|
Minaxolone
Minaxolone (CCI-12923) is a neuroactive steroid which was developed as a general anesthetic but was withdrawn before registration due to toxicity seen with long-term administration in rats, and hence was never marketed. It is a positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor, as well as, less potently, a positive allosteric modulator of the glycine receptor. Chemistry See also * Alfadolone * Alfaxolone * Ganaxolone * Hydroxydione * Pregnanolone * Renanolone Renanolone ( INN), or 11-ketopregnanolone, also known as 5β-pregnan-3α-ol-11,20-dione, is a synthetic neuroactive steroid which is described as a general anesthetic but was never introduced for clinical use. Its isomers, alfaxolone and alfadolon ... References General anesthetics Neurosteroids Secondary alcohols Ethers Dimethylamino compounds Ketones GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators Glycine receptor agonists Pregnanes {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurosteroids
Neurosteroids, also known as neuroactive steroids, are endogenous or exogenous steroids that rapidly alter neuronal excitability through interaction with ligand-gated ion channels and other cell surface receptors. The term ''neurosteroid'' was coined by the French physiologist Étienne-Émile Baulieu and refers to steroids synthesized in the brain. The term, ''neuroactive steroid'' refers to steroids that can be synthesized in the brain, or are synthesized by an endocrine gland, that then reach the brain through the bloodstream and have effects on brain function. The term neuroactive steroids was first coined in 1992 by Steven Paul and Robert Purdy. In addition to their actions on neuronal membrane receptors, some of these steroids may also exert effects on gene expression via nuclear steroid hormone receptors. Neurosteroids have a wide range of potential clinical applications from sedation to treatment of epilepsy and traumatic brain injury. Ganaxolone, a synthetic analog of the end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroactive Steroid
Neurosteroids, also known as neuroactive steroids, are endogenous or exogenous steroids that rapidly alter neuronal excitability through interaction with ligand-gated ion channels and other cell surface receptors. The term ''neurosteroid'' was coined by the French physiologist Étienne-Émile Baulieu and refers to steroids synthesized in the brain. The term, ''neuroactive steroid'' refers to steroids that can be synthesized in the brain, or are synthesized by an endocrine gland, that then reach the brain through the bloodstream and have effects on brain function. The term neuroactive steroids was first coined in 1992 by Steven Paul and Robert Purdy. In addition to their actions on neuronal membrane receptors, some of these steroids may also exert effects on gene expression via nuclear steroid hormone receptors. Neurosteroids have a wide range of potential clinical applications from sedation to treatment of epilepsy and traumatic brain injury. Ganaxolone, a synthetic analog of the end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfaxolone
Alfaxalone, also known as alphaxalone or alphaxolone and sold under the brand name Alfaxan, is a neuroactive steroid and general anesthetic which is used currently in veterinary practice as an induction agent for anesthesia and as an injectable anesthetic. Though it is more expensive than other induction agents, it often preferred due to the lack of depressive effects on the cardiovascular system. The most common side effect seen in current veterinary practice is respiratory depression when Alfaxan is administered concurrently with other sedative and anesthetic drugs; when premedications aren't given, veterinary patients also become agitated and hypersensitive when waking up. Alfaxalone works as a positive allosteric modulator on GABAA receptors and, at high concentrations, as a direct agonist of the GABAA receptor. It is cleared quickly by the liver, giving it a relatively short terminal half-life and preventing it from accumulating in the body, lowering the chance of overdos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganaxolone
Ganaxolone, sold under the brand name Ztalmy, is a medication used to treat seizures in people with cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 deficiency disorder, cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5) deficiency disorder (CDD). Ganaxolone was approved for medical use in the United States in March 2022. Pharmacology Mechanism of action The exact mechanism of action for ganaxolone is unknown; however, results from animal studies suggest that it acts by blocking seizure propagation and elevating seizure thresholds. Ganaxolone is thought to modulate both synapse, synaptic and extrasynaptic GABAA receptors to normalize over-excited neurons. Ganaxolone's activation of the extrasynaptic receptor is an additional mechanism that provides stabilizing effects that potentially differentiates it from other drugs that increase GABA signaling. Ganaxolone binds to allosteric sites of the GABAA receptor to modulate and open the Chloride channel, chloride ion channel, resulting in a Hyperpolarization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxydione
Hydroxydione, as hydroxydione sodium succinate (, , ) (brand names Viadril, Predion, and Presuren), also known as 21-Hydroxy-5β-pregnane-3,20-dione, is a neuroactive steroid which was formerly used as a general anesthetic, but was discontinued due to incidence of thrombophlebitis in patients. It was introduced in 1957, and was the first neuroactive steroid general anesthetic to be introduced for clinical use, an event which was shortly preceded by the observation in 1954 of the sedative properties of progesterone in mice. Chemistry Related compounds include alfadolone, alfaxolone, dihydrodeoxycorticosterone, ganaxolone, minaxolone, pregnanolone, and renanolone Renanolone ( INN), or 11-ketopregnanolone, also known as 5β-pregnan-3α-ol-11,20-dione, is a synthetic neuroactive steroid which is described as a general anesthetic but was never introduced for clinical use. Its isomers, alfaxolone and alfadolon .... References {{GABAA receptor positive modulators 5β-Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Anesthetics
General anaesthetics (or anesthetics, see spelling differences) are often defined as compounds that induce a loss of consciousness in humans or loss of righting reflex in animals. Clinical definitions are also extended to include an induced coma that causes lack of awareness to painful stimuli, sufficient to facilitate surgical applications in clinical and veterinary practice. General anaesthetics do not act as analgesics and should also not be confused with sedatives. General anaesthetics are a structurally diverse group of compounds whose mechanisms encompasses multiple biological targets involved in the control of neuronal pathways. The precise workings are the subject of some debate and ongoing research. General anesthetics elicit a state of general anesthesia. It remains somewhat controversial regarding how this state should be defined. General anesthetics, however, typically elicit several key reversible effects: immobility, analgesia, amnesia, unconsciousness, and reduced a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
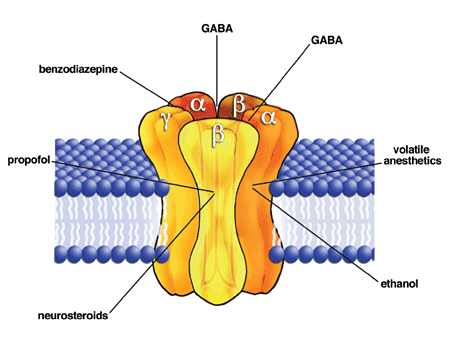
GABAA Receptor Positive Allosteric Modulators
In pharmacology, GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators are positive allosteric modulator (PAM) molecules that increase the activity of the GABAA receptor protein in the vertebrate central nervous system. GABA is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Upon binding, it triggers the GABAA receptor to open its chloride channel to allow chloride ions into the neuron, making the cell hyperpolarized and less likely to fire. GABAA PAMs increase the effect of GABA by making the channel open more frequently or for longer periods. However, they have no effect if GABA or another agonist is not present. Unlike GABAA receptor agonists, GABAA PAMs do not bind at the same active site as the γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter molecule: they affect the receptor by binding at a different site on the protein. This is called allosteric modulation. In psychopharmacology, GABAA receptor PAMs used as drugs have mainly sedative and anxiolytic effects. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketones
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' is methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids (e.g., testosterone), and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considered ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylamino Compounds
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around 40%. An estimated 270,000 tons were produced in 2005. Structure and synthesis The molecule consists of a nitrogen atom with two methyl substituents and one proton. Dimethylamine is a weak base and the pKa of the ammonium CH3--CH3 is 10.73, a value above methylamine (10.64) and trimethylamine (9.79). Dimethylamine reacts with acids to form salts, such as dimethylamine hydrochloride, an odorless white solid with a melting point of 171.5 °C. Dimethylamine is produced by catalytic reaction of methanol and ammonia at elevated temperatures and high pressure: :2 CH3OH + NH3 → (CH3)2NH + 2 H2O Natural occurrence Dimethylamine is found quite widely distributed in animals and plants, and is present in many foods at the level of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethers
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent C–O–C linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxygen in ethers, alcohols, and water is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnanolone
Pregnanolone, also known as eltanolone, is an endogenous inhibitory neurosteroid which is produced in the body from progesterone. It is closely related to allopregnanolone, which has similar properties. Biological activity Pregnanolone is a positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor, as well as a negative allosteric modulator of the glycine receptor. Biological function Pregnanolone has sedative, anxiolytic, anesthetic, and anticonvulsant effects. During pregnancy, pregnanolone and allopregnanolone are involved in sedation and anesthesia of the fetus. Biochemistry Pregnanolone is synthesized from progesterone via the enzymes 5β-reductase and 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, with 5β-dihydroprogesterone occurring as a metabolic intermediate. The elimination half-life of pregnanolone is between 0.9 and 3.5 hours. Chemistry Pregnanolone, also known as 3α,5β-tetrahydroprogesterone (3α,5β-THP) or as 5β-pregnan-3α-ol-20-one, is a naturally occurring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |