|
Minimotif Miner
Minimotif Miner is a program and database designed to identify minimotifs in any protein. Minimotifs are short contiguous peptide sequences that are known to have a function in at least one protein. Minimotifs are also called sequence motifs or short linear motifs or SLiMs. These are generally restricted to one secondary structure element and are less than 15 amino acids in length. Description Functions can be binding motifs that bind another macromolecule or small compound, that induce a covalent modification of minimotif, or are involved in protein trafficking :''This article deals with protein targeting in eukaryotes unless specified otherwise.'' Protein targeting or protein sorting is the biological mechanism by which proteins are transported to their appropriate destinations within or outside the c ... of the protein containing the minimotif. The basic premise of Minimotif Miner is that is a short peptide sequence is known to have a function in one protein, may have a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases spans formal techniques and practical considerations, including data modeling, efficient data representation and storage, query languages, security and privacy of sensitive data, and distributed computing issues, including supporting concurrent access and fault tolerance. A database management system (DBMS) is the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS software additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Motif
In biology, a sequence motif is a nucleotide or amino-acid sequence pattern that is widespread and usually assumed to be related to biological function of the macromolecule. For example, an ''N''-glycosylation site motif can be defined as ''Asn, followed by anything but Pro, followed by either Ser or Thr, followed by anything but Pro residue''. Overview When a sequence motif appears in the exon of a gene, it may encode the "structural motif" of a protein; that is a stereotypical element of the overall structure of the protein. Nevertheless, motifs need not be associated with a distinctive secondary structure. " Noncoding" sequences are not translated into proteins, and nucleic acids with such motifs need not deviate from the typical shape (e.g. the "B-form" DNA double helix). Outside of gene exons, there exist regulatory sequence motifs and motifs within the " junk", such as satellite DNA. Some of these are believed to affect the shape of nucleic acids (see for example RN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
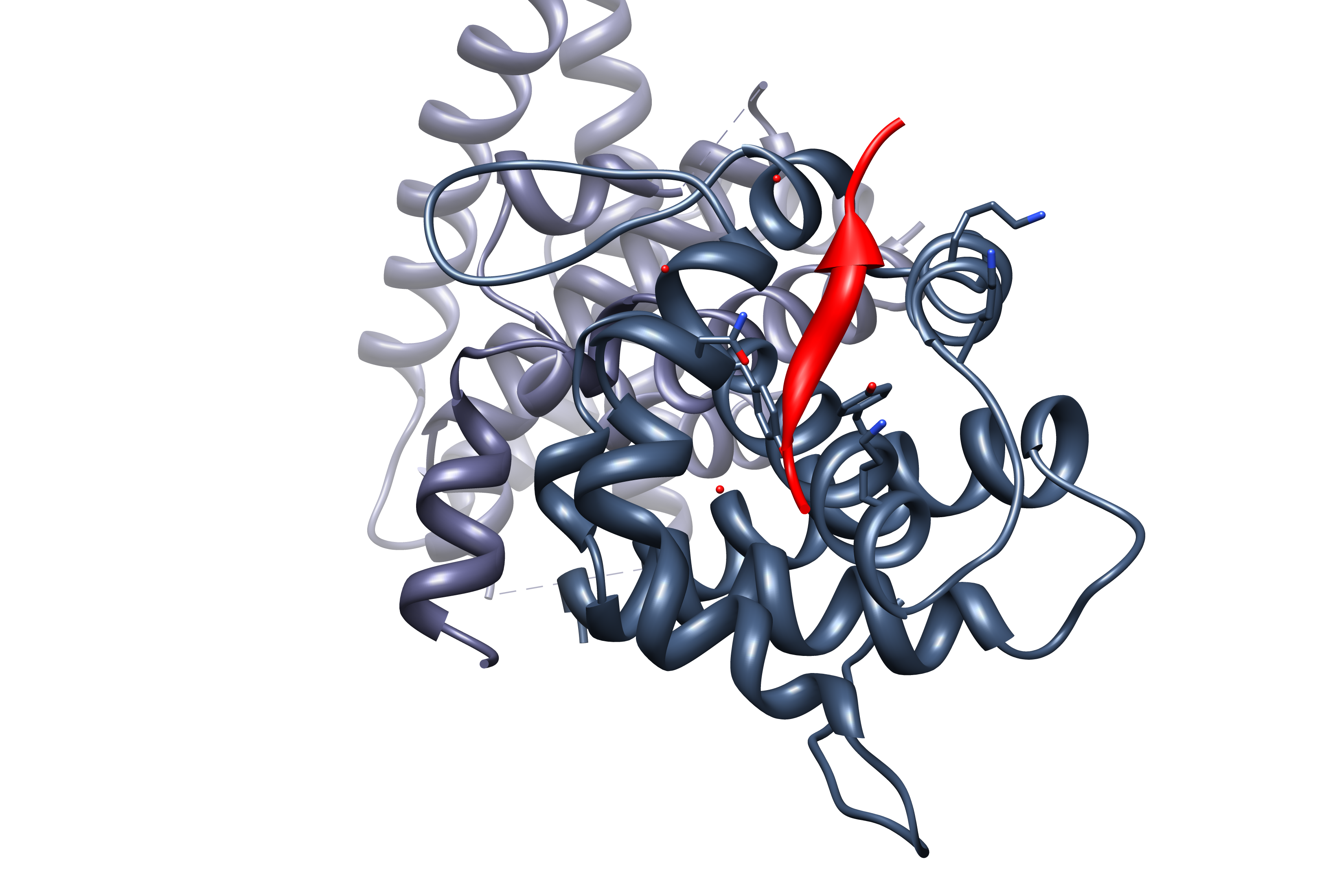
Short Linear Motif
In molecular biology short linear motifs (SLiMs), linear motifs or minimotifs are short stretches of protein sequence that mediate protein–protein interaction. The first definition was given by Tim Hunt: "The sequences of many proteins contain short, conserved motifs that are involved in recognition and targeting activities, often separate from other functional properties of the molecule in which they occur. These motifs are linear, in the sense that three-dimensional organization is not required to bring distant segments of the molecule together to make the recognizable unit. The conservation of these motifs varies: some are highly conserved while others, for example, allow substitutions that retain only a certain pattern of charge across the motif." Attributes SLiMs are generally situated in intrinsically disordered regions (over 80% of known SLiMs), however, upon interaction with a structured partner secondary structure is often induced. The majority of annotated SLiMs con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Trafficking
:''This article deals with protein targeting in eukaryotes unless specified otherwise.'' Protein targeting or protein sorting is the biological mechanism by which proteins are transported to their appropriate destinations within or outside the cell. Proteins can be targeted to the inner space of an organelle, different intracellular membranes, the plasma membrane, or to the exterior of the cell via secretion. Information contained in the protein itself directs this delivery process. Correct sorting is crucial for the cell; errors or dysfunction in sorting have been linked to multiple diseases. History In 1970, Günter Blobel conducted experiments on protein translocation across membranes. Blobel, then an assistant professor at Rockefeller University, built upon the work of his colleague George Palade. Palade had previously demonstrated that non-secreted proteins were translated by free ribosomes in the cytosol, while secreted proteins (and target proteins, in general) wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNPs
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, at a specific base position in the human genome, the G nucleotide may appear in most individuals, but in a minority of individuals, the position is occupied by an A. This means that there is a SNP at this specific position, and the two possible nucleotide variations – G or A – are said to be the alleles for this specific position. SNPs pinpoint differences in our susceptibility to a wide range of diseases, for example age-related macular degeneration (a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of the disease) or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (a SNP in the PNPLA3 gene is associated with incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotic Linear Motif Resource
The Eukaryotic Linear Motif (ELM) resource is a biological database, computational biology resource (developed at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL)) for investigating short linear motifs (SLiMs) in eukaryote, eukaryotic proteins. It is currently the largest collection of linear motif classes with annotation, annotated and experimentally validated linear motif instances. Linear motifs are specified as patterns using regular expression rules. These expressions are used in the ELM prediction pipeline which detects putative motif instances in protein sequences. To improve the predictive power, context-based rules and logical filters are being developed and applied to reduce the amount of false positives matches. As of 2010 ELM contained 146 different motifs that annotate more than 1300 experimentally determined instances within proteins. The current version of the ELM server provides filtering by cell compartment, phylogeny, globular domain clash (using the Simple Modul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physical structure of biological macromolecules is known as molecular biology. Molecular biology was first described as an approach focused on the underpinnings of biological phenomena - uncovering the structures of biological molecules as well as their interactions, and how these interactions explain observations of classical biology. In 1945 the term molecular biology was used by physicist William Astbury. In 1953 Francis Crick, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and colleagues, working at Medical Research Council unit, Cavendish laboratory, Cambridge (now the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology), made a double helix model of DNA which changed the entire research scenario. They proposed the DNA structure based on previous research done by Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |