|
Military Of Ryukyu
The military of the Ryukyu Kingdom defended the kingdom from 1429 until 1879. It had roots in the late army of Chūzan, which became the Ryukyu Kingdom under the leadership of King Shō Hashi. The Ryukyuan military operated throughout the Ryukyu Islands, the East China Sea, and elsewhere that Ryukyuan ships went. Ryukyu primarily fought with other Ryukyuan kingdoms and chiefdoms, but also Japanese samurai from Satsuma Domain and pirates. Soldiers were stationed aboard ships and Ryukyuan fortifications. The Ryukyuan military declined after the 17th century. History Early history ''Chūzan Seikan'', the first official history of Ryukyu, details the military victories of Shō Hashi. He first captured Ōzato Castle in 1403, then overthrew King Bunei of Chūzan in 1407,Historians have variously claimed 1405, 1406, and 1407. installing his father as king. He moved the capital from Urasoe to Shuri. During the early 1410s, ''aji'', Ryukyuan feudal lords, under the rule of Hokuzan g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryukyu Kingdom
The Ryukyu Kingdom, Middle Chinese: , , Classical Chinese: (), Historical English names: ''Lew Chew'', ''Lewchew'', ''Luchu'', and ''Loochoo'', Historical French name: ''Liou-tchou'', Historical Dutch name: ''Lioe-kioe'' was a kingdom in the Ryukyu Islands from 1429 to 1879. It was ruled as a tributary state of imperial Ming China by the Ryukyuan monarchy, who unified Okinawa Island to end the Sanzan period, and extended the kingdom to the Amami Islands and Sakishima Islands. The Ryukyu Kingdom played a central role in the maritime trade networks of medieval East Asia and Southeast Asia despite its small size. The Ryukyu Kingdom became a vassal state of the Satsuma Domain of Japan after the invasion of Ryukyu in 1609 but retained ''de jure'' independence until it was transformed into the Ryukyu Domain by the Empire of Japan in 1872. The Ryukyu Kingdom was formally annexed and dissolved by Japan in 1879 to form Okinawa Prefecture, and the Ryukyuan monarchy was integrated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunei (Ryukyu)
was King of Chūzan. He was the second and last ruler of the Satto dynasty. Biography Bunei inherited the throne upon the death of his father, King Satto. His reign saw the continuation of many of the previous trends and developments; in particular, Bunei sought to continue to develop commercial ties between Ryūkyū and China. A special headquarters was built in Naha for Chinese envoys and similar missions, and a trading center was established nearby. In addition, the royal annals began to be compiled; the '' Rekidai Hoan'' (Treasury of Royal Succession) was first compiled in 1403. This period saw a great proliferation of trade and cultural interaction between the three Okinawan polities and other states in the region; sources seem to indicate, however, that only Chūzan successfully established relations with the Ashikaga shogunate of Japan in this period. An embassy was sent to Siam in 1409, and relations with kingdoms in Java and Sumatra remained strong, having been establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chūzan Seifu
was an official history of the Ryūkyū Kingdom compiled between 1697 and 1701 by a group of scholar-officials led by Sai Taku. It was a Kanbun translated version of ''Chūzan Seikan''. Later, it was rewritten into Classical Chinese by Sai Taku's famous son Sai On in 1725, and expanded each year until 1876. See also *List of Cultural Properties of Japan - writings (Okinawa) *Chūzan Seikan *Kyūyō is an official history of the Ryūkyū Kingdom compiled between 1743 and 1745 by a group of scholar-officials led by . Written in kanbun, and numbering twenty-two scrolls, a supplementary volume in three scrolls documents relations with Satsuma, ... References Japanese chronicles Ryukyu Kingdom 1690s books 1700s books Edo-period history books {{japan-hist-book-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zakimi Castle
is a Ryukyuan ''gusuku'' in Yomitan, Okinawa. It is in ruins, but the walls and foundations have been restored. In 2000, Zakimi Castle was designated as a World Heritage Site, as a part of the Gusuku Sites and Related Properties of the Kingdom of Ryukyu. History It was built between 1416 and 1422 by the renowned Ryukyuan general Gosamaru, a project which involved workers from as far away as the Amami Islands, and was partly constructed with materials taken from nearby Yamada Castle."Gosamaru." ''Okinawa konpakuto jiten'' (沖縄コンパクト事典, "Okinawa Compact Encyclopedia")Ryukyu Shimpo(琉球新報). 1 March 2003. Accessed 25 July 2009. Zakimi Castle oversaw the northern portion of central Okinawa Island. The fortress has two inner courts, each with an arched gate. This is Okinawa's first stone arch gate featuring the unique keystone masonry of the Ryukyus. Before and during World War II, the castle was used as a gun emplacement by the Japanese. After the war it was used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakijin Castle
is a Ryukyuan ''gusuku'' located in Nakijin, Okinawa. It is currently in ruins. In the late 14th century, the island of Okinawa consisted of three principalities: Nanzan to the south, Chūzan in the central area, and Hokuzan in the north. Nakijin was the capital of Hokuzan. The fortress includes several sacred Utaki groves, reflecting the castle's role as a center of religious activity. It is today known for the Hikan cherries which bloom in northern Okinawa between mid-January and early February, providing the first cherry blossoms each year in Japan. In 2000, Nakijin Castle was designated as a World Heritage Site, as a part of the Gusuku Sites and Related Properties of the Kingdom of Ryukyu. History Though there had been Lords of Nakijin prior to the creation of the Hokuzan kingdom, and thus some form of chiefly residence can be presumed to have been on or near the site before, it is believed that the ''gusuku'' form of Nakijin castle only emerged at the founding of the kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunigami, Okinawa
is a village in Kunigami District, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. It occupies the north tip of Okinawa Island, with the East China Sea to the west, Pacific Ocean to the east, and villages of Higashi and Ōgimi to the south. As of 2015, the village has a population of 4,908 and a population density of 25.20 persons per km2. The total area is 194.80 km2. History According to ''Chūzan Seikan'', the goddess Amamikyu consecrated the first utaki in Asa Forest at Hedo, in what is now Kunigami; the forest is also mentioned in ''Omoro Sōshi''. Ceramics from the Jōmon-period resemble those found in the Amami Islands. ''Chūzan Seikan'' records the prayers of the Kunigami council for the recovery of Shō Sei after an abortive attempt to occupy Amami Ōshima in 1537, while ''Kyūyō'' recounts the appointment of the son of the Kunigami Oyakata as ''aji'' after the successful takeover of the Amami Islands by Shō Gen in 1571. Kunigami District was established in 1896 and, upon the ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nago, Okinawa
''Nagu'', Kunigami: ''Naguu'' is a city located in the northern part of Okinawa Island, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. As of December 2012, the city has an estimated population of 61,659 and a population density of 288 persons per km2. Its total area is 210.30 km2. History Nago Castle was built in the 14th century and served as the home of the Aji of Nago Magiri. Nago had always been one of the major settlements in Northern Okinawa, and a major port along with Unten. Nago Magiri became Nago town in 1907. Nago was upgraded to city status on August 1, 1970 with the merger of nine smaller towns and villages. Nago hosted Expo '75 in a park which utilized a monorail train to move tourists to each exhibit. Its most popular exhibit was the Japanese Floating City; similar to an oil rig, the city floated on large pontoons which allowed it to be moved. If the city was threatened with a typhoon, it would move close to shore, fill the pontoons with sea water and sit on the ocean floo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shuri, Okinawa
''Sui'' or ''Shui'', Northern Ryukyuan languages, Northern Ryukyuan: ''Shiyori'' is a district of the city of Naha, Okinawa. It was formerly a separate city in and of itself, and the royal capital of the Ryūkyū Kingdom. A number of famous historical sites are located in Shuri, including Shuri Castle, the Shureimon gate, Sunuhyan-utaki (a sacred space of the native Ryukyuan religion), and royal mausoleum Tamaudun, all of which are designated World Heritage Sites by UNESCO. Originally established as a castle town surrounding the royal palace, Shuri ceased to be the capital when the kingdom was abolished and incorporated into Japan as Okinawa prefecture. In 1896, Shuri was made a of the new prefectural capital, Naha, though it was made a separate city again in 1921. In 1954, it was merged again into Naha. History Medieval and early modern periods Shuri Castle was first built during the reign of Shunbajunki (r. 1237–1248), who ruled from nearby Urasoe Castle.George H. Kerr, K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yomitan, Okinawa
is a village located in Nakagami District, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. Geography Yomitan is located on the western coast of the central part of Okinawa Island. The village is bound to the north by Onna, to the east by Okinawa City, to the south by Kadena, and to the west by the East China Sea. 31.5% of the land area is zoned for agriculture, 35.7% is zoned as forest, 12.3% is zoned for housing, and the remaining 20.6% is zoned for other uses. History Originally known as , it was part of the Kingdom of Chūzan during the Sanzan period.Uezato, Takashi. ''Ryūkyū Sengoku Rekidan'' (in Japanese). Naha: Border Ink Publishing, 2015. 40-41. In 1416, the Aji of Yomitanzan Magiri, Gosamaru, helped Shō Hashi invade Hokuzan. Although Gosamaru lived in Yamada Castle, Shō Hashi allowed him to build Zakimi Castle. The castle, along with other castle sites in Okinawa, was designated a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in November 2000. The port of Hamanaga, which was located in the nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urasoe, Okinawa
is a city located in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. The neighboring municipalities are Naha to the south, Ginowan to the north, and Nishihara to the east. As of November 2012, the city has an estimated population of 113,718 and a population density of 5,956.9 persons per km2. The total area is 19.09 km2. United States Marine Corps base Camp Kinser is located on the city's coast. Etymology The name "Urasoe" is made up of two kanji characters. The first, , means "a coastal area", and the second, , means "ruling" or "uniting". The name is a reference to "ruling over many areas". Geography Urasoe sits to the south of Okinawa Island. Urasoe is rugged and hilly to the east, and the city slopes gently to the East China Sea in the west. Urasoe, while formerly agricultural, has become heavily urbanized due to its proximity to the prefectural capital of Naha. Neighboring municipalities *Naha *Ginowan * Nishihara Transportation The city is served by Naha Airport and the Okinawa Expr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hananchi
was a local ruler of Okinawa Island, who was given the title of King of Sanhoku. Contemporary sources on Han'anchi are very scarce. He first appeared in Chinese diplomatic records in 1396 and his last contact was of 1415. His blood relationship with Min, the preceding King of Sanhoku, is unknown. After 1415, the King of Sanhoku did not contact China again. The Chinese records suggest that the Chinese had no information on when and how the king disappeared. Because the King of Chūzan continued tributary missions, the Chinese later speculated that the Kings of Sannan and Sanhoku had been removed by the King of Chūzan. His real name is unknown. Modern attempts to decipher the enigmatic un-Okinawan name ''Han'anchi'' point to Haneji (羽地), a settlement in northern Okinawa (part of modern-day Nago City). ''Han'anchi'' can be either a corrupt form of ''Haneji'' or a contraction of ''Haneji Aji'' (local ruler of Haneji). The name suggests some connection to the settlement, but it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
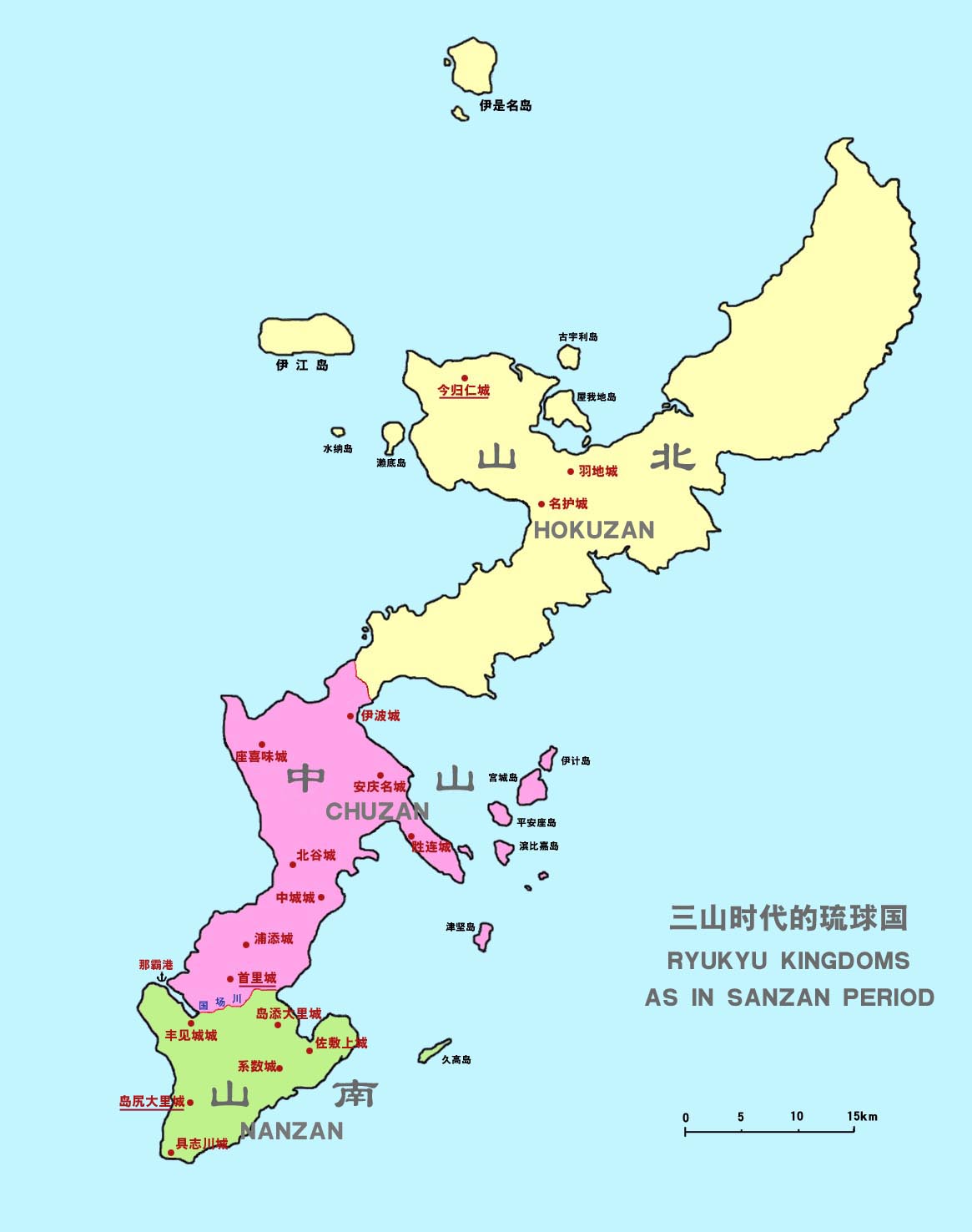
Hokuzan
, also known as before the 18th century, located in the north of Okinawa Island, was one of three independent political entities which controlled Okinawa in the 14th century during Sanzan period. The political entity was identified as a tiny country, a kingdom, or a principality by modern historians, however the ruler of Hokuzan was in fact not "kings" at all, but petty lords with their own retainers owing their direct service, and their own estates. Okinawa, previously controlled by a number of local chieftains or lords, loosely bound by a paramount chieftain or king of the entire island, split into these three more solidly defined kingdoms within a few years after 1314; the Sanzan period thus began, and would end roughly one hundred years later, when Chūzan's King Shō Hashi conquered Hokuzan in 1416 and Nanzan in 1429. After the unification of Ryukyu, Hokuzan became one of three nominal '' fu'' (, lit. "prefectures") of the Ryukyu Kingdom without administrative function. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

