|
Mikhail Skorodumov
Mikhail Fedorovich Skorodumov (russian: Михаил Федорович Скородумов; 189215 November 1963, Los Angeles) was a Russian general who participated in World War I, the White movement, and founded the Nazi-allied Russian Corps in Serbia during World War II. Skorodumov was born in 1892. He graduated the 1st Cadet Corps and the Pavlovsk Military Academy in 1912, as a sub-lieutenant of the Pavlovsk detachment. In 1914 with his detachment he was sent to the front. He was awarded the St. Vladimir order for bravery in battle, during which he was heavily wounded and consequently placed off duty. Skorodumov lobbied strongly to return to the front, and in 1915 was taken prisoner by the Germans. He unsuccessfully tried to escape three times, and after seven months of imprisonment returned to St. Petersburg in a prisoner exchange agreement (thanks partly to the lobbying of Grand Duchess Maria Pavlovna). He was awarded the Cross of St. George for bravery. In the wake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyotr Nikolayevich Wrangel
Baron Pyotr Nikolayevich Wrangel (russian: Пётр Никола́евич барон Вра́нгель, translit=Pëtr Nikoláevič Vrángel', p=ˈvranɡʲɪlʲ, german: Freiherr Peter Nikolaus von Wrangel; April 25, 1928), also known by his nickname the Black Baron, was a Russians, Russian officer of Baltic German origin in the Imperial Russian Army. During the later stages of the Russian Civil War, he was commanding general of the anti-Bolshevik White movement, White Army in Southern Russia. After his side lost the civil war in 1920, he left Russia. He was known as one of the most prominent exiled White émigrés and military dictator of South Russia (1919–1920), South Russia (as commander in chief). Family Wrangel was born in Zarasai, Novalexandrovsk, Kovno Governorate in the Russian Empire (now Zarasai, Lithuania) as the son of Baron (1847–1923) and Maria Dimitrievna Demetieva-Maikova (1856–1944). The Baltic German nobility, Baltic German noble Wrangel family was part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoemaking
Shoemaking is the process of making footwear. Originally, shoes were made one at a time by hand, often by groups of shoemakers, or cobblers (also known as '' cordwainers''). In the 18th century, dozens or even hundreds of masters, journeymen and apprentices (both men and women) would work together in a shop, dividing up the work into individual tasks. A customer could come into a shop, be individually measured, and return to pick up their new shoes in as little as a day. Everyone needed shoes, and the median price for a pair was about one day’s wages for an average journeyman. The shoemaking trade flourished in the eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries but began to be affected by industrialization in the later nineteenth century. Traditional handicraft shoemaking has now been largely superseded in volume of shoes produced by industrial mass production of footwear, but not necessarily in quality, attention to detail, or craftsmanship. Today, most shoes are made on a volum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boris Shteifon
Boris Aleksandrovich Shteifon (russian: Борис Александрович Штейфон; 6 December 1881 – 30 April 1945) was a general lieutenant in the Imperial Russian Army, who subsequently served as a general in the Russian anti-communist White army, and as the leader of the Nazi-allied Russian Corps in the German occupied territory of Serbia during World War II. Biography Boris Shteifon was born in 1881 in Kharkov (now in Ukraine). His father was a Jewish merchant converted to Orthodox Christianity, his mother was the daughter of a Russian Orthodox deacon. He graduated from the Chuguyivske Junker Infantry School, one of the premier schools of the Imperial Russian Army, and went to serve as a second lieutenant in the 124th Infantry Regiment based at Voronezh. He first saw combat in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905, during which he was injured with a concussion. He was also awarded for bravery and excellence five times, receiving the Order of St. Vladimir alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe. The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one organisation. On 20 April 1934, oversight of the Gestapo passed to the head of the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS), Heinrich Himmler, who was also appointed Chief of German Police by Hitler in 1936. Instead of being exclusively a Prussian state agency, the Gestapo became a national one as a sub-office of the (SiPo; Security Police). From 27 September 1939, it was administered by the Reich Security Main Office (RSHA). It became known as (Dept) 4 of the RSHA and was considered a sister organisation to the (SD; Security Service). During World War II, the Gestapo played a key role in the Holocaust. After the war ended, the Gestapo was declared a criminal organisation by the International Military Tribunal (IMT) at the Nuremberg trials. History After Adol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Liberation Movement
The Russian Liberation Movement (russian: Русское Освободительное Движение) was a movement in the Soviet Union that sought to create an anti-communist armed force during the Second World War that would topple Joseph Stalin's regime. The movement included Russians and other nationalities that lived in the Soviet Union and was then referred to as the Liberation Movement of the Peoples of Russia (russian: Освободительное Движение Народов России, links=no). History The movement began spontaneously at the outbreak of the Soviet-German War in June 1941. White Russian émigrés, who were veterans of the White movement, began seeking sympathetic ears in the German Armed Forces (the Wehrmacht) and trying to find a means of creating armed units that would be used on the Eastern Front, such as the Russian Corps. Meanwhile, some captured Soviet officers switched sides, including General Andrey Vlasov. The German propaganda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Front (World War II)
The Eastern Front of World War II was a Theater (warfare), theatre of conflict between the European Axis powers against the Soviet Union (USSR), Polish Armed Forces in the East, Poland and other Allies of World War II, Allies, which encompassed Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, Northeast Europe (Baltic states, Baltics), and Southeast Europe (Balkans) from 22 June 1941 to 9 May 1945. It was known as the Great Patriotic War (term), Great Patriotic War in the Soviet Union – and still is in some of its successor states, while almost everywhere else it has been called the ''Eastern Front''. In present-day German and Ukrainian historiography the name German-Soviet War is typically used. The battles on the Eastern Front of the Second World War constituted the largest military confrontation in history. They were characterised by unprecedented ferocity and brutality, wholesale destruction, mass deportations, and immense loss of life due to combat, starvation, expos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partisans (Yugoslavia)
The Yugoslav Partisans,Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian, Slovene: , or the National Liberation Army, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Narodnooslobodilačka vojska (NOV), Народноослободилачка војска (НОВ); mk, Народноослободителна војска (НОВ); sl, Narodnoosvobodilna vojska (NOV) officially the National Liberation Army and Partisan Detachments of Yugoslavia, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Narodnooslobodilačka vojska i partizanski odredi Jugoslavije (NOV i POJ), Народноослободилачка војска и партизански одреди Југославије (НОВ и ПОЈ); mk, Народноослободителна војска и партизански одреди на Југославија (НОВ и ПОЈ); sl, Narodnoosvobodilna vojska in partizanski odredi Jugoslavije (NOV in POJ) was the communist-led anti-fascist resistance to the Axis powers (chiefly Germany) in occupied Yugoslavia during World War II. Led by Josip Broz Tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Emigre
White is the lightness, lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully diffuse reflection, reflect and scattering, scatter all the visible spectrum, visible wavelengths of light. White on television and computer screens is created by a mixture of red, blue, and green light. The color white can be given with white pigments, especially titanium dioxide. In ancient Egypt and ancient Rome, priestesses wore white as a symbol of purity, and Romans wore white togas as symbols of citizenship. In the Middle Ages and Renaissance a white unicorn symbolized chastity, and a white lamb sacrifice and purity. It was the royal color of the kings of France, and of the monarchist movement that opposed the Bolsheviks during the Russian Civil War (1917–1922). Greek and Roman temples were faced with white marble, and beginning in the 18th century, with the advent of neoclassical archite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast Europe, Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Srba, Hrvata i Slovenaca, Краљевина Срба, Хрвата и Словенаца; sl, Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev), but the term "Yugoslavia" (literally "Land of South Slavs") was its colloquial name due to its origins."Kraljevina Jugoslavija! Novi naziv naše države. No, mi smo itak med seboj vedno dejali Jugoslavija, četudi je bilo na vseh uradnih listih Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev. In tudi drugi narodi, kakor Nemci in Francozi, so pisali že prej v svojih listih mnogo o Jugoslaviji. 3. oktobra, ko je kralj Aleksander podpisal "Zakon o nazivu in razdelitvi kraljevine n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Kutepov
Alexander Pavlovich Kutepov ( rus, Алекса́ндр Па́влович Куте́пов; 28 September 1882 in Cherepovets, Novgorod Governorate, Russian Empire – 26 January 1930 in Paris, France) served as an officer in the anti-communist Volunteer Army during the Russian Civil War of 1917-1923. From 1928 to 1930 he chaired the Russian All-Military Union (ROVS). Зинкевич М. МГенерал Александр Павлович Кутепов- "В течение трёх лет, с конца 1917 и по ноябрь 1920 года, на наших глазах полковник Кутепов вырос в незаурядного начальника крупных войсковых соединений и администратора. ..После смерти генерала, барона П.Н. Врангеля и Великого Князя Николая Николаевича генерал Кутепов стал во главе Русского Общ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
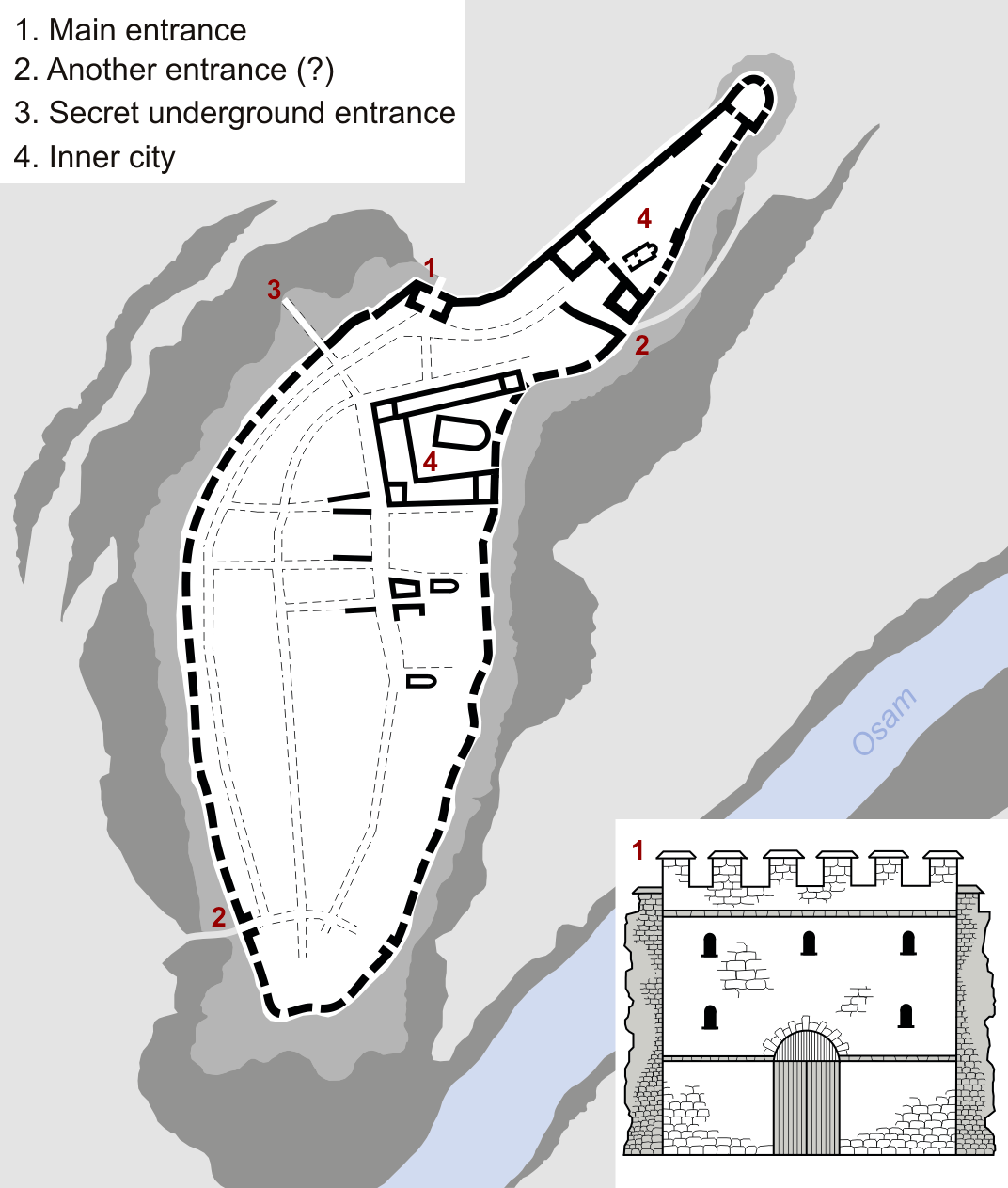
Lovech
Lovech ( bg, Ловеч, Lovech, ) is a List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, city in north-central Bulgaria. It is the administrative centre of the Lovech Province and of the subordinate Lovech Municipality. The city is located about northeast from the capital city of Sofia. Near Lovech are the towns of Pleven, Troyan and Teteven. Name The name is possibly derived from the Slavic root ''lov'', "hunting" + the Slavic suffix ''-ech''. Geography Lovech is situated in the Balkan Mountains, Forebalkan area of northern Bulgaria, on both sides of the river Osam, and unifies both mountainous and plain relief. The eastern part of the town is surrounded by a 250 m high plateau, where the largest park in Lovech, ''Stratesh'', is located, and the southwestern part is surrounded by the hills ''Hisarya'' and ''Bash Bunar''. In the northwest the relief gradually changes to the plains of the neighbouring Pleven Province. The average altitude of Lovech is about 200 m above mean sea level. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |