|
Military Operations In Ladakh (1948)
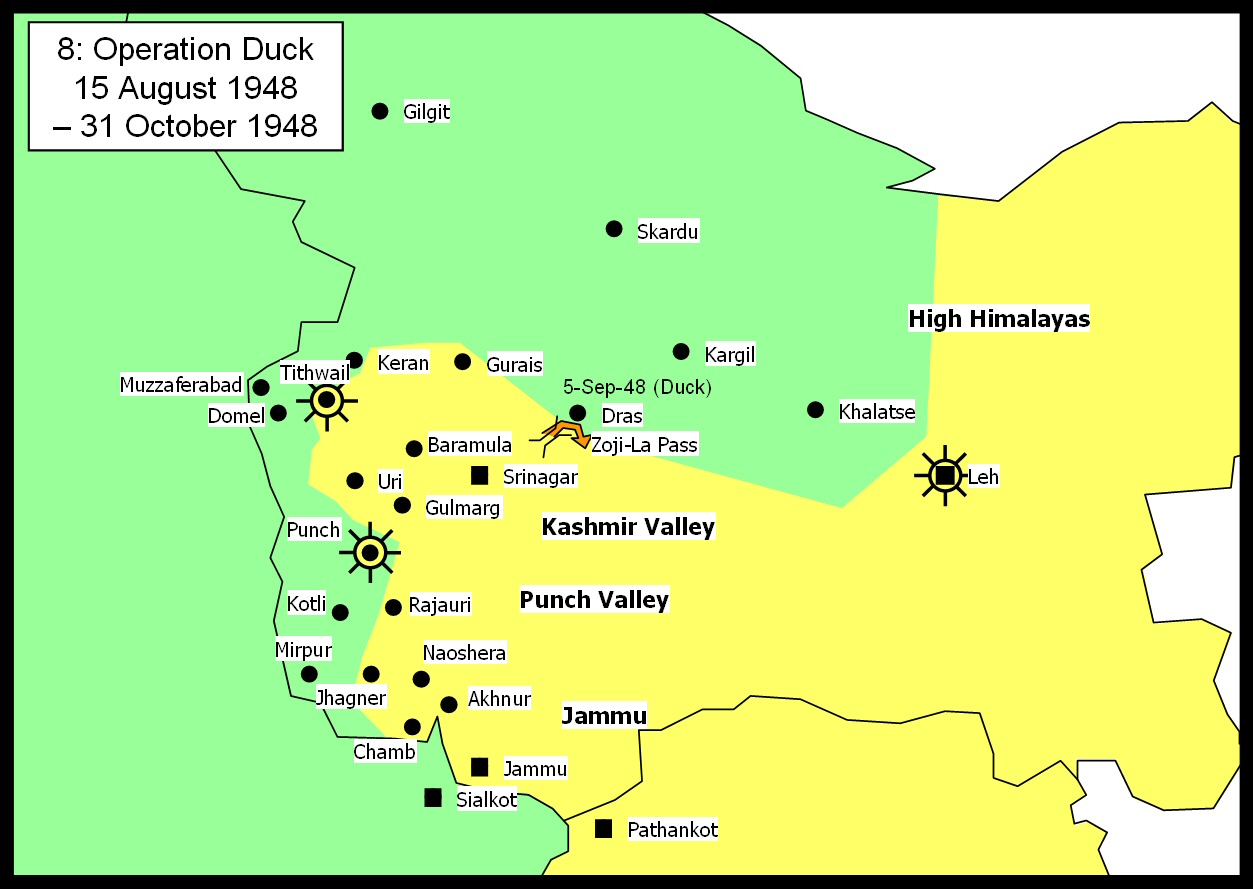
Military operations took place in Ladakh in 1948 during the Indo-Pakistani War of 1947, conflict in Jammu and Kashmir between the Indian Army and Pakistani raiders infiltrated to capture the Kashmir and Jammu (princely state), kingdom of Jammu and Kashmir. The eviction of this invading force of tribal raiders, who enjoyed numerical superiority, better lines of communication, commanding high ground and superior logistics, was a major military achievement for the small force of India, Indian soldiers. Relief of Leh Pakistani raiders had besieged and reduced Skardu in early 1948.. It was vital that Leh, the next likely target, be relieved before it was attacked by the raiders. Maj Prithi Chand, a Lahaul and Spiti district, Lahauli officer with a band of 40 volunteers from the 2nd Battalion, Dogra Regiment began a hazardous mid-winter ascent of Zojila pass on 16 February 1948, with rifles and ammunition for the garrison. They reached Leh on 8 March, where an ad hoc force for defence wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu and Kashmir, state of India, located in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent in the vicinity of the Karakoram and westernmost Himalayan mountain ranges. From 1947 to 2019, Ladakh was part of the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir, which has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since the partition of the subcontinent in 1947." Quote: "Jammu and Kashmir: Territory in northwestern India, subject to a dispute between India and Pakistan. It has borders with Pakistan and China." Ladakh is bordered by the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east, the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh to the south, both the Indian-administered union territory of Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), Jammu and Kashmir and the Pakistan-administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th Light Cavalry
The 7th Light Cavalry previously the 28th Light Cavalry, was a regular army cavalry regiment in the British Indian Army. It was raised in 1784 under the East India Company. The regiment later saw service on the North West Frontier and in World War I and World War II. In 1947, it was allocated to the new Indian Army, where it continues to exist as the 7th Light Cavalry History Formation and early history The history of this regiment can be traced to 1784 when a force of cavalry was hired from the Nawab of Arcot by the East India Company. These regiments subsequently mutinied over pay issues. The regiments involved were disbanded and from their remnants, volunteers formed the 2nd Madras Cavalry. This new regiment would eventually become the 7th Light Cavalry. The title was first changed to that of 3rd Madras Native Cavalry. Under this designation the regiment first saw action during the Third Mysore War in 1790, against Tipu Sultan. The regiment was next in action during the Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kargil Town
Kargil ( lbj, ) is a city and a joint capital of the union territory of Ladakh, India. It is also the headquarters of the Kargil district. It is the second-largest city in Ladakh after Leh. Kargil is located to the east of Srinagar in Jammu and Kashmir, and to the west of Leh. It is the centre point of the Suru River. Etymology The name ''Kargil'' is said to derive from the words ''Khar'', meaning castle, and ''rKil'' meaning "centre". "Kargil denotes a place between many forts, a central place where people could stay". It appears to be a fitting description for a place that is equidistant from Srinagar, Leh and Skardu Historically, the region around Kargil was called Purig. A major study of the history of Purig is included in the 1987 book ''Qadeem Ladakh'' by Kacho Sikander Khan, which includes genealogies of various dynasties that ruled the region. History Kargil is the main town in the historical region of Purig, which consists of the Suru river basin. It was n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dras
Dras (also spelt Drass, ISO transliteration: '), also known locally in Shina as Himababs, Hembabs, or Humas, is a town and hill station, near Kargil city in the Kargil district of the union territory of Ladakh in India. It is on the National Highway 1 (India), NH 1 (former name National Highway 1D (India, old numbering), NH 1D before List of National Highways in India by highway number, renumbering of all national highways) between Zoji La pass and Kargil city. A tourist hub for its high altitude trekking routes and tourist sites, it is often called "The Gateway to Ladakh". The government's official spelling of the town is Drass. Etymology Traditionally, Dras is known as ''Hem-babs'', which means "snow land" with the word "Hem" meaning snow. The average temperature of Dras in winter is -20 degrees Celsius. Geography Dras is often called "The Gateway to Ladakh". It is at a height of Dras lies in the centre of the valley of the same name (Dras valley). Dras is 140 k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nubra Valley
Nubra, also called Dumra, is a historical region of Ladakh, India that is currently administered as a subdivision and a tehsil in the Leh district. Its inhabited areas form a tri-armed valley cut by the Nubra and Shyok rivers. Its Tibetan name ''Dumra'' means a "valley of flowers". Demands have been raised and BJP has hinted at creation of Nubra as a new district.3,000 Demonstrate for Separate District in Sub-Zero Temperatures at Kargil The Wire, 06/FEB/2020. , the headquarters of Nubra, is 120 km north from , the capital of Ladakh. The |
Shyok River
The Shyok River is a tributary of the Indus River that flows through northern Ladakh and enters Gilgit–Baltistan, spanning some . The Shyok River originates at the Rimo Glacier, one of the tongues of Siachen Glacier. Its alignment is very unusual, originating from the Rimo glacier, it flows in a southeasterly direction and, joining the Pangong range, it takes a northwestern turn, flowing parallel to its previous path. Shyok Valley widens at the confluence with the Nubra River but suddenly turns into a narrow gorge near Yagulung (), continuing through Bogdang, Turtuk and Tyakshi before crossing into Baltistan. The valley again widens near its Saltoro River junction at Ghursay. The river joins the Indus at Keris, east of the town of Skardu. The Nubra River, originating from the Siachen glacier, also behaves like the Shyok. Before Diskit, the southeasterly flowing river Nubra takes a northwest turn on meeting the river Shyok. The similarity in the courses of these two importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamayuru Monastery
Lamayuru or Yuru Monastery ( "Eternal Monastery") is a Tibetan Buddhist monastery in Lamayouro, Leh district, Ladakh, India. It is situated on the Srinagar-Leh highway east of the Fotu La at a height of . History A. H. Francke states that, "according to popular tradition," it was originally the foremost Bon monastery in Ladakh; its name means sauwastika and is a popular symbol in Bon for "eternity". Yungdrung is the name of the most popular school of Bon. It is currently affiliated with the Drikung Kagyu school of Buddhism. The Drikung history states that the Indian scholar Naropa (956-1041 CE) allegedly caused a lake which filled the valley to dry up and founded Lamayuru Monastery. The oldest surviving building at Lamayuru is a temple called Seng-ge-sgang, at the southern end of the Lamayuru rock, which is attributed to the famous builder-monk Rinchen Zangpo (958-1055 CE). Rinchen Zangpo was charged by the king of Ladakh to build 108 gompas, and certainly many gompas in Lad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent. It is bounded by the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang to the northeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east (both parts of China), by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south, by Pakistan to the west, and by Afghanistan to the northwest. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan and comprise three areas: Azad Kashmir, Gilgit, and Baltistan, ... The southern and southeastern portions constitute the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir. The Indian- and Pakistani-administered portions are divided by a "line of control" agreed to in 1972, although neither country recognizes it as an international boundary. In addition, China became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kargil War Memorial (28606066885)
The Kargil War Memorial, also known as Dras War Memorial, is a war memorial built by the Indian Army in the town of Dras, near Kargil city in Kargil district of Ladakh, India, commemorating the 1999 Kargil War between India and Pakistan. The memorial is located on the Srinagar-Leh National Highway 1D, about 5 km from the city centre across the Tiger Hill, Kargil. History In the winter of 1998–99, the Pakistani Army crossed the Line of Control (LoC) and occupied numerous heights in Indian State of Jammu and Kashmir. Pakistani forces were dominating the National Highway and roads connecting Leh (Ladakh) and Kargil to Srinagar. The Indian Army launched Operation Vijay ("Victory") in May 1999 to retake the territory, leading to fierce battles in the harsh mountain environment. The operation continued for over two months, leading to a stalemate, and eventual withdrawal of Pakistani troops on the intervention nd instructions of USA, to avoid full-scale war between two nuclea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matayan
For Hinduism in India, the Matayan is the sole authority to administer the Muthappan temple, found in the Kannur district of Kerala state, south India. See also * Sree Muthappan *Muthappan temple Parassinikadavu Muthappan temple is a temple, located at Parassinikadavu in Anthoor Municipality on the banks of the Valapattanam river about from Taliparamba and from Kannur City in Kannur District, Kerala, India. Thiyya community urayi ... References Hinduism in India {{Hindu-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordnance QF 25 Pounder
The Ordnance QF 25-pounder, or more simply 25-pounder or 25-pdr, was the major British field gun and howitzer during the Second World War. Its calibre is 3.45-inch (87.6 mm). It was introduced into service just before the war started, combining both high-angle and direct-fire abilities, a relatively high rate of fire, and a reasonably lethal shell in a highly mobile piece. It remained the British Army's primary artillery field piece well into the 1960s, with smaller numbers serving in training units until the 1980s. Many Commonwealth of Nations countries used theirs in active or reserve service until about the 1970s and ammunition for the weapon is currently being produced by Pakistan Ordnance Factories. Initial production was slow, but by 1945, over 12,000 had been manufactured. The 25-pounder was probably the most outstanding field artillery piece used by British and Commonwealth forces in the Second World War, being durable, easy to operate and versatile. Design The desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodendera Subayya Thimayya
General Kodendera Subayya Thimayya (31 March 1906 - 18 December 1965) was a distinguished soldier of the Indian Army who served as Chief of Army Staff from 1957 to 1961 in the crucial years leading up to the conflict with China in 1962. Gen. Thimayya was the only Indian to command an Infantry brigade in battle during the Second World War and is regarded as the most distinguished combat officer the Indian Army has produced. After the Korean War, Thimayya headed a United Nations unit dealing with the repatriation of prisoners of war. After his retirement from the Army, he was appointed Commander of the United Nations Peace Keeping Force in Cyprus from July 1964 to December 1965 and died in Cyprus while on active duty on 18 December 1965. Early life and education Kodandera Subayya Thimayya was born in Madikeri, the district town of Kodagu (formerly known as Coorg), Karnataka, on 31 March 1906, to Subayya and Sitamma. His family was one of the leading coffee planters in the area. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |