|
Milkymist Case Acryl V6 1
M-Labs (formerly known as the Milkymist project) is a company and community who develop, manufacture and sell advanced open hardware devices and software. It is known for the Milkymist system-on-chip (SoC) which is a commercialized system-on-chip designs with free HDL source code. M-Labs technologies have been reused in diverse applications. For example, NASA's Communication Navigation and Networking Reconfigurable Testbed (CoNNeCT) experiment uses the memory controller that was originally developed for the Milkymist One and published under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL). The project was presented at several open source and hacker conferences such as the Chaos Communication Congress, FOSDEM, Libre Software Meeting, and Libre Graphics Meeting 2011. It was also featured on the ''Make'' magazine blog and the Milkymist One board was included in their "ultimate open source hardware gift guide 2010". Milkymist SoC The Milkymist system-on-chip uses the LatticeMic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Hardware
Open-source hardware (OSH) consists of physical artifact (software development), artifacts of technology designed and offered by the open-design movement. Both free and open-source software (FOSS) and open-source hardware are created by this open-source#Society, open-source culture movement and apply a like concept to a variety of components. It is sometimes, thus, referred to as FOSH (free and open-source hardware). The term usually means that information about the hardware is easily discerned so that others can make it – coupling it closely to the Maker culture, maker movement. Hardware design (i.e. mechanical drawings, circuit diagram, schematics, bills of material, printed circuit board, PCB layout data, hardware description language, HDL source code and integrated circuit layout data), in addition to the software that device driver, drives the hardware, are all released under free/Libre content, libre terms. The original sharer gains feedback and potentially improvements on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Management Unit
A memory management unit (MMU), sometimes called paged memory management unit (PMMU), is a computer hardware unit having all memory references passed through itself, primarily performing the translation of virtual memory addresses to physical addresses. An MMU effectively performs virtual memory management, handling at the same time memory protection, cache control, bus arbitration and, in simpler computer architectures (especially 8-bit systems), bank switching. Overview Modern MMUs typically divide the virtual address space (the range of addresses used by the processor) into pages, each having a size which is a power of 2, usually a few kilobytes, but they may be much larger. The bottom bits of the address (the offset within a page) are left unchanged. The upper address bits are the virtual page numbers. Page table entries Most MMUs use an in-memory table of items called a "page table", containing one "page table entry" (PTE) per page, to map virtual page numbers to ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QEMU
QEMU is a free and open-source emulator (Quick EMUlator). It emulates the machine's processor through dynamic binary translation and provides a set of different hardware and device models for the machine, enabling it to run a variety of guest operating systems. It can interoperate with Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) to run virtual machines at near-native speed. QEMU can also do emulation for user-level processes, allowing applications compiled for one architecture to run on another. Licensing QEMU was written by Fabrice Bellard and is free software, mainly licensed under the GNU General Public License (GPL for short). Various parts are released under the BSD license, GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) or other GPL-compatible licenses. Operating modes QEMU has multiple operating modes: ;User-mode emulation: In this mode QEMU runs single Linux or Darwin/macOS programs that were compiled for a different instruction set. System calls are thunked for endianness and for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU GPL
The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or simply GPL) is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the four freedoms to run, study, share, and modify the software. The license was the first copyleft for general use and was originally written by the founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), Richard Stallman, for the GNU Project. The license grants the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. These GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. It is more restrictive than the Lesser General Public License and even further distinct from the more widely used permissive software licenses BSD, MIT, and Apache. Historically, the GPL license family has been one of the most popular software licenses in the free and open-source software domain. Prominent free software programs licensed under the GPL include the Linux kernel a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
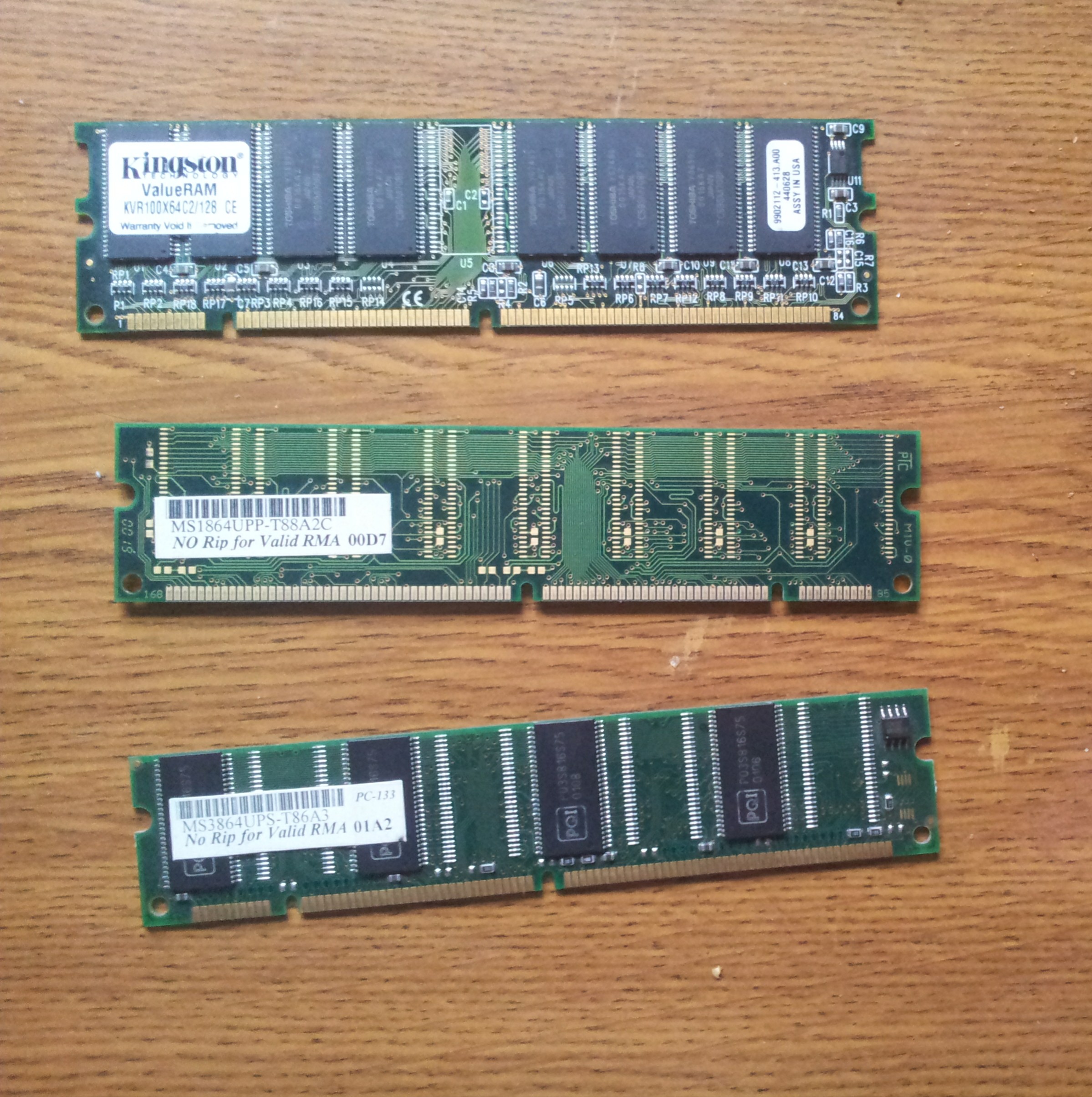
SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions only delayed by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memory a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Memory Access
Direct memory access (DMA) is a feature of computer systems and allows certain hardware subsystems to access main system memory independently of the central processing unit (CPU). Without DMA, when the CPU is using programmed input/output, it is typically fully occupied for the entire duration of the read or write operation, and is thus unavailable to perform other work. With DMA, the CPU first initiates the transfer, then it does other operations while the transfer is in progress, and it finally receives an interrupt from the DMA controller (DMAC) when the operation is done. This feature is useful at any time that the CPU cannot keep up with the rate of data transfer, or when the CPU needs to perform work while waiting for a relatively slow I/O data transfer. Many hardware systems use DMA, including disk drive controllers, graphics cards, network cards and sound cards. DMA is also used for intra-chip data transfer in multi-core processors. Computers that have DMA channels can trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wishbone (computer Bus)
The Wishbone Bus is an open source hardware computer bus intended to let the parts of an integrated circuit communicate with each other. The aim is to allow the connection of differing cores to each other inside of a chip. The Wishbone Bus is used by many designs in the OpenCores project. Wishbone is intended as a "logic bus". It does not specify electrical information or the bus topology. Instead, the specification is written in terms of "signals", clock cycles, and high and low levels. This ambiguity is intentional. Wishbone is made to let designers combine several designs written in Verilog, VHDL or some other logic-description language for electronic design automation (EDA). Wishbone provides a standard way for designers to combine these hardware logic designs (called "cores"). Wishbone is defined to have 8, 16, 32, and 64-bit buses. All signals are synchronous to a single clock but some slave responses must be generated combinatorially for maximum performance. Wishbone per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milkymist One And Flickernoise
M-Labs (formerly known as the Milkymist project) is a company and community who develop, manufacture and sell advanced open hardware devices and software. It is known for the Milkymist system-on-chip (SoC) which is a commercialized system-on-chip designs with free HDL source code. M-Labs technologies have been reused in diverse applications. For example, NASA's Communication Navigation and Networking Reconfigurable Testbed (CoNNeCT) experiment uses the memory controller that was originally developed for the Milkymist One and published under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL). The project was presented at several open source and hacker conferences such as the Chaos Communication Congress, FOSDEM, Libre Software Meeting, and Libre Graphics Meeting 2011. It was also featured on the ''Make'' magazine blog and the Milkymist One board was included in their "ultimate open source hardware gift guide 2010". Milkymist SoC The Milkymist system-on-chip uses the LatticeMic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very Long Instruction Word
Very long instruction word (VLIW) refers to instruction set architectures designed to exploit instruction level parallelism (ILP). Whereas conventional central processing units (CPU, processor) mostly allow programs to specify instructions to execute in sequence only, a VLIW processor allows programs to explicitly specify instructions to execute in parallel. This design is intended to allow higher performance without the complexity inherent in some other designs. Overview The traditional means to improve performance in processors include dividing instructions into substeps so the instructions can be executed partly at the same time (termed ''pipelining''), dispatching individual instructions to be executed independently, in different parts of the processor (''superscalar architectures''), and even executing instructions in an order different from the program (''out-of-order execution''). These methods all complicate hardware (larger circuits, higher cost and energy use) because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floating Point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can be represented as a base-ten floating-point number: 12.345 = \underbrace_\text \times \underbrace_\text\!\!\!\!\!\!^ In practice, most floating-point systems use base two, though base ten (decimal floating point) is also common. The term ''floating point'' refers to the fact that the number's radix point can "float" anywhere to the left, right, or between the significant digits of the number. This position is indicated by the exponent, so floating point can be considered a form of scientific notation. A floating-point system can be used to represent, with a fixed number of digits, numbers of very different orders of magnitude — such as the number of meters between galaxies or between protons in an atom. For this reason, floating-poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture Mapping Unit
In computer graphics, a texture mapping unit (TMU) is a component in modern graphics processing units (GPUs). They are able to rotate, resize, and distort a bitmap image to be placed onto an arbitrary plane of a given 3D model as a texture, in a process called texture mapping. In modern graphics cards it is implemented as a discrete stage in a graphics pipeline, whereas when first introduced it was implemented as a separate processor, e.g. as seen on the Voodoo2 graphics card. Background and history The TMU came about due to the compute demands of sampling and transforming a flat image (as the texture map) to the correct angle and perspective it would need to be in 3D space. The compute operation is a large matrix multiply, which CPUs of the time (early Pentiums) could not cope with at acceptable performance. In 2013, TMUs are part of the shader pipeline and decoupled from the Render Output Pipelines (ROPs). For example, in AMD's Cypress GPU, each shader pipeline (of which th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LLVM
LLVM is a set of compiler and toolchain technologies that can be used to develop a front end for any programming language and a back end for any instruction set architecture. LLVM is designed around a language-independent intermediate representation (IR) that serves as a portable, high-level assembly language that can be optimized with a variety of transformations over multiple passes. LLVM is written in C++ and is designed for compile-time, link-time, run-time, and "idle-time" optimization. Originally implemented for C and C++, the language-agnostic design of LLVM has since spawned a wide variety of front ends: languages with compilers that use LLVM (or which do not directly use LLVM but can generate compiled programs as LLVM IR) include ActionScript, Ada, C#, Common Lisp, PicoLisp, Crystal, CUDA, D, Delphi, Dylan, Forth, Fortran, Free Basic, Free Pascal, Graphical G, Halide, Haskell, Java bytecode, Julia, Kotlin, Lua, Objective-C, OpenCL, PostgreSQL's SQL and PLpg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |