|
Mines And Geosciences Bureau Region 13 (Philippines)
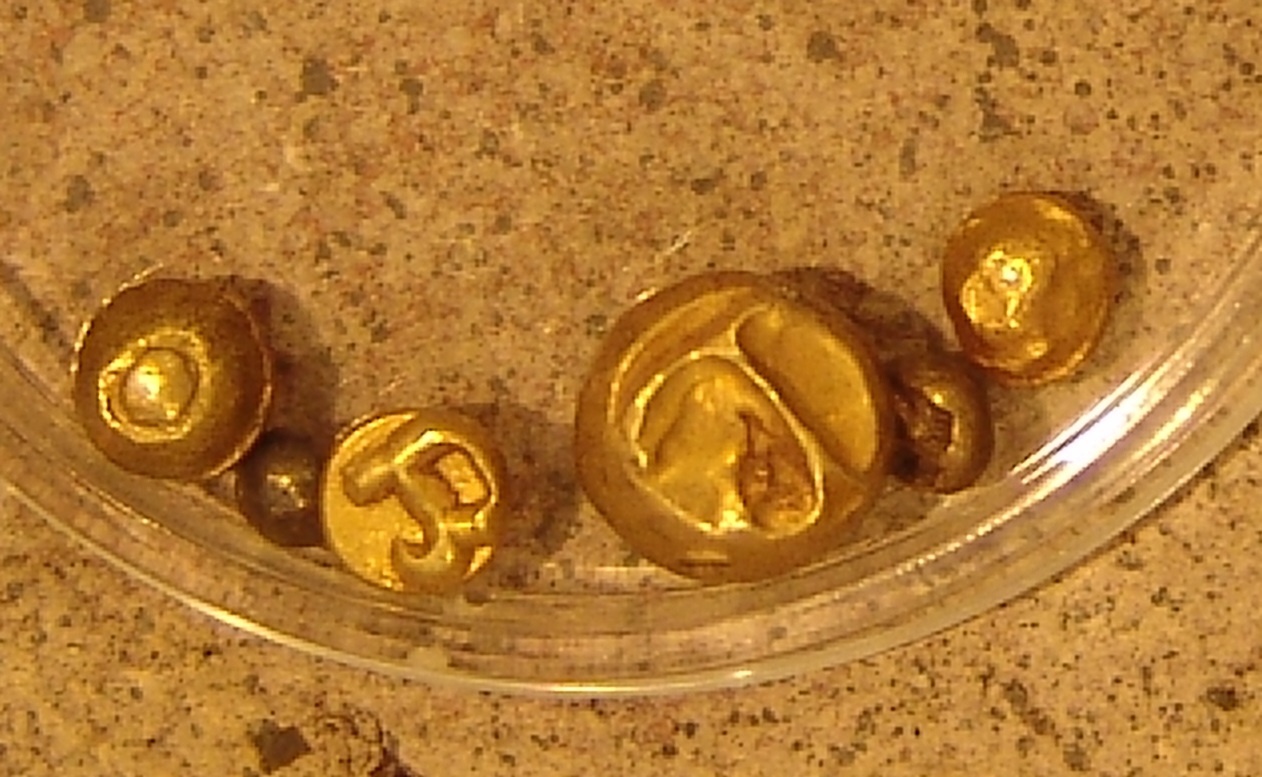
Caraga Region is located at northeastern part of Mindanao. It includes the five provinces of Dinagat Province, Surigao del Norte, Surigao del Sur, Agusan del Norte and Agusan del Sur. Caraga Region is now hosting several mining projects producing various mineral commodities particularly but not limited to gold, copper, chrome, nickel, iron and limestone for concrete cement production. This makes the Department of Environment and Natural Resources, Mines and Geosciences Bureau, Regional Office No. 13 is located in Surigao City, rather than Butuan City (the region's capital), by virtue of Sec. 2, Republic Act No. 7901 - An Act Creating Region XIII to be known as the Caraga Administrative Region, and for other purposes with Office located in Surigao City plays important role in the region's economy, job generation, social and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine Peso
The Philippine peso, also referred to by its Tagalog name ''piso'' (Philippine English: , , plural pesos; tl, piso ; sign: ₱; code: PHP), is the official currency of the Philippines. It is subdivided into 100 ''sentimo'', also called centavos. The Philippine peso sign is denoted by the symbol "₱", introduced under American rule in place of the original peso sign "$" used throughout Spanish America. Alternative symbols used are "PHP", "PhP", "Php", or just "P". The monetary policy of the Philippines is conducted by the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP), established on July 3, 1993, as its central bank. It produces the country's banknotes and coins at its Security Plant Complex, which is set to move to New Clark City in Capas, Tarlac."Overview of the BSP" Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) Official Website. Retrieved on October 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyry (geology)
Porphyry ( ) is a textural term for an igneous rock consisting of coarse-grained crystals such as feldspar or quartz dispersed in a fine-grained silicate-rich, generally aphanitic matrix or groundmass. The larger crystals are called phenocrysts. In its non-geologic, traditional use, the term ''porphyry'' refers to the purple-red form of this stone, valued for its appearance. The term ''porphyry'' is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "purple". Purple was the color of royalty, and the "imperial porphyry" was a deep purple igneous rock with large crystals of plagioclase. Some authors claimed the rock was the hardest known in antiquity. Thus, "imperial"-grade porphyry was prized for monuments and building projects in Imperial Rome and thereafter. Subsequently, the name was given to any igneous rocks with large crystals. The adjective ''porphyritic'' now refers to a certain texture of igneous rock regardless of its chemical and mineralogical composition. Its chief characteris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diorite
Diorite ( ) is an intrusive igneous rock formed by the slow cooling underground of magma (molten rock) that has a moderate content of silica and a relatively low content of alkali metals. It is intermediate in composition between low-silica (mafic) gabbro and high-silica ( felsic) granite. Diorite is found in mountain-building belts (''orogens'') on the margins of continents. It has the same composition as the fine-grained volcanic rock, andesite, which is also common in orogens. Diorite has been used since prehistoric times as decorative stone. It was used by the Akkadian Empire of Sargon of Akkad for funerary sculptures, and by many later civilizations for sculptures and building stone. Description Diorite is an intrusive igneous rock composed principally of the silicate minerals plagioclase feldspar (typically andesine), biotite, hornblende, and sometimes pyroxene. The chemical composition of diorite is intermediate, between that of mafic gabbro and felsic grani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
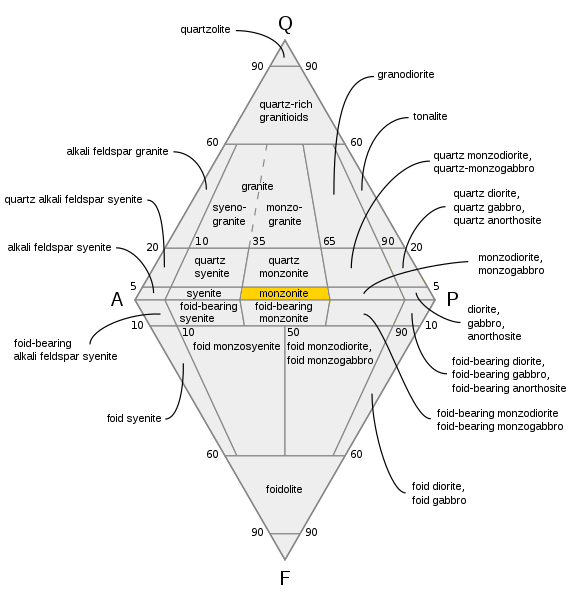
Monzonite
Monzonite is an igneous intrusive rock, formed by slow cooling of underground magma that has a moderate silica content and is enriched in alkali metal oxides. Monzonite is composed mostly of plagioclase and alkali feldspar. Syenodiorite is an obsolescent term for monzonite or for monzodiorite.Le Maitre, R.W., ''Igneous Rocks: A Classification and Glossary of Terms'' Cambridge University Press, 2nd ed, pp. 113 Larvikite is a particular form of monzonite. Description Monzonite is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) igneous rock. Such rocks are classified by their relative percentages of quartz, plagioclase, alkali feldspar, and feldspathoid (the QAPF classification). Monzonite is defined as rock having less than 5% quartz in its QAPF fraction and in which alkali feldspar makes up between 35% and 65% of the total feldspar content. If quartz constitutes greater than 5% of the QAPF fraction, the rock is termed a quartz monzonite, while if feldspathoids are present as up to 10% of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroclastic Rock
Pyroclastic rocks (derived from the el, πῦρ, links=no, meaning fire; and , meaning broken) are clastic rocks composed of rock fragments produced and ejected by explosive volcanic eruptions. The individual rock fragments are known as pyroclasts. Pyroclastic rocks are a type of volcaniclastic deposit, which are deposits made predominantly of volcanic particles. 'Phreatic' pyroclastic deposits are a variety of pyroclastic rock that forms from volcanic steam explosions and they are entirely made of accidental clasts. 'Phreatomagmatic' pyroclastic deposits are formed from explosive interaction of magma with groundwater. Unconsolidated accumulations of pyroclasts are described as tephra. Tephra may become lithified to a pyroclastic rock by cementation or chemical reactions as the result of the passage of hot gases (fumarolic alteration) or groundwater (e.g. hydrothermal alteration and diagenesis) and burial, or, if it is emplaced at temperatures so hot that the soft glassy pyrocl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial planet, rocky planet or natural satellite, moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of volcanism on Venus, Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar mare, lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Miocene
The Middle Miocene is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages: the Langhian and Serravallian stages. The Middle Miocene is preceded by the Early Miocene. The sub-epoch lasted from 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma to 11.608 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago). During this period, a sharp drop in global temperatures took place. This event is known as the Middle Miocene Climate Transition. For the purpose of establishing European Land Mammal Ages The European Land Mammal Mega Zones (abbreviation: ELMMZ, more commonly known as European land mammal ages or ELMA) are zones in rock layers that have a specific assemblage of fossils (biozones) based on occurrences of fossil assemblages of Europe ... this sub-epoch is equivalent to the Astaracian age. External links GeoWhen Database - Middle Miocene .02 02 * * {{geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''olígos'', "few") and (''kainós'', "new"), and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major changes during the Oligocene included a global expansion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by Chicxulub impact, an asteroid impact and possibly volcanism, marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of living species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. In the Pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope Carbon-13, 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope Carbon-12, 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Popigai impact structure, Siberia and in what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |