|
Mikhail Kazakov
Mikhail Ilyich Kazakov (; – 25 December 1979) was an army general of the Soviet Army and a Hero of the Soviet Union. After serving as an ordinary soldier in the final stages of the Russian Civil War, Kazakov became a political commissar during the 1920s but shifted over to command and staff positions from the mid-1920s. He rose to chief of staff the Central Asian Military District by the time Operation Barbarossa began, and 1942 and 1943 served as chief of staff and deputy commander of fronts, with a stint as commander of the 69th Army during the Third Battle of Kharkov. Kazakov commanded the 10th Guards Army from early 1944 as it advanced into the Baltic states and blockaded the Courland Pocket. Postwar, he rose to command of the Southern Group of Forces and the Leningrad Military District, ending his career as first deputy chief of the General Staff. Early life and Russian Civil War A Russian, Kazakov was born to a peasant family on 9 October 1901 in the village of Veli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velikusha
Velikusha (russian: Великуша) is a rural locality (a village) in Kichmengskoye Rural Settlement, Kichmengsko-Gorodetsky District, Vologda Oblast, Russia. The population was 36 as of 2002. There are 2 streets. Geography Velikusha is located 32 km southwest of Kichmengsky Gorodok Kichmengsky Gorodok (russian: Кичменгский Городок) is a rural locality (a '' selo'') and the administrative center of Kichmengsko-Gorodetsky District, Vologda Oblast, Russia, located on the left bank of the Yug River, at its conf ... (the district's administrative centre) by road. Yelovino is the nearest rural locality. References Rural localities in Kichmengsko-Gorodetsky District {{KichmengskoGorodetsky-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Kazakov
Mikhail Ilyich Kazakov (; – 25 December 1979) was an army general of the Soviet Army and a Hero of the Soviet Union. After serving as an ordinary soldier in the final stages of the Russian Civil War, Kazakov became a political commissar during the 1920s but shifted over to command and staff positions from the mid-1920s. He rose to chief of staff the Central Asian Military District by the time Operation Barbarossa began, and 1942 and 1943 served as chief of staff and deputy commander of fronts, with a stint as commander of the 69th Army during the Third Battle of Kharkov. Kazakov commanded the 10th Guards Army from early 1944 as it advanced into the Baltic states and blockaded the Courland Pocket. Postwar, he rose to command of the Southern Group of Forces and the Leningrad Military District, ending his career as first deputy chief of the General Staff. Early life and Russian Civil War A Russian, Kazakov was born to a peasant family on 9 October 1901 in the village of Veli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
46th Rifle Division (RSFSR)
The 46th Rifle Division was a rifle division of the Red Army. History The division was formed in 1923 as a territorial unit, assigned to the 14th Rifle Corps of the Ukrainian Military District. Based in Kiev, it included the 136th, 137th, and 138th Rifle Regiments. Its regiments received the honorifics Pre-Dnieper, Kiev, and Pereyaslavl, respectively, by 1930. Reorganized as a cadre unit in 1931, it became part of the Kiev Military District when the Ukrainian Military District was split on 17 May 1935. The division transferred to the Zhitomir Army Group of the Kiev Special Military District on 26 July 1938 during another reorganization. The 46th was soon transferred to Irkutsk, assigned to the Transbaikal Military District. It was reorganized under peacetime tables of organization and equipment with an authorized strength of 6,000 personnel in April 1940. When Operation Barbarossa, the German invasion of the Soviet Union, began on 22 June 1941, the division was assigned to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Front (RSFSR)
The Southern Front () was a front of the Red Army during the Russian Civil War, formed twice. The front was first formed in September 1918, fighting against the White Don Cossacks and the Volunteer Army in southeastern Russia. It advanced into the North Caucasus in January 1919, but was forced to retreat from eastern Ukraine by an attack of the Armed Forces of South Russia (AFSR) in May and June. The Southern Front then retreated in the face of the latter's Moscow offensive, launching a counterattack in August that advanced into northeastern Ukraine and to the Don River. With its rear disrupted by White cavalry raids, the front retreated north in September and early October, moving as far as Orel. In October the front launched a counteroffensive, defeating the AFSR, leading to the latter's precipitate retreat to the Black Sea by early January. The front was redesignated the Southwestern Front on January 10, 1920, at the beginning of the Red advance into the North Caucasus. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkhangelsk
Arkhangelsk (, ; rus, Арха́нгельск, p=ɐrˈxanɡʲɪlʲsk), also known in English as Archangel and Archangelsk, is a city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina near its mouth into the White Sea. The city spreads for over along the banks of the river and numerous islands of its delta. Arkhangelsk was the chief seaport of medieval and early modern Russia until 1703, when it was replaced by the newly-founded Saint Petersburg. A railway runs from Arkhangelsk to Moscow via Vologda and Yaroslavl, and air travel is served by the Talagi Airport and the smaller Vaskovo Airport. As of the 2021 Census, the city's population was 301,199. Coat of arms The arms of the city display the Archangel Michael in the act of defeating the Devil. Legend states that this victory took place near where the city stands, hence its name, and that Michael still stands watch over the city to prevent the Devil's return. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutionary Committee (Soviet Union)
{{no footnotes, date=May 2016A revolutionary committee or revkom (russian: Революционный комитет, ревком) were Bolshevik-led organizations in Soviet Russia and other Soviet republics established to serve as provisional governments and temporary Soviet administrations in territories under the control of the Red Army in 1918–1920, during the Russian Civil War and foreign military intervention. The forms of their work were inherited from Military Revolutionary Committees of the Russian Revolution of 1917. The name was borrowed from the history of the French Revolution, where ''comités révolutionnaires'' were created, the superior ones being the Committee of Public Safety and Committee of General Security. Revolutionary committees were often created in anticipation of the advances of the Red Army. In some cases they were created in places remote from the intended place of action, as was the case with the Provisional Polish Revolutionary Committee. In oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key moment in the larger Russian Revolution of 1917–1923. It was the second revolutionary change of government in Russia in 1917. It took place through an armed insurrection in Petrograd (now Saint Petersburg) on . It was the precipitating event of the Russian Civil War. The October Revolution followed and capitalized on the February Revolution earlier that year, which had overthrown the Tsarist autocracy, resulting in a liberal provisional government. The provisional government had taken power after being proclaimed by Grand Duke Michael, Tsar Nicholas II's younger brother, who declined to take power after the Tsar stepped down. During this time, urban workers began to organize into councils ( soviets) wherein revolutionaries criticized t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet General Staff
The General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation (russian: Генеральный штаб Вооружённых сил Российской Федерации, General'nyy shtab Vooruzhonnykh sil Rossiyskoy Federatsii) is the military staff of the Russian Armed Forces. It is the central organ of the military command of the Armed Forces Administration and oversees operational command of the armed forces under the Russian Ministry of Defence. As of 2012, the Chief of the General Staff is Army General Valery Gerasimov and since 2014, the First Deputy Chief of the General Staff is Colonel General Nikolai Bogdanovsky. The General Staff Building is located in Moscow on Znamenka Street in the Arbat District. Together with the Main Building of the Ministry of Defense and several Staff directorate office buildings nearby, it forms the so-called "Arbat military district" as it is often referred to among the military personnel to outline the highest supreme command of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
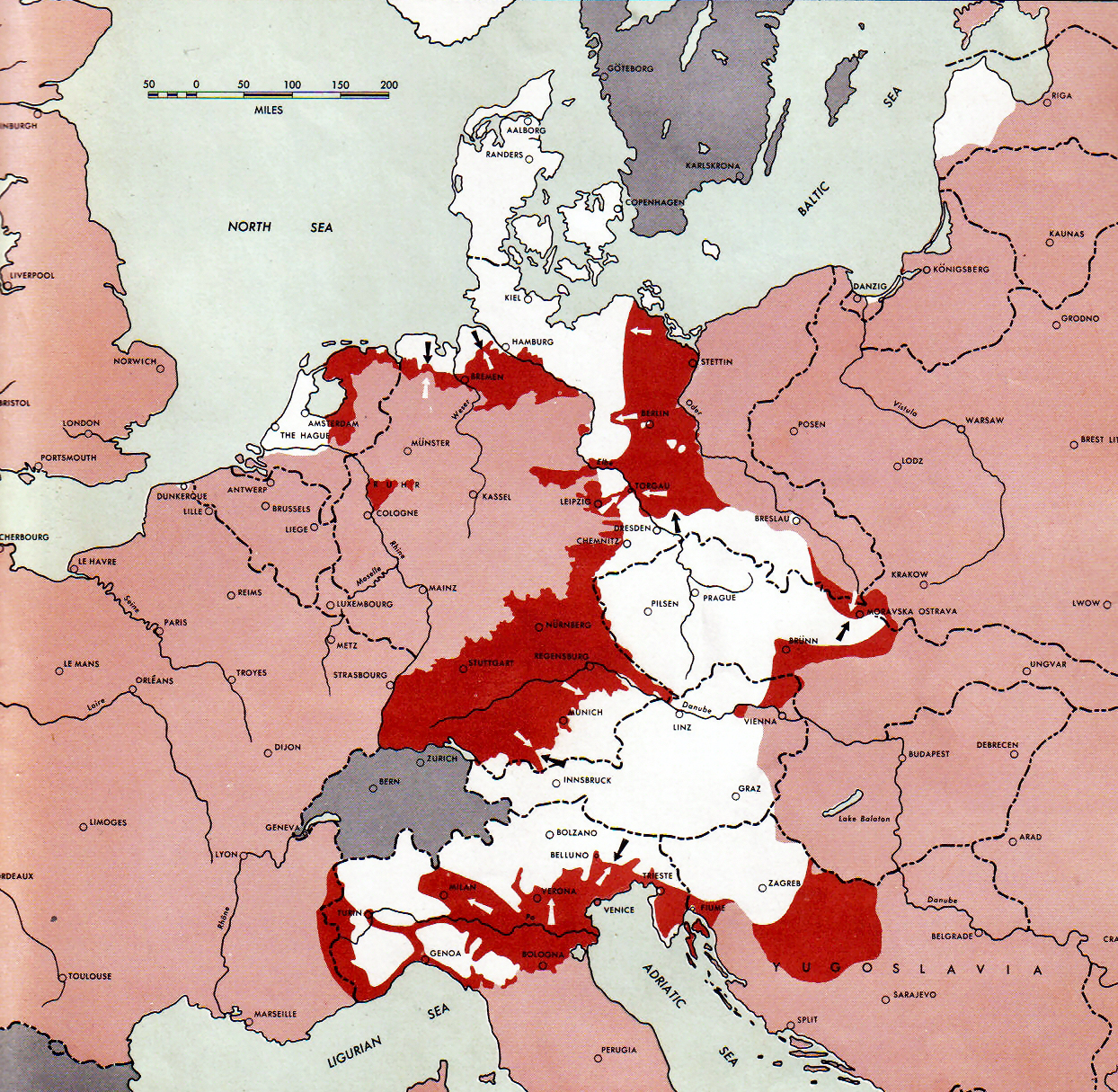
Courland Pocket
The Courland Pocket (Blockade of the Courland army group), (german: Kurland-Kessel)/german: Kurland-Brückenkopf (Courland Bridgehead), lv, Kurzemes katls (Courland Cauldron) or ''Kurzemes cietoksnis'' (Courland Fortress)., group=lower-alpha was an area of the Courland Peninsula where Army Group North of Nazi Germany and the Reichskommissariat Ostland were cut off and surrounded by the Red Army for almost a year, lasting from July 1944 until 10 May 1945. The pocket was created during the Red Army's Baltic Offensive, when forces of the 1st Baltic Front reached the Baltic Sea near Memel (Klaipėda) during its lesser Memel Offensive Operation phases. This action isolated the German Army Group North from the rest of the German forces, having been pushed from the south by the Red Army, standing in a front between Tukums and Libau in Latvia, with the Baltic Sea in the West, the Irbe Strait in the North and the Gulf of Riga in the East behind the Germans. Renamed Army Group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
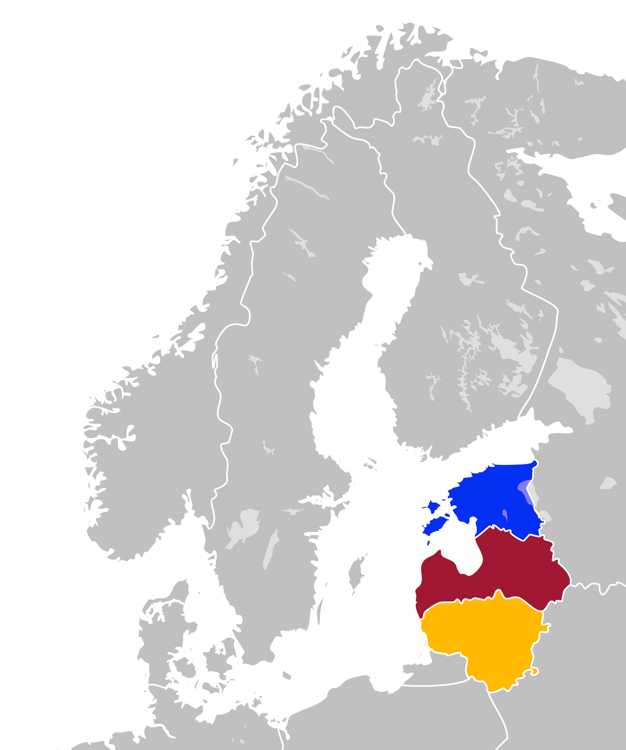
Baltic States
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics. All three Baltic countries are classified as high-income economies by the World Bank and maintain a very high Human Development Index. The three governments engage in intergovernmental and parliamentary cooperation. There is also frequent cooperation in foreign and security policy, defence, energy, and transportation. The term "Baltic states" ("countries", "nations", or similar) cannot be used unambiguously in the context of cultural areas, national identity, or language. While the majori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Battle Of Kharkov
The Third Battle of Kharkov was a series of battles on the Eastern Front of World War II, undertaken by Army Group South of Nazi Germany against the Soviet Red Army, around the city of Kharkov between 19 February and 15 March 1943. Known to the German side as the Donets Campaign, and in the Soviet Union as the Donbas and Kharkov operations, the German counterstrike led to the recapture of the cities of Kharkov and Belgorod. As the German 6th Army was encircled in the Battle of Stalingrad, the Red Army undertook a series of wider attacks against the rest of Army Group South. These culminated on 2 January 1943 when the Red Army launched Operation Star and Operation Gallop, which between January and early February broke German defenses and led to the Soviet recapture of Kharkov, Belgorod, Kursk, as well as Voroshilovgrad and Izium. The Soviet victories caused participating Soviet units to over-extend themselves. Freed on 2 February by the surrender of the German 6th Army, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after Frederick Barbarossa ("red beard"), a 12th-century Holy Roman emperor and German king, put into action Nazi Germany's ideological goal of conquering the western Soviet Union to repopulate it with Germans. The German aimed to use some of the conquered people as forced labour for the Axis war effort while acquiring the oil reserves of the Caucasus as well as the agricultural resources of various Soviet territories. Their ultimate goal was to create more (living space) for Germany, and the eventual extermination of the indigenous Slavic peoples by mass deportation to Siberia, Germanisation, enslavement, and genocide. In the two years leading up to the invasion, Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union signed political and economic pacts fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)