Reconstruction of Imperial Order in Seventeenth-century China'', Vol. 1 (1985), , p. 77 China's armies also benefited from an advanced logistics system as well as a rich strategic tradition, beginning with Sun Tzu's ''The Art of War'', that deeply influenced military thought. History of military organization The military history of China stretches from roughly 2200 BC to the present day. Chinese armies were advanced and powerful, especially after the Warring States period. These armies were tasked with the twofold goal of defending China and her subject peoples from foreign intruders, and with expanding China's territory and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
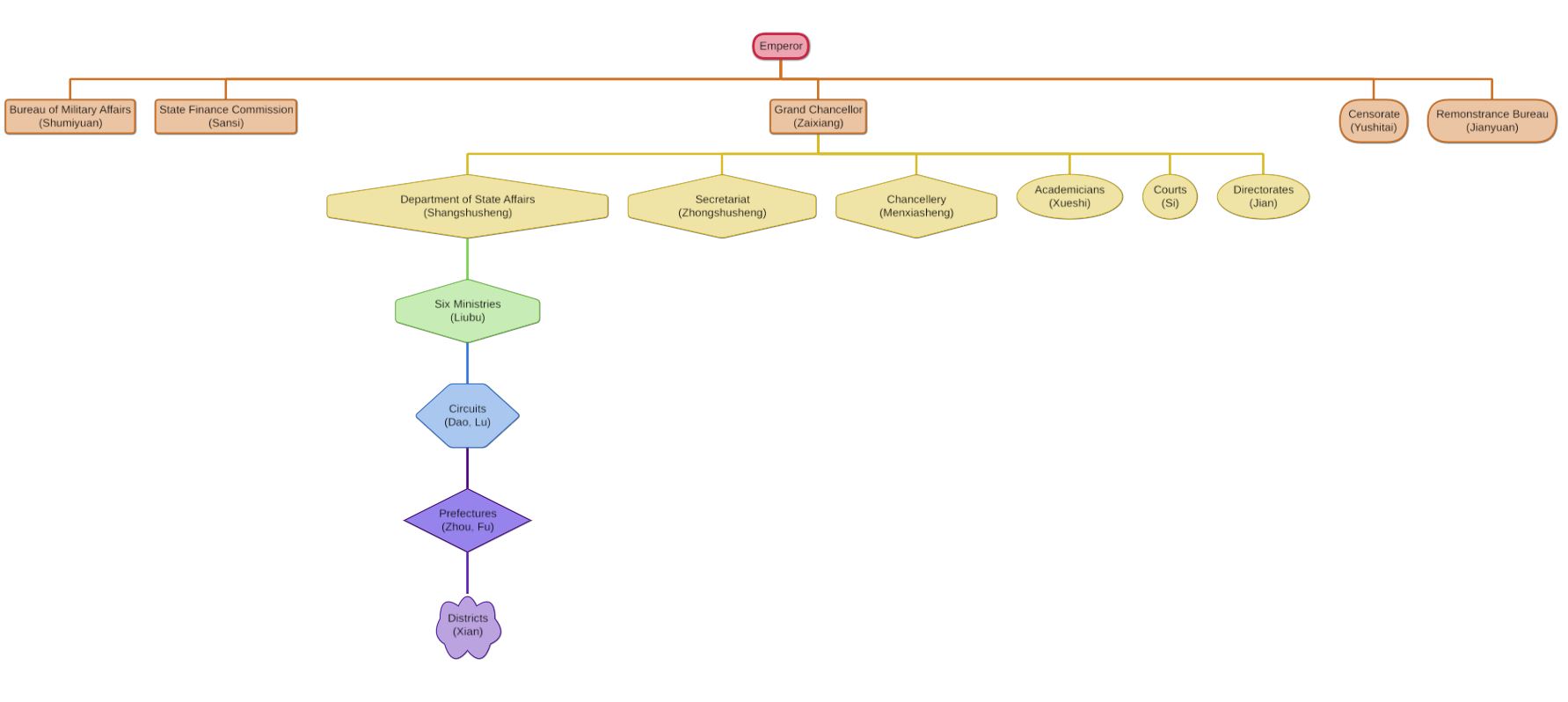
Three Departments And Six Ministries
The Three Departments and Six Ministries () system was the primary administrative structure in imperial China from the Sui dynasty (581–618) to the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368). It was also used by Balhae (698–926) and Goryeo (918–1392) and various other kingdoms in Manchuria, Korea and Vietnam. The Three Departments were three top-level administrative structures in imperial China. They were the Central Secretariat, responsible for drafting policy, the Chancellery, responsible for reviewing policy and advising the emperor, and the Department of State Affairs, responsible for implementing policy. The former two were loosely joined as the Secretariat-Chancellery during the late Tang dynasty, Song dynasty and in the Korean kingdom of Goryeo. The Six Ministries (also translated as Six Boards) were direct administrative organs of the state under the authority of the Department of State Affairs. They were the Ministries of Personnel, Rites, War, Justice, Works, and Revenue. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of State Affairs
The Shangshu Sheng (), sometimes translated as the Department of State Affairs or the Imperial Secretariat, was one of the departments of the Three Departments and Six Ministries government structure. It was the primary executive institution of imperial China, head of the Six Ministries, the Nine Courts, and the Three Directorates (sometimes five). The Six Ministries consisted of the Ministry of Personnel, the Ministry of Revenue, the Ministry of Rites, the Ministry of War, the Ministry of Justice, and the Ministry of Works. The Department of State of Affairs existed in one form or another from the Han dynasty (206 BC – 9 AD) until the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368), but was never re-established in the following Ming dynasty. Origin The Department of State Affairs originated as one of the posts of the Six Chief Stewards (''liushang'' 六尚) that were responsible for headgear, wardrobe, food, the bath, the bedchamber and for writing (''shangshu'' 尚書, literally "presenting writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapters, 11th century BC), the '' Bamboo Annals'' (c. 296 BC) and the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (c. 91 BC) describe a Xia dynasty before the Shang, but no writing is known from the period, and Shang writings do not indicate the existence of the Xia. The Shang ruled in the Yellow River valley, which is commonly held to be the cradle of Chinese civilization. However, Neolithic civilizations originated at various cultural centers along both the Yellow River and Yangtze River. These Yellow River and Yangtze civilizations arose millennia before the Shang. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is among the world's oldest civilizations and is regarded as one of the cradles of civilization. The Zhou dynasty (1046–256 BC) supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Government
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump regimes ruled by remnants of the Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (r. 1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the navy's dockyards in Nanjing were the largest in the world. He also took great care breaking the power of the court eunuchs and unr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
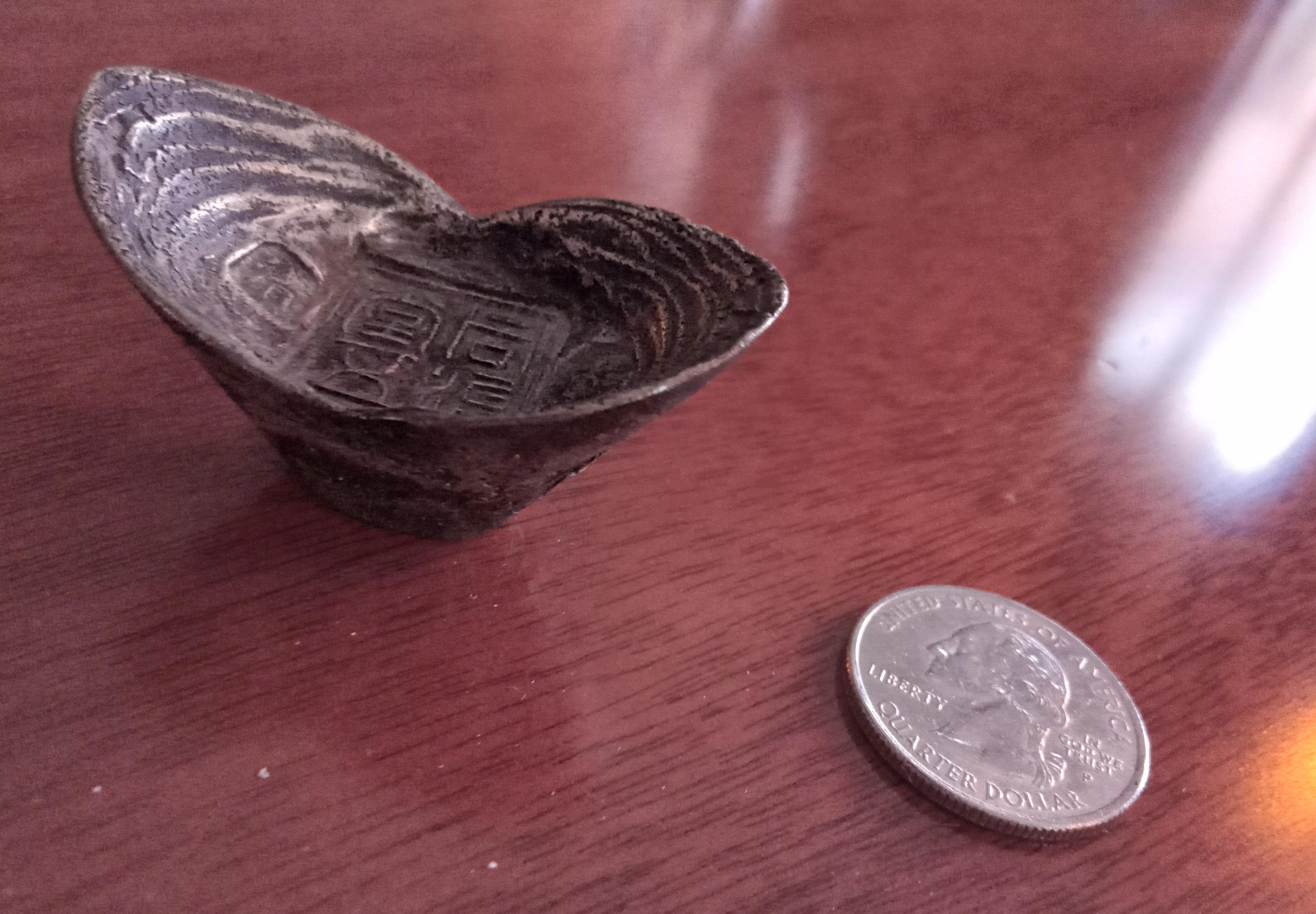
Tael
Tael (),"Tael" entry at the . also known as the tahil and by , can refer to any one of several used in and |
Chinese Republic Ministry Of War
The Ministry of War () of the Republic of China was the cabinet level department charged with administering the Army of the Chinese Republic from 1912-1946. Organizational structure The Ministry of War supervised: * General Affairs Department * Military Affairs Service * Quartermaster Service * Ordnance Service * Medical Service Ministers of War * Feng Yuxiang (馮玉祥): 1928–1929 * Lu Zhonglin (鹿鍾麟): 1929 * Chen Yi (陳儀): 1929 * Lu Zhonglin (鹿鍾麟): 1929 * Zhu Shouguang (朱綬光): 1929–1930 * He Yingqin (何應欽): 1930 - 1944 * Chen Cheng (陳誠): 1944 - 1945 See also * Imperial Chinese Ministry of War * Ministry of National Defense of the Republic of China * National Revolutionary Army The National Revolutionary Army (NRA; ), sometimes shortened to Revolutionary Army () before 1928, and as National Army () after 1928, was the military arm of the Kuomintang (KMT, or the Chinese Nationalist Party) from 1925 until 1947 in China ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Imperial China
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The major types of political systems in the modern era are democracies, monarchies, and authoritarian and totalitarian regimes. Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, aristocracy, timocracy, oligarchy, democracy, theocracy, and tyranny. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and mixed governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Six Ministries
The Three Departments and Six Ministries () system was the primary administrative structure in imperial China from the Sui dynasty (581–618) to the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368). It was also used by Balhae (698–926) and Goryeo (918–1392) and various other kingdoms in Manchuria, Korea and Vietnam. The Three Departments were three top-level administrative structures in imperial China. They were the Central Secretariat, responsible for drafting policy, the Chancellery, responsible for reviewing policy and advising the emperor, and the Department of State Affairs, responsible for implementing policy. The former two were loosely joined as the Secretariat-Chancellery during the late Tang dynasty, Song dynasty and in the Korean kingdom of Goryeo. The Six Ministries (also translated as Six Boards) were direct administrative organs of the state under the authority of the Department of State Affairs. They were the Ministries of Personnel, Rites, War, Justice, Works, and Revenue. Duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of The Ming Dynasty
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The major types of political systems in the modern era are democracies, monarchies, and authoritarian and totalitarian regimes. Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, aristocracy, timocracy, oligarchy, democracy, theocracy, and tyranny. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and mixed govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of The Tang Dynasty
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The major types of political systems in the modern era are democracies, monarchies, and authoritarian and totalitarian regimes. Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, aristocracy, timocracy, oligarchy, democracy, theocracy, and tyranny. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and mixed govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |