|
Military Necessity
Military necessity, along with distinction, and proportionality, are three important principles of international humanitarian law governing the legal use of force in an armed conflict. Attacks Military necessity is governed by several constraints: an attack or action must be intended to help in the military defeat of the enemy; it must be an attack on a military objective,Article 52 of ''Additional Protocol I to the Geneva Conventions'' provides a widely accepted definition of military objective: "In so far as objects are concerned, military objectives are limited to those objects which by their nature, location, purpose or use make an effective contribution to military action and whose total or partial destruction, capture or neutralization, in the circumstances ruling at the time, offers a definite military advantage" (Source: ). and the harm caused to civilians or civilian property must be proportional and not "excessive in relation to the concrete and direct military advan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distinction (law)
''Distinction'' is a principle under international humanitarian law governing the laws of war, legal use of force in an armed conflict, whereby belligerents must distinguish between combatants and noncombatants (civilians). Combatant in this instance means persons entitled to directly participate in hostilities and thus are not afforded immunity from being directly targeted in situations of armed conflict. Civilian in this instance means civilians who are non-combatants. The definition of "civilian" under international humanitarian law is by no means settled, as further clarity and explanation is needed in regards to determining precisely when, how and for how long a civilian loses his or her protection from targeting. Article 51.3 of Protocol I to the Geneva Conventions explains that "Civilians shall enjoy the protection afforded by this section, unless and for such time as they take a direct part in hostilities". ''Distinction'' and ''proportionality (international humanitarian la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The International Criminal Court And The 2003 Invasion Of Iraq
A preliminary examination of possible war crimes committed by United Kingdom (UK) military forces during the invasion of Iraq in March 2003 was started by the ICC in 2005 and closed in 2006. The preliminary examination was reopened in 2014 in the light of new evidence. 2005–2006 preliminary examination The Prosecutor of the International Criminal Court (ICC) reported in February 2006 that he had received 240 communications in connection with the invasion of Iraq in March 2003 which alleged that various war crimes had been committed. The overwhelming majority of these communications came from individuals and groups within the United States and the United Kingdom. Many of these complaints concerned the British participation in the invasion, as well as the alleged responsibility for torture deaths while in detention in British-controlled areas. On February 9, 2006, the Prosecutor, Luis Moreno-Ocampo, published a letterLuis Moreno-Ocampo (9 February 2006). . Retrieved on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shimoda 1963
Shimoda may refer to: Places in Japan * Shimoda, Shizuoka, a city in Shizuoka Prefecture ** Shimoda Ropeway, an aerial tramway which climbs Mount Nesugata *Shimoda, Aomori, a town in Aomori Prefecture * Shimoda Station, a railway station in Oirase, Aomori Prefecture Other uses * Shimoda (surname), a Japanese surname * Siege of Shimoda (1590), in Shimoda, Shizuoka * Shimoda bugyō, 19th-century Japanese title equivalent to commissioner, overseer or governor * Shimoda Conference, series of unofficial dialogues between the United States and Japan *Treaty of Shimoda The Treaty of Shimoda (下田条約, ''Shimoda Jouyaku'') (formally Treaty of Commerce and Navigation between Japan and Russia 日露和親条約, ''Nichi-Ro Washin Jouyaku'') of February 7, 1855, was the first treaty between the Russian Empire, a ... (1855), between Japan and Russia See also *'' Ryuichi Shimoda v. The State'', a court case by a group of five survivors of the atomic attacks on Hiroshima and Nagasaki *'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
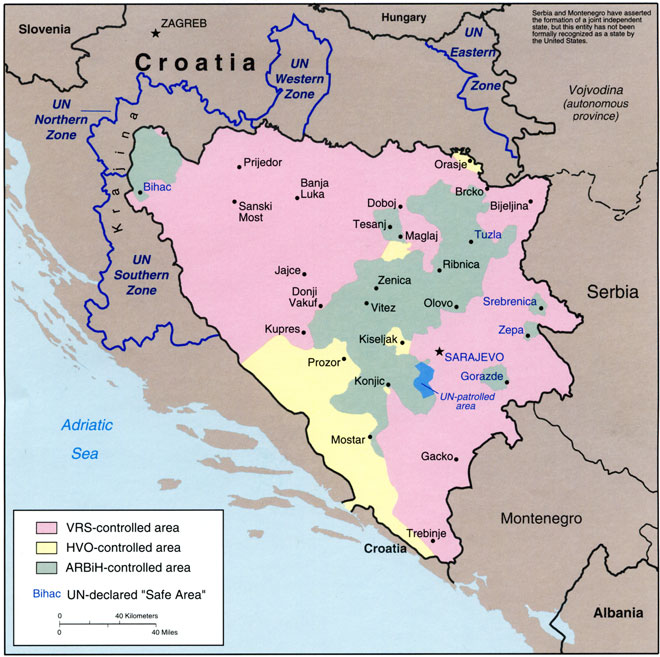
Srebrenica Massacre
The Srebrenica massacre ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Masakr u Srebrenici, Масакр у Сребреници), also known as the Srebrenica genocide ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Genocid u Srebrenici, Геноцид у Сребреници), was the July 1995 genocide, genocidal killing of more than 8,000 Bosniaks, Bosniak Islam in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Muslim men and boys in and around the town of Srebrenica, during the Bosnian War. The killings were perpetrated by units of the Bosnian Serb Army of Republika Srpska (VRS) command responsibility, under the command of Ratko Mladić. The Scorpions (paramilitary), Scorpions, a paramilitary unit from Republic of Serbia (1992–2006), Serbia, who had been part of the Serbian Interior Ministry until 1991, also participated in the massacre. Prior to the massacre, United Nations (UN) had declared the Siege of Srebrenica, besieged enclave of Srebrenica, in eastern Bosnia (region), Bosnia, a "United Nations Safe Areas, safe ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Criminal Tribunal For The Former Yugoslavia
The International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY) was a body of the United Nations that was established to prosecute the war crimes that had been committed during the Yugoslav Wars and to try their perpetrators. The tribunal was an ''ad hoc'' court located in The Hague, Netherlands. It was established by Resolution 827 of the United Nations Security Council, which was passed on 25 May 1993. It had jurisdiction over four clusters of crimes committed on the territory of the former Yugoslavia since 1991: grave breaches of the Geneva Conventions, violations of the laws or customs of war, genocide, and crimes against humanity. The maximum sentence that it could impose was life imprisonment. Various countries signed agreements with the UN to carry out custodial sentences. A total of 161 persons were indicted; the final indictments were issued in December 2004, the last of which were confirmed and unsealed in the spring of 2005. The final fugitive, Goran Hadžić, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aiding And Abetting
Aiding and abetting is a legal doctrine related to the guilt of someone who aids or abets (encourages, incites) another person in the commission of a crime (or in another's suicide). It exists in a number of different countries and generally allows a court to pronounce someone guilty for aiding and abetting in a crime even if they are not the principal offender. The words aiding, abetting and accessory are closely used but have differences. While aiding means providing support or assistance to someone, committing a crime in exchange of a commission or compensation, abetting means encouraging someone else to commit a crime. Accessory is someone who in fact assists "commission of a crime committed primarily by someone else". Canada In Canada, a person who aids or abets in the commission of a crime is treated the same as a principal offender under the criminal law. Section 21(1) of the ''Criminal Code'' provides that: :Every one is a party to an offence who ::(a) actually commits it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipal Law
Municipal law is the national, domestic, or internal law of a sovereign state and is defined in opposition to international law. Municipal law includes many levels of law: not only national law but also state, provincial, territorial, regional, or local law. The state may regard them as distinct categories of law, but international law is largely uninterested in the distinction and treats them all as one. Similarly, international law makes no distinction between the ordinary law of the state and its constitutional law Constitutional law is a body of law which defines the role, powers, and structure of different entities within a State (polity), state, namely, the executive (government), executive, the parliament or legislature, and the judiciary; as well as th .... Article 27 of the Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties from 1969 provides that if a treaty conflicts with a state's municipal law (including the state's constitution), the state is still obliged to meet its obl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome Statute
The Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court is the treaty that established the International Criminal Court (ICC). It was adopted at a diplomatic conference in Rome, Italy on 17 July 1998Michael P. Scharf (August 1998)''Results of the Rome Conference for an International Criminal Court''. The American Society of International Law. Retrieved on 31 January 2008. and it entered into force on 1 July 2002. As of November 2019, 123 states are party to the statute. Among other things, the statute establishes the court's functions, jurisdiction and structure. The Rome Statute established four core international crimes: genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and the crime of aggression. Those crimes "shall not be subject to any statute of limitations". Under the Rome Statute, the ICC can only investigate and prosecute the four core international crimes in situations where states are "unable" or "unwilling" to do so themselves; the jurisdiction of the court is complement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |