|
Milecovirus
''Letovirinae'' is a subfamily of viruses within the family ''Coronaviridae'', where it is the only subfamily besides the more diverse ''Orthocoronavirinae'' (coronaviruses). ''Letovirinae'' contains one accepted genus, ''Alphaletovirus'', which contains one accepted subgenus, ''Milecovirus'', which contains one accepted species, ''Microhyla letovirus 1'' (MLeV). This species was discovered in 2018 and is hosted by the ornate chorus frog (''Microhyla fissipes''). Other, as yet unaccepted species in the ''Letovirinae'' have been discovered in Pacific salmon ('' Oncorhynchus''), and in Murray River carp (Cyprinus ''Cyprinus'' is the genus of typical carps in family Cyprinidae. Most species in the genus are of East Asia origin with only the common carp (''C. carpio'') in Western Asia and Europe; this invasive species has also been introduced to many othe ...). References External links * Coronaviridae Virus subfamilies Virus genera {{Virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronaviridae
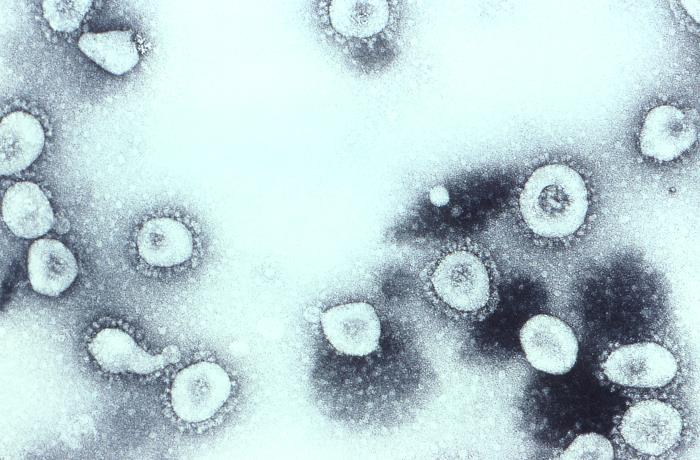
''Coronaviridae'' is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect amphibians, birds, and mammals. The group includes the subfamilies ''Letovirinae'' and ''Orthocoronavirinae;'' the members of the latter are known as coronaviruses. The viral genome is 26–32 kilobases in length. The particles are typically decorated with large (~20 nm), club- or petal-shaped surface projections (the "peplomers" or "spikes"), which in electron micrographs of spherical particles create an image reminiscent of the solar corona. Virology The 5' and 3' ends of the genome have a cap and poly(A) tract, respectively. The viral envelope, obtained by budding through membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) or Golgi apparatus, invariably contains two virus-specified glycoprotein species, known as the spike (S) and membrane (M) proteins. The spike protein makes up the large surface projections (sometimes known as peplomers), while the membrane protein is a triple-spanning t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end subfamily botanical names with "-oideae", and zoological names with "-inae". See also * International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants * International Code of Zoological Nomenclature * Rank (botany) * Rank (zoology) In biological classification, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms (a taxon) in an ancestral or hereditary hierarchy. A common system consists of species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain. While ... Sources {{biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthocoronavirinae
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold (which is also caused by other viruses, predominantly rhinoviruses), while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19, which is causing the ongoing pandemic. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis. Coronaviruses constitute the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'', in the family ''Coronaviridae'', order '' Nidovirales'' and realm '' Riboviria''. They are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and a nucleocapsid of helical symmetry. The genome size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 26 to 32 kilobases, one of the largest among RNA viruses. They have characteristic club-shaped spikes that project from their surface, which in el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microhyla Fissipes
''Microhyla fissipes'' (commonly known as the ornate chorus frog) is a microhylid frog from East and Southeast Asia, from southern and central China and Taiwan to the Malay Peninsula. It was previously considered to be the same species as '' Microhyla ornata'' of South Asia; thus the common names ornate narrow-mouthed frog or ornamented pygmy frog can refer to either species. Description As microhylids in general, ''Microhyla fissipes'' is a small frog: males reach and females in snout-vent length. Tadpoles are correspondingly small, about in total length. Habitat and behaviour ''Microhyla fissipes'' is a common and widespread species. It can be found in many habitat types including lowland scrub forests, grassland, agricultural land, pastureland and urban areas. Sub- fossorial in habit, it is also found in forest floor leaf-litter. It is mostly nocturnal, only active diurnally during the rainy season. It breeds in rain pools and other bodies of still water. It tolerates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncorhynchus
''Oncorhynchus'' is a genus of fish in the family Salmonidae; it contains the Pacific salmon and Pacific trout. The name of the genus is derived from the Greek ὄγκος (ónkos, “lump, bend”) + ῥύγχος (rhúnkhos, “snout”), in reference to the hooked snout (the "kype") that the males develop during mating season. Range Salmon and trout with native ranges in waters draining to the Pacific Ocean are members of the genus. Their range extends from Beringia southwards, roughly to Taiwan in the west and Mexico to the east. In North America, some subspecies of '' O. clarkii'' are native in the Rocky Mountains and Great Basin, while others are native to the Rio Grande and western tributaries of the Mississippi River Basin which drain to the Gulf of Mexico, rather than to the Pacific. Several species of ''Oncorhynchus'' have been introduced into non-native waters around the globe, establishing self-sustaining wild populations. The six Pacific salmons of ''Oncorhync ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprinus Carpio Carpio
''Cyprinus carpio carpio'' is a subspecies of the common carp that is commonly found in Europe. They are native to much of Europe (notably the Danube and Volga Rivers) and can also be found in the Caucasus and Central Asia. Mitochondrial DNA analysis shows a difference between ''C. carpio carpio'' and '' Carpio carpio haematopterus''. They are omnivorous in nature and feed on mollusks, insects, crustaceans and seeds. Though dark in color, there are some wild caught specimens which are colored orange (maybe domesticated ones that are only released into the rivers). This subspecies has also been domesticated in European ponds for hundreds of years. They are considered as an invasive species in the state of Washington Washington commonly refers to: * Washington (state), United States * Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States ** A metonym for the federal government of the United States ** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ... and fishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus Subfamilies
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |