|
Millennium Cross
The Millennium Cross ( mk, Милениумски крст, ''Mileniumski krst'') is a 66-metre (217 ft) tall cross situated on the top of Vodno Mountain in the Republic of North Macedonia above the capital city of Skopje. Built in 2002, it is one of the tallest crosses worldwide. It was constructed to serve as a memorial for 2,000 years of Christianity in Macedonia and to honour biblical passages citing the evangelisation activities of St. Paul within the region. The monument has become a symbol associated with or representing Skopje. As a landmark, the cross has turned into a tourist destination with the best observation point to see the panorama of the capital city. Design structure The monument is based on a grid design, similar to the French Eiffel Tower and has the traditional shape of a Christian cross without other additions or elements. It is constructed on a twelve column platform symbolically representing the twelve apostles. Inside the cross there is an elevator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial View Of The Millennium Cross
Aerial may refer to: Music * ''Aerial'' (album), by Kate Bush * ''Aerials'' (song), from the album ''Toxicity'' by System of a Down Bands * Aerial (Canadian band) *Aerial (Scottish band) *Aerial (Swedish band) Performance art *Aerial silk, apparatus used in aerial acrobatics * Aerialist, an acrobat who performs in the air Recreation and sport *Aerial (dance move) * Aerial (skateboarding) *Aerial adventure park, ropes course with a recreational purpose * Aerial cartwheel (or side aerial), gymnastics move performed in acro dance and various martial arts *Aerial skiing, discipline of freestyle skiing * Front aerial, gymnastics move performed in acro dance Technology Antennas * Aerial (radio), a radio ''antenna'' or transducer that transmits or receives electromagnetic waves ** Aerial (television), an over-the-air television reception antenna Mechanical * Aerial fire apparatus, for firefighting and rescue * Aerial work platform, for positioning workers Optical * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Towers
Several extant building fulfill the engineering definition of a tower: "a tall human structure, always taller than it is wide, for public or regular operational access by humans, but not for living in or office work, and are ''self-supporting'' or ''free-standing'', which means no guy-wires for support." This definition excludes continuously habitable buildings and skyscrapers as well as radio and TV masts. Also excluded because they are not designed for public or regular operational access are bridge towers or pylons, wind turbines, chimneys, transmission towers, sculptures and most large statues and obelisks. Towers are most often built to use their height for various purposes, and can stand alone or as part of a larger structure. Some common purposes are for telecommunications, and as a viewing platform. The Tokyo Skytree, completed in February 2012, is , making it the tallest tower, and third-tallest free-standing structure in the world. Entirely self-supported towers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
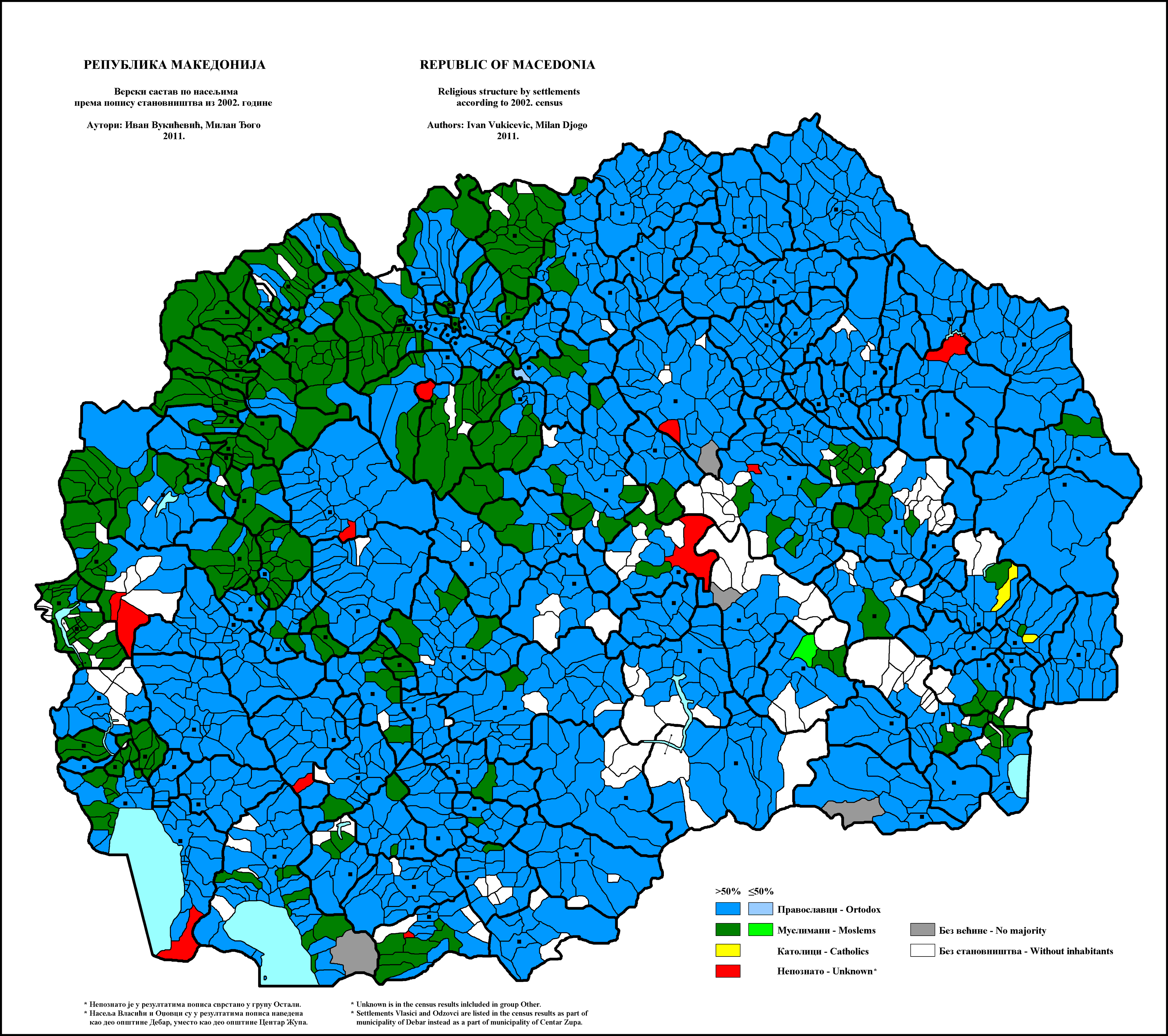
Islam In North Macedonia
Muslims in North Macedonia represent a third of the nation's total population according to the census of 2002, making Islam the second most widely professed religion in the country. Muslims in North Macedonia follow Sunni Islam of the Hanafi madhhab. Some northwestern and western regions of the country have Muslim majorities. A large majority of all the Muslims in the country are ethnic Albanians, with the rest being primarily Turks, Romani, Bosniaks or Torbeš. Population Ethnicity Historical population The following table shows the Muslim population and percentage for each given year. The Muslim percentage in Macedonia generally decreased from 1904 to 1961 but began to rise again due to high fertility rate among Muslim families, reaching 33.33% in 2002. According to the census of 2021, the share of Muslims was 32.17% of the total (resident) population, which was slightly lower compared to 33.33% in the census of 2002. *Geographical distribution (according to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church In North Macedonia
The Catholic Church in North Macedonia is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope in Rome and is one of the major religious communities that exist on the territory of the Republic of North Macedonia. Catholic believers from North Macedonia mostly include Albanians, Macedonians and Croats and are most concentrated in the Skopje Statistical Region and the Southeastern Statistical Region of North Macedonia. There are around 20,000 Catholics in the country — around 1% of the total population. The beginning of Christianity in North Macedonia In the 6th century, Emperor Justinian I (born in Tauresium, today's Gradište in North Macedonia) advanced the status of Christianity across the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire, and is venerated in both the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Roman Catholic Church. After Justinian I, the next cycle in which Christianity began to spread began in the 9th century, when Clement of Ohrid and Saint Naum instit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanians In North Macedonia
The Albanians in North Macedonia ( sq, Shqiptarët në Maqedoninë e Veriut, mk, Албанци во Северна Македонија) are the second largest ethnic group in North Macedonia, forming 446,245 individuals or 24.3% of the resident population. Of the 2,097,319 total population in the 2021 census (including self-enumerated diaspora), 619,187 or 29.52% are Albanians. Geography The Albanian minority is concentrated mostly in the western, north-western and partially middle area of the country with small communities located in the south-west. The largest Albanian communities are in the municipalities of Tetovo (71.3% of the total population), Gostivar (55.3%), Debar (54.8%), Struga (50.6%), Kičevo (41.3%), Kumanovo (26.0%), and Skopje (22.9%). Toponymy A number of placenames in North Macedonia have been considered as being ultimately derived through Albanian. Some cases include: *Štip (''Shtip'' in Albanian) is a city in eastern North Macedonia. It was known in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbian Orthodox Church
The Serbian Orthodox Church ( sr-Cyrl, Српска православна црква, Srpska pravoslavna crkva) is one of the autocephalous (ecclesiastically independent) Eastern Orthodox Christian denomination, Christian churches. The majority of the population in Serbia, Montenegro and the Republika Srpska entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina are members of the Serbian Orthodox Church. It is organized into metropolis (religious jurisdiction), metropolitanates and eparchies, located primarily in Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, and Croatia. Other congregations are located in the Serb diaspora. The Serbian Patriarch serves as first among equals in his church. The current patriarch is Porfirije, Serbian Patriarch, Porfirije, enthroned on 19 February 2021. The Church achieved Autocephaly, autocephalous status in 1219, under the leadership of Saint Sava, becoming the independent Archbishopric of Žiča. Its status was elevated to that of a patriarchate in 1346, and was kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedonian Nationalism
Macedonian nationalism (, ) is a general grouping of nationalist ideas and concepts among ethnic Macedonians that were first formed in the late 19th century among separatists seeking the autonomy of the region of Macedonia from the Ottoman Empire. The idea evolved during the early 20th century alongside the first expressions of ethnic nationalism among the Slavs of Macedonia. The separate Macedonian nation gained recognition after World War II when the "Socialist Republic of Macedonia" was created as part of Yugoslavia. Afterwards the Macedonian historiography has established historical links between the ethnic Macedonians and events and Bulgarian figures from the Middle Ages up to the 20th century. Following the independence of the Republic of Macedonia in the late 20th century, issues of Macedonian national identity have become contested by the country's neighbours, as some adherents to aggressive Macedonian nationalism, called ''Macedonism'', hold more extreme beliefs such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppelmayr Garaventa Group
Doppelmayr/Garaventa Group is an international manufacturer of ropeways and people movers for ski areas, urban transport, amusement parks, and material handling systems. As of 2019, the group have produced over 15,000 installations in 96 countries. The Doppelmayr/Garaventa Group was formed in 2002 when Doppelmayr of Wolfurt, Austria merged with Garaventa AG of Switzerland to form the world's largest ropeway manufacturer. __TOC__ History Doppelmayr was founded in Wolfurt, Austria, in 1892 (originally as Konrad Doppelmayr & Sohn), and has manufactured ropeways from 1937. Garaventa was founded in 1928. In 1967, , the grandson of the founder, Konrad Doppelmayr, and son of Austrian businessman Emil Doppelmayr, became managing director of the company. As alpine recreation rapidly expanded around the world during the last half of the 20th century, Artur led and established the Vorarlberg cable car company as the world leader. In 1996, Doppelmayr Holding AG acquired Von Roll Seil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . The euro is divided into 100 cents. The currency is also used officially by the institutions of the European Union, by four European microstates that are not EU members, the British Overseas Territory of Akrotiri and Dhekelia, as well as unilaterally by Montenegro and Kosovo. Outside Europe, a number of special territories of EU members also use the euro as their currency. Additionally, over 200 million people worldwide use currencies pegged to the euro. As of 2013, the euro is the second-largest reserve currency as well as the second-most traded currency in the world after the United States dollar. , with more than €1.3 trillion in circulation, the euro has one of the highest combined values of banknotes and coins in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It is a landlocked country bordering Kosovo to the northwest, Serbia to the north, Bulgaria to the east, Greece to the south, and Albania to the west. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical Macedonia (region), region of Macedonia. Skopje, the capital and largest city, is home to a quarter of the country's 1.83 million people. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians, a South Slavs, South Slavic people. Albanians in North Macedonia, Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks in North Macedonia, Turks, Romani people in North Macedonia, Romani, Serbs in North Macedonia, Serbs, Bosniaks in North Macedonia, Bosniaks, Aromanians in North Mace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cableway
Cable transport is a broad class of transport modes that have cables. They transport passengers and goods, often in vehicles called cable cars. The cable may be driven or passive, and items may be moved by pulling, sliding, sailing, or by drives within the object being moved on cableways. The use of pulleys and balancing of loads moving up and down are common elements of cable transport. They are often used in mountainous areas where cable haulage can overcome large differences in elevation. Common modes of cable transport Aerial transport Forms of cable transport in which one or more cables are strung between supports of various forms and cars are suspended from thes cables. * Aerial tramway * Chairlift * Funitel * Gondola lift * Ski lift * Zip line Cable railways Forms of cable transport where cars on rails are hauled by cables. The rails are usually steeply inclined and usually at ground level. * Cable car * Funicular Other Other forms of cable-hauled transpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)



