|
Mimesis (biology)
In biology, mimesis (from ancient Greek μίμησις ''mímēsis'', "imitation") refers to a form of crypsis where living creatures mimic the form, colour and posture of their surroundings to avoid being noticed from their surroundings by predators depending on sight. Mimesis is a form of crypsis and thus differs from mimicry, which is a form of aposematism.Schaefer, Matthias: ''Wörterbuch der Ökologie'', volume 4, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg, Berlin 2005. {{ISBN, 3-8274-0167-4. In English mimesis is often counted as a form of mimicry. Mimesis can be divided by the type of objects being mimicked: * ''Zoomimesis'' refers to mimicry of different animals. Contrary to mimicry, in zoomimesis the model animal is neither poisonous or capable of putting up a fight. Examples include various visitor species of ants (myrmecophily), resembling the ants in whose nests they live. * ''Phytomimesis'' refers to mimicry of plants or parts of plants. Some geometer moths resemble thin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furcula Furcula
''Furcula furcula'', the sallow kitten, is a moth from the family Notodontidae. It was first described by the Swedish entomologist Carl Alexander Clerck in 1759 from a specimen found in Sweden. Distribution The moth can be found in Europe (including the Mediterranean region), Anatolia and through Asia to China. It is also found in North America. Description The sallow kitten is grey/white and has a wingspan of 27 to 35 mm. The first part of the wing has a large grey middle band. It differs from the poplar kitten ('' Furcula bifida'') in its generally smaller size, but more especially in the shape of the black line forming the outer margin of the central band; this is always more or less angled or dentate towards the front margin of the wings, whereas, in the poplar kitten, this portion of the line forms a clean curve. The flight period ranges from April to the end of August. Depending on location the moth has one or two generations per year and is attracted to light. ; Ova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deinopis Subrufa
''Asianopis subrufa'' (also called the rufous net-casting spider) is a species of net-casting spiders. It occurs in Australia (Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania) and in New Zealand. It is a nocturnal hunter, having excellent eyesight, and hunts using a silken net to capture its prey. They feed on a variety of insects – ants, beetles, crickets and other spiders. They can vary in color from fawn to pinkish brown or chocolate brown. Females are about 25 mm in body length, males about 22 mm. They are not dangerous to humans. This species is often found on a few strands of web in forest, woodland and heathland, or on flat surfaces, for example on the outside of houses. Taxonomy ''Asianopis subrufa'' was first described by Ludwig Koch in 1878. The generic name is a combination of the word "Asia", referring to the distribution and the genus ''Deinopis''. The species name ''subrufa'' is Latin Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drepanepteryx Phalaenoides
''Drepanepteryx'' is a genus of insects belonging to the family Hemerobiidae Hemerobiidae is a family of Neuropteran insects commonly known as brown lacewings, comprising about 500 species in 28 genera. Most are yellow to dark brown, but some species are green. They are small; most have forewings 4–10 mm long (som .... The species of this genus are found in Eurasia. Species: * '' Drepanepteryx algida'' (Erichson, 1851) * '' Drepanepteryx calida'' (Krüger, 1922) References {{Taxonbar, from=Q10476574 Hemerobiiformia Neuroptera genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papilio Cresphontes
The giant swallowtail (''Papilio cresphontes'') is the largest butterfly in North America. It is abundant through many parts of eastern North America; populations from western North America and down into Panama are now (as of 2014) considered to belong to a different species, '' Papilio rumiko''. Though it is often valued in gardens for its striking appearance, its larval stage can be a serious pest to citrus farms, which has earned its caterpillars the names orange dog or orange puppy. The giant swallowtail caterpillars possess remarkable camouflage from predators by closely resembling bird droppings. They use this, along with their osmeteria, to defend against predators such as wasps, flies, and vertebrates. Geographic range The giant swallowtail is common across the United States, reaching as far north as southern New England and southern Canada. South of the United States, it is found in parts of Mexico and also found in Jamaica and Cuba. The species was historically conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swallowtail Butterfly
Swallowtail butterflies are large, colorful butterflies in the family Papilionidae, and include over 550 species. Though the majority are tropical, members of the family inhabit every continent except Antarctica. The family includes the largest butterflies in the world, the birdwing butterflies of the genus '' Ornithoptera''. Swallowtails have a number of distinctive features; for example, the papilionid caterpillar bears a repugnatorial organ called the osmeterium on its prothorax. The osmeterium normally remains hidden, but when threatened, the larva turns it outward through a transverse dorsal groove by inflating it with fluid. The forked appearance in some of the swallowtails' hindwings, which can be seen when the butterfly is resting with its wings spread, gave rise to the common name ''swallowtail''. As for its formal name, Linnaeus chose ''Papilio'' for the type genus, as ''papilio'' is Latin for "butterfly". For the specific epithets of the genus, Linnaeus applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buff-tip
The buff-tip (''Phalera bucephala'') is a moth of the family Notodontidae. It is found throughout Europe and in Asia to eastern Siberia. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. Description This is a fairly large, heavy-bodied species with a wingspan of 55–68 mm. The forewings are grey with a large prominent buff patch at the apex. As the thoracic hair is also buff, the moth resembles a broken twig when at rest. The hindwings are creamy white. This moth flies at night in June and July and sometimes comes to light, although it is not generally strongly attracted. The young larvae are gregarious, becoming solitary later. The older larva is very striking, black with white and yellow lines. It feeds on many trees and shrubs (see list below). The species overwinters as a pupa. # ''The flight season refers to the British Isles. This may vary in other parts of the range.'' Natural History Historically, the buff-tip mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
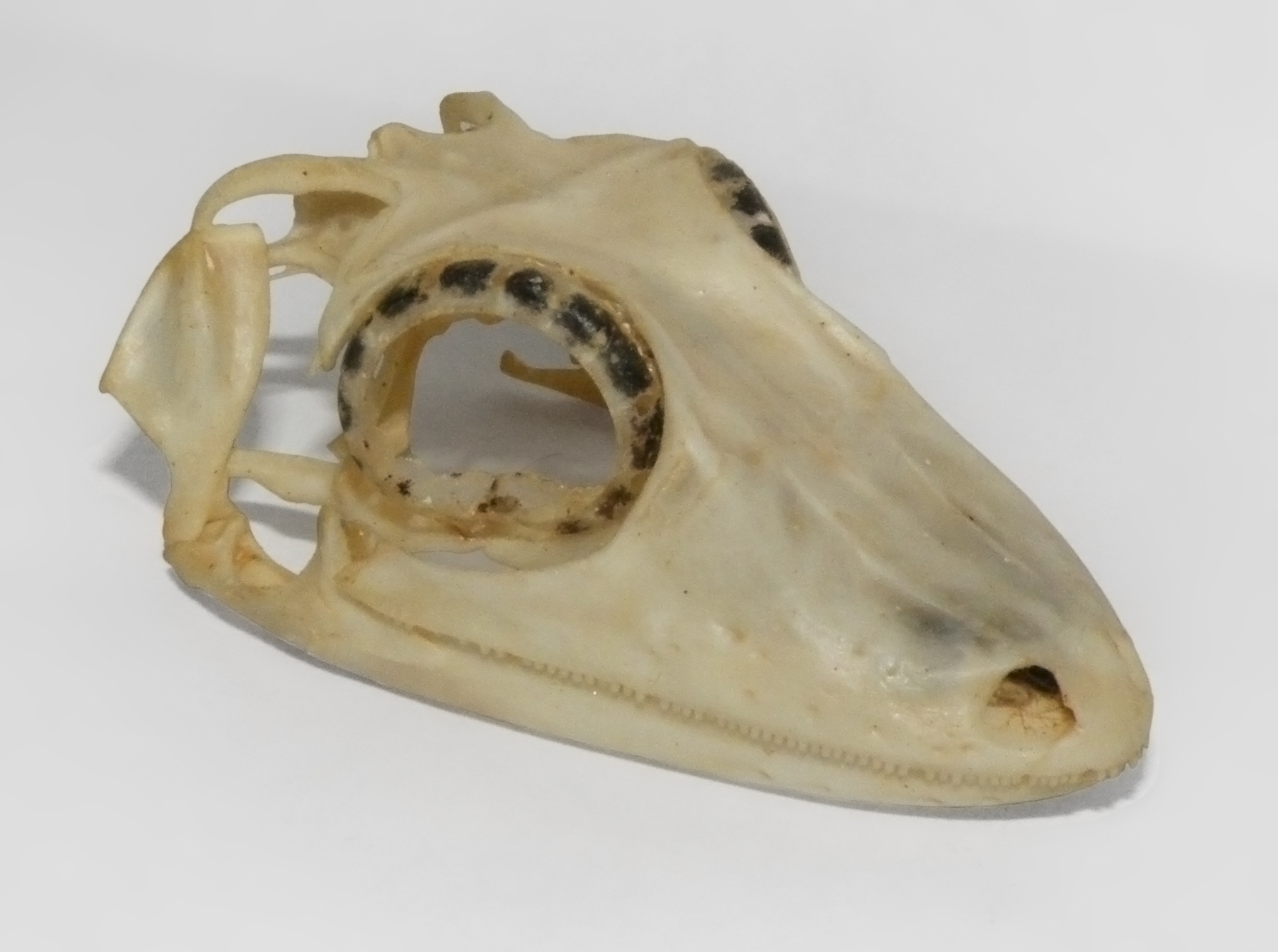
Uroplatus
''Uroplatus'' is a genus of gecko Geckos are small, mostly carnivorous lizards that have a wide distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. Belonging to the infraorder Gekkota, geckos are found in warm climates throughout the world. They range from . Geckos ar ...s, commonly referred to as leaf-tail geckos or flat-tailed geckos, which are endemism, endemic to Madagascar and its coastal islands, such as Nosy Be. They are nocturnal, insectivorous lizards found exclusively in primary forest, primary and secondary forest. Etymology The Genus, generic name, ''Uroplatus'', is a Latinization of two Ancient Greek, Greek words: "ourá" (οὐρά) meaning "tail" and "platys" (πλατύς) meaning "flat". Description Geckos of the genus ''Uroplatus'' are nocturnal and arboreal. They range in total length (including tail) from about for ''U. giganteus'' to for ''U. ebenaui''. Larger species of ''Uroplatus'' are distinguished among geckos in having the largest nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In Maxine N. Lurie and Marc Mappen (eds.) ''Encyclopedia of New Jersey'', Rutgers University Press, . Amber is used in jewelry and has been used as a healing agent in folk medicine. There are five classes of amber, defined on the basis of their chemical constituents. Because it originates as a soft, sticky tree resin, amber sometimes contains animal and plant material as inclusions. Amber occurring in coal seams is also called resinite, and the term ''ambrite'' is applied to that found specifically within New Zealand coal seams. Etymology The English word ''amber'' derives from Arabic (ultimately from Middle Persian ''ambar'') via Middle Latin ''ambar'' and Middle French ''ambre''. The word was adopted in Middle English in the 14th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments, but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the larval stage will consume food to fuel their transition into the adult form. In some organisms like polychaetes and barnacles, adults are immobil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quiver
A quiver is a container for holding arrows, bolts, ammo, projectiles, darts, or javelins. It can be carried on an archer's body, the bow, or the ground, depending on the type of shooting and the archer's personal preference. Quivers were traditionally made of leather, wood, furs, and other natural materials, but are now often made of metal or plastic. Etymology The English word quiver has its origins in Old French, written as quivre, cuevre or coivre. Types Belt quiver The most common style of quiver is a flat or cylindrical container suspended from the belt. They are found across many cultures from North America to China. Many variations of this type exist, such as being canted forwards or backwards, and being carried on the dominant hand side, off-hand side, or the small of the back. Some variants enclose almost the entire arrow, while minimalist "pocket quivers" consist of little more than a small stiff pouch that only covers the first few inches. The Bayeux Tapestry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microlepidoptera
Microlepidoptera (micromoths) is an artificial (i.e., unranked and not monophyletic) grouping of moth families, commonly known as the 'smaller moths' (micro, Lepidoptera). These generally have wingspans of under 20 mm, and are thus harder to identify by external phenotypic markings than macrolepidoptera. They present some lifestyles which the larger Lepidoptera do not have, but this is not an identifying mark. Some hobbyists further divide this group into separate groups, such as leaf miners or rollers, stem or root borers, and then usually follow the more rigorous scientific taxonomy of lepidopterans. Efforts to stabilize the term have usually proven inadequate. Diversity Vernacular usage divides the Lepidoptera simply into smaller and larger or into more-primitive and less-primitive groups: microlepidoptera and macrolepidoptera, respectively. Intuitively, the "micros" are any lepidopteran not currently placed in the macrolepidoptera. This paraphyletic assemblage, howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |