|
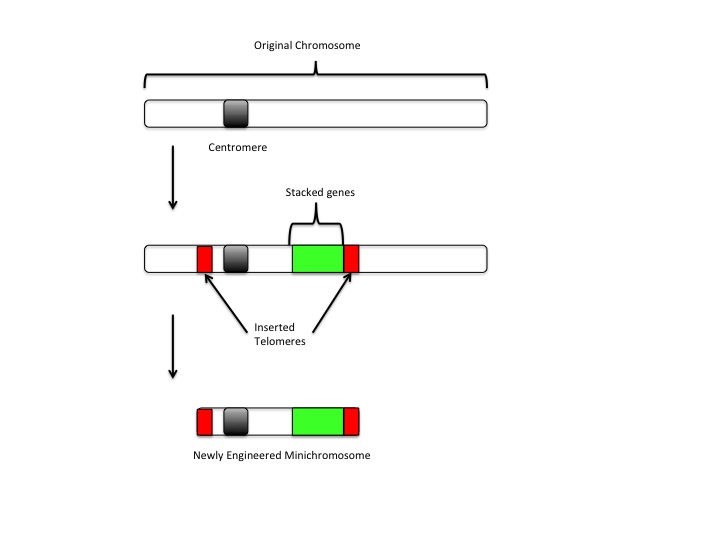
Minichromosome
A minichromosome is a small chromatin-like structure resembling a chromosome and consisting of centromeres, telomeres and replication origins but little additional genetic material. They replicate autonomously in the cell during cellular division. Minichromosomes may be created by natural processes as chromosomal aberrations or by genetic engineering. Structure Minichromosomes can be either linear or circular pieces of DNA. By minimizing the amount of unnecessary genetic information on the chromosome and including the basic components necessary for DNA replication (centromere, telomeres, and replication sequences), molecular biologists aim to construct a chromosomal platform which can be utilized to insert or present new genes into a host cell. Production Producing minichromosomes by genetic engineering techniques involves two primary methods, the '' de novo'' (bottom-up) and the top-down approach. ''De novo'' The minimum constituent parts of a chromosome (centromere, telome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
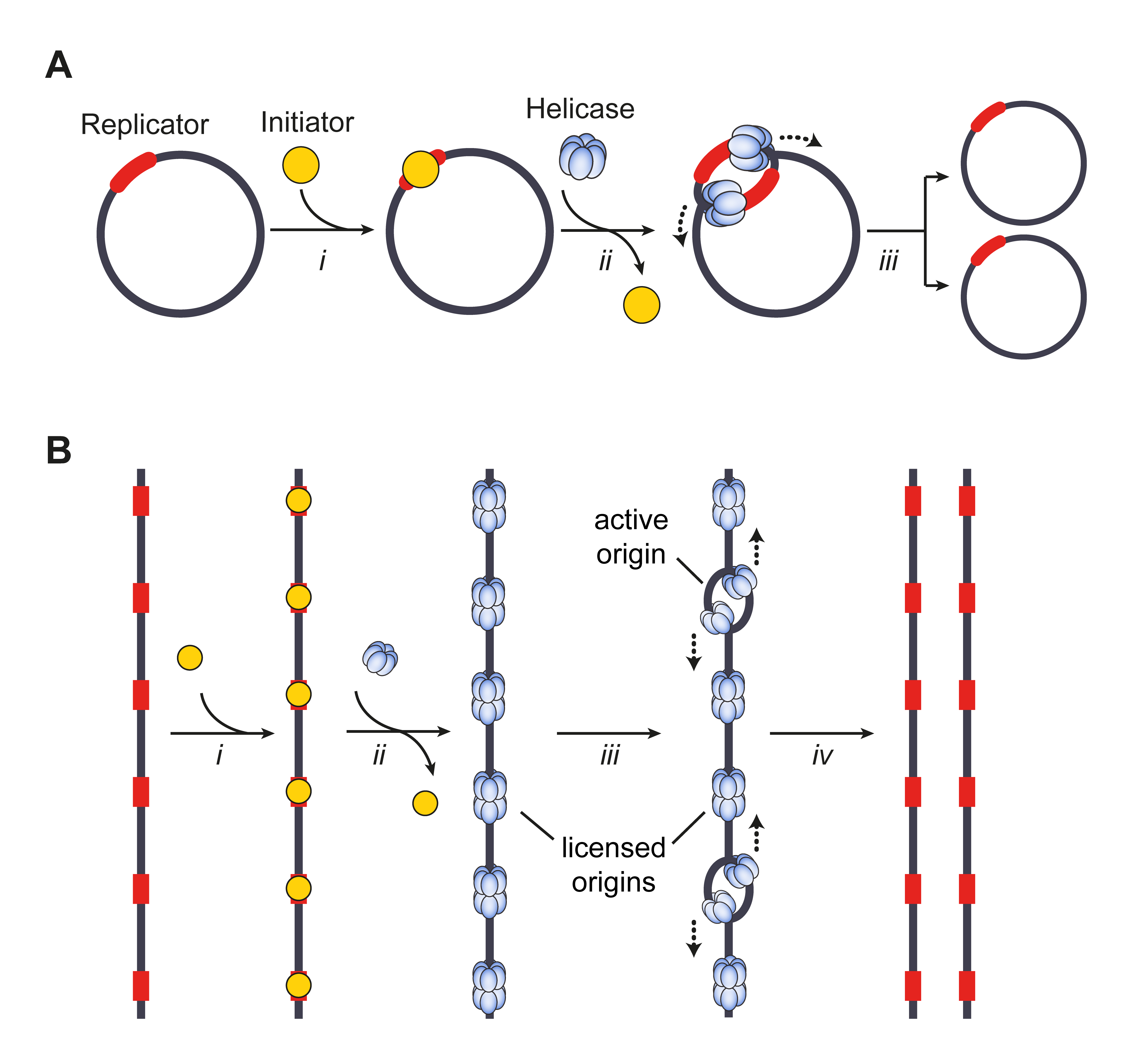
Mini Chromosome Maintenance
The minichromosome maintenance protein complex (MCM) is a DNA helicase essential for genomic DNA replication. Eukaryotic MCM consists of six gene products, Mcm2–7, which form a heterohexamer. As a critical protein for cell division, MCM is also the target of various checkpoint pathways, such as the S-phase entry and S-phase arrest checkpoints. Both the loading and activation of MCM helicase are strictly regulated and are coupled to cell growth cycles. Deregulation of MCM function has been linked to genomic instability and a variety of carcinomas. History and structure The minichromosome maintenance proteins were named after a yeast genetics screen for mutants defective in the regulation of DNA replication initiation. The rationale behind this screen was that if replication origins were regulated in a manner analogous to transcription promoters, where transcriptional regulators showed promoter specificity, then replication regulators should also show origin specificity. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replication Origin
The origin of replication (also called the replication origin) is a particular sequence in a genome at which replication is initiated. Propagation of the genetic material between generations requires timely and accurate duplication of DNA by semiconservative replication prior to cell division to ensure each daughter cell receives the full complement of chromosomes. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License This can either involve the replication of DNA in living organisms such as prokaryotes and eukaryotes, or that of DNA or RNA in viruses, such as double-stranded RNA viruses. Synthesis of daughter strands starts at discrete sites, termed replication origins, and proceeds in a bidirectional manner until all genomic DNA is replicated. Despite the fundamental nature of these events, organisms have evolved surprisingly divergent strategies that control replication onset. Although the specific replication or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telomere Mediated Minichromosome Production
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes. Although there are different architectures, telomeres, in a broad sense, are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In most, if not all species possessing them, they protect the terminal regions of chromosomal DNA from progressive degradation and ensure the integrity of linear chromosomes by preventing DNA repair systems from mistaking the very ends of the DNA strand for a double-strand break. Discovery In the early 1970s, Soviet theorist Alexei Olovnikov first recognized that chromosomes could not completely replicate their ends; this is known as the "end replication problem". Building on this, and accommodating Leonard Hayflick's idea of limited somatic cell division, Olovnikov suggested that DNA sequences are lost every time a cell replicates until the loss reaches a critical level, at which point cell division e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microchromosome
A microchromosome (μChr) is a type of very small chromosome which is a typical component of the karyotype of birds, some reptiles, fish, and amphibians; they have yet to be found in mammals. They are less than 20 Mb in size; chromosomes which are greater than 40 Megabase, Mb in size are known as macrochromosomes (MChrs), while those between 20 and 40 Mb are classified as intermediate chromosomes. Microchromosomes are characteristically very small and often cytogenetically indistinguishable in a karyotype. While originally thought to be insignificant fragments of chromosomes, in species where they have been studied they have been found to be rich in genes and high in GC content. In chickens, microchromosomes have been estimated to contain between 50 and 75% of all genes. The presence of microchromosomes makes ordering and identifying chromosomes into a coherent karyotype particularly difficult. During metaphase, they appear merely as 0.5-1.5 μm long specks. Their small size and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |