|
Milestone
A milestone is a numbered marker placed on a route such as a road, railway, railway line, canal or border, boundary. They can indicate the distance to towns, cities, and other places or landmarks like Mileage sign, mileage signs; or they can give their position on the route relative to some datum location. On roads they are typically located at the side or in a Central reservation, median or central reservation. They are alternatively known as mile markers (sometimes abbreviated MMs), mileposts or mile posts (sometimes abbreviated MPs). A "kilometric point" is a term used in Metrication, metricated areas, where distances are commonly measured in kilometres instead of miles. "Distance marker" is a generic unit-agnostic term. Milestones are installed to provide linear referencing points along the road. This can be used to reassure travellers that the proper path is being followed, and to indicate either distance travelled or the remaining distance to a destination. Such refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero Milestone
The Zero Milestone is a zero mile marker monument in Washington, D.C., erected in 1923 as the initial milestone from which all road distances in the United States would be measured. Location The monument stands just south of the White House at the north edge of the Ellipse, within President's Park. Atop the monument is a bronze 16-point compass rose with a very small worn-down pyramid at its center whose top serves as a National Geodetic Survey benchmark (HV1847). * Coordinates: ( NAD83) * Altitude: 8.382 m (27.50 ft) ( NAVD88) Description Designed by Washington architect Horace Peaslee, the monolith is about 2 feet square and about 4 feet high. It is made of precambrian Milford granite from Milford, Massachusetts, light pinkish to greenish gray, with spots of black biotite mica. The bronze disk on top of the milestone is "an adaptation from ancient portolan charts of the so-called ''wind roses'' or ''compass roses'' from the points of which extende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a imperial unit, British imperial unit and United States customary unit of length; both are based on the older English unit of Unit of length, length equal to 5,280 Foot (unit), English feet, or 1,760 yards. The statute mile was standardised between the Commonwealth of Nations and the United States by an international yard and pound, international agreement in 1959, when it was formally redefined with respect to SI units as exactly . With qualifiers, ''mile'' is also used to describe or translate a wide range of units derived from or roughly equivalent to the #Roman, Roman mile (roughly ), such as the #Nautical, nautical mile (now exactly), the #Italian, Italian mile (roughly ), and the li (unit), Chinese mile (now exactly). The Romans divided their mile into 5,000 (), but the greater importance of furlongs in the Kingdom of England#Tudor period, Elizabethan-era England meant th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Milestone
The ''Milliarium Aureum'' (; ), or the "Golden Milestone," was a monument, probably of marble or gilded bronze, erected by the Augustus, Emperor Augustus near the Temple of Saturn in the central Roman Forum, Forum of Ancient Rome. All roads were considered to begin at this monument and all mile zero, distances in the Roman Empire were measured relative to it. On it perhaps were listed all the major cities in the empire and distances to them, though the monument's precise location and inscription has remained a matter of debate among historians. According to the 19th century ecclesiastical historian Philip Schaff, the phrase "wikt:all roads lead to Rome, all roads lead to Rome" is a reference to the ''Milliarium Aureum''—the specific point to which all roads were said to lead. A marble structure speculated to be the base of the milestone is present in the Roman Forum. History According to Cassius Dio, Augustus, in his position as ''curator viarum'', erected the monument in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
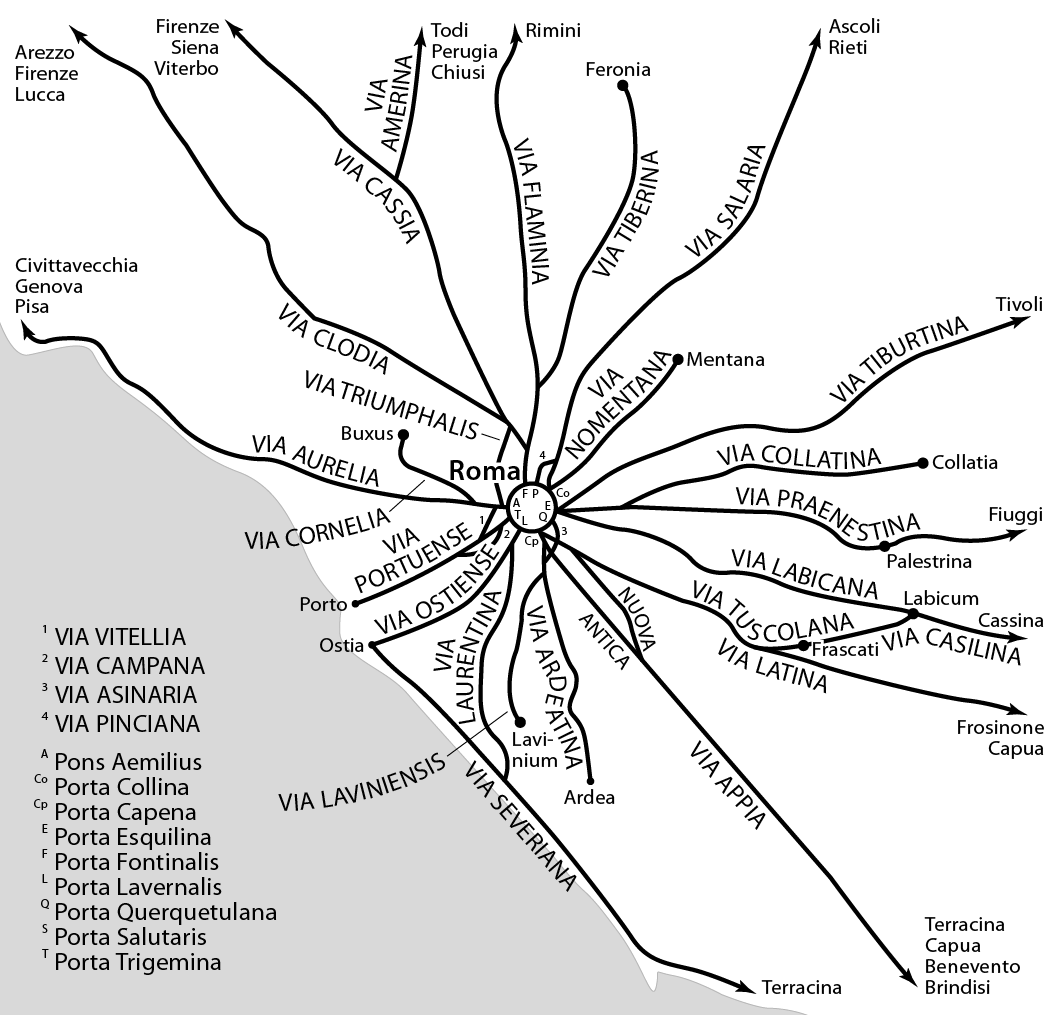
Roman Road
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, 1986. At the peak of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miliarium
A miliarium () was a cylindrical, oval or parallelepiped column placed on the edge of Roman roads to mark the distances every thousand passus (double Roman steps), that is, every mile.A passus is an ancient Roman unit of length that is 2 gradūs. One passus is . There are 1000 passus in one mille, which was sometimes referred to as a ''mille passus''. A passus was roughly the pace step of a single legionary. Today, this is equivalent to a distance of approximately 1480 meters. The stone known as the '' Milliarium Aureum'' was the point used to indicate the distance to Rome from any point in the Roman Empire. Background The columns were made of granite, marble or whatever local stone was available. Each had a cubic or square pedestal and measured between , with a diameter of . Miliarium were widely used by Roman road builders and were an important part of any road network. In those times, the distance that could be travelled each day was sometimes only a few miles. Many mili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Referencing
Linear referencing, also called linear reference system or linear referencing system (LRS), is a method of spatial referencing over linear or curvilinear elements, such as roads or rivers. In LRS, the locations of physical features are described Parametric curve, parametrically in terms of a single curvilinear coordinate, typically the distance traveled from a fixed point, such as a milestone. It is an alternative to referencing by geographic coordinates, which would involve two coordinates, latitude and longitude. Point features (e.g. a signpost) are located by a single distance value while linear features (e.g. a no-passing zone) are delimited by two distance values, corresponding to beginning and end. If the subjacent linear referencing element or route is changed, only the linear coordinates of those locations on the changed segment need to be updated. Linear referencing is suitable for management of data related to linear features like roads, railways, oil and gas transmissio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milion
The Milion ( or , ''Mílion''; ) was a marker from which all distances across the Roman Empire were measured. Erected by Septimius Severus in the 3rd century AD in the city of Byzantium, it became the zero-mile marker for the empire upon the re-founding of the city as Constantinople in 330 AD. Thereafter, it would serve as the starting-place for the measurement of distances for all the roads leading to the cities of the Eastern Roman Empire. It thus served the same function as the Golden Milestone (') in Rome's forum, erected by Augustus. The domed building of the Milion rested on four large arches and, over the centuries, it was expanded and decorated with several statues and paintings. Though it had survived the sack of Constantinople in 1204 and the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople in 1453, it disappeared by the start of the 16th century in the Ottoman era. During excavations in the 1960s, some partial fragments of the Milion were discovered under houses in the area. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mileage Sign
A mileage sign, sometimes also called a route confirmation sign or simply a distance sign in certain contexts, is a type of road sign along highways that displays the distance from the current point on a highway to a certain city, destination, or a junction to another highway. Their purpose is to inform drivers of the distance to a destination they are traveling to, as well as other destinations reachable along the route. The destinations listed can range from a short distance away, such as a few miles or kilometers, to long distances away, from several hundred or even thousands of miles or kilometers away. Unlike most road signs, mileage signs remain roughly consistent throughout the world, with the only differences being background colors on signs and the units of measurement used. In countries whose languages are written from Right-to-left script, right-to-left, such as Arabic or Hebrew, distances instead appear on the left and destinations on the right. Functionality Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metrication
Metrication or metrification is the act or process of converting to the metric system of measurement. All over the world, countries have transitioned from local and traditional Unit of measurement, units of measurement to the metric system. This process began in French Revolution, France during the 1790s, and has persistently advanced over two centuries, accumulating into 95% of the world officially only using the International System of Units, modern metric system. Nonetheless, this also highlights that certain countries and sectors are either still transitioning or have chosen not to fully adopt the metric system. Overview The process of metrication is typically initiated and overseen by a country's government, generally motivated by the necessity of establishing a uniform measurement system for effective international cooperation in fields like trade and science. Governments achieve metrication through either mandatory changes to existing units within a specified timeframe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is typically not Foliation (geology), foliated (Layered intrusion, layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphosed limestone, but its use in stonemasonry more broadly encompasses unmetamorphosed limestone. The extraction of marble is performed by quarrying. Marble production is dominated by four countries: China, Italy, India and Spain, which account for almost half of world production of marble and decorative stone. Because of its high hardness and strong wear resistance, and because it will not be deformed by temperature, marble is often used in Marble sculpture, sculpture and construction. Etymology The word "marble" derives from the Ancient Greek (), from (), "crystalline rock, shin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Technology
Ancient Greek technology developed during the 5th century BC, continuing up to and including the Roman period, and beyond. Inventions that are credited to the ancient Greeks include the gear, screw, rotary mills, bronze casting techniques, water clock, water organ, the torsion catapult, the use of steam to operate some experimental machines and toys, and a chart to find prime numbers. Many of these inventions occurred late in the Greek period, often inspired by the need to improve weapons and tactics in war. However, peaceful uses are shown by their early development of the watermill, a device which pointed to further exploitation on a large scale under the Romans. They developed surveying and mathematics to an advanced state, and many of their technical advances were published by philosophers, like Archimedes and Heron. Water technology Some fields that were encompassed in the area of water resources (mainly for urban use) included groundwater exploitation, construction of aqued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |