|
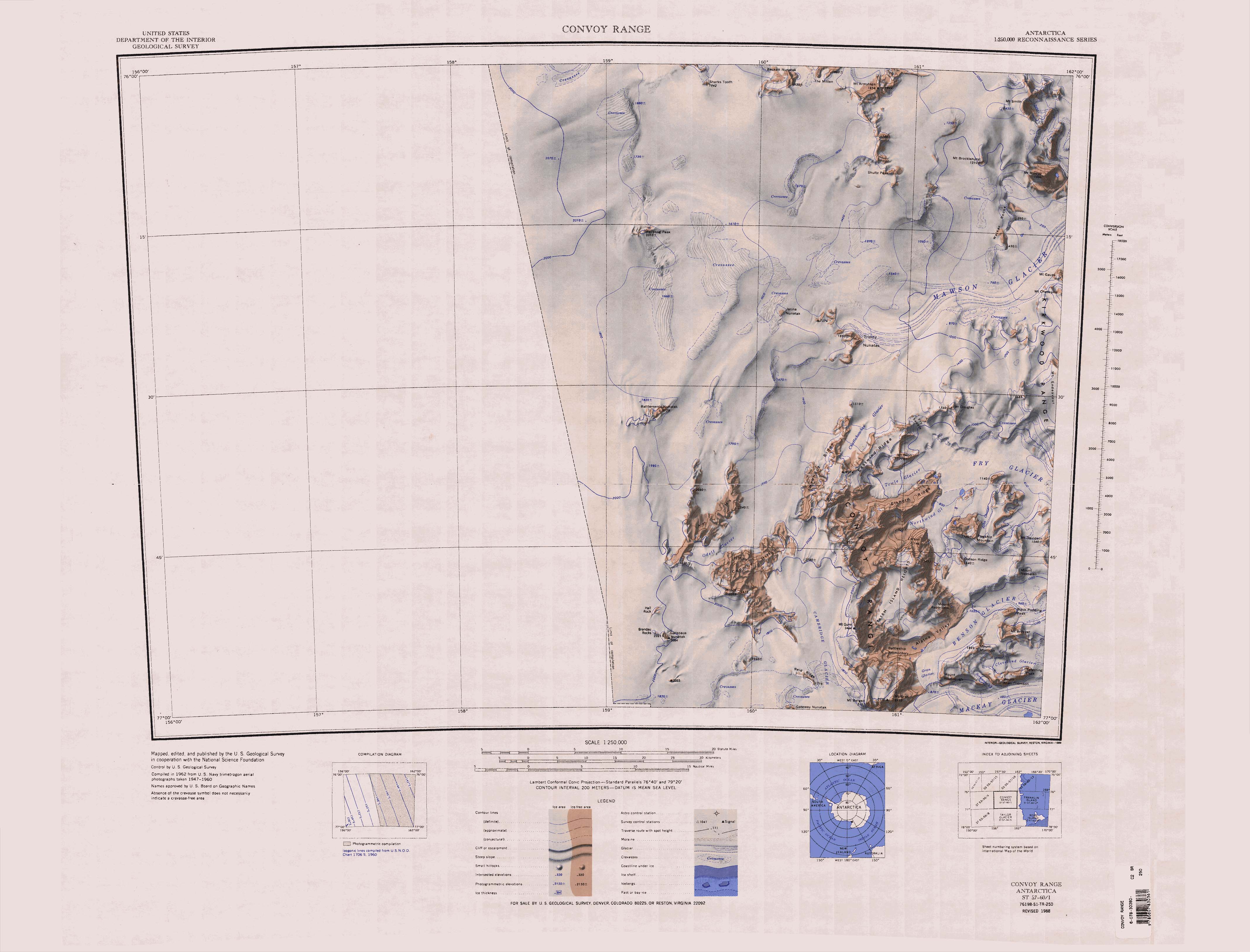
Midship Glacier
Midship Glacier () is a broad flat glacier filling the bulk of Alatna Valley and having its origin on the slopes of Mount Morrison (Victoria Land), Mount Morrison to the south, in the Convoy Range, Victoria Land, Antarctica. From 1957 this ice body was considered part of Benson Glacier, however, it was determined by a 1989–90 New Zealand Antarctic Research Programme field party (led by Trevor Chinn (glaciologist), Trevor Chinn) that although it abuts against the main Benson Glacier at Jetsam Moraine, this glacier makes no contribution of ice to the Benson as its dominant ice flow is northward across its length. With the identification of Midship Glacier as a distinct feature, the application of Benson Glacier has been restricted to the ice flowing eastward from Flight Deck Névé to the terminus in Granite Harbour. The name was approved by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1993 as recommended by the New Zealand Geographic Board. References Glaciers of Victoria L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as Crevasse, crevasses and Serac, seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alatna Valley
Alatna Valley (sometimes incorrectly spelled ''Atlanta Valley'') is an ice-free valley lying 4 miles (6 km) north of Mount Gran and trending east-northeast for about 10 miles (16 km) along the southeast side of the Convoy Range. It is one of the northernmost of the McMurdo Dry Valleys. Parker Calkin, U.S. geologist, made stratigraphic studies in the valley during the 1960–1961 season. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1963 for the gasoline tanker which participated in Operation Deep Freeze Operation Deep Freeze (OpDFrz or ODF) is codename for a series of United States missions to Antarctica, beginning with "Operation Deep Freeze I" in 1955–56, followed by "Operation Deep Freeze II", "Operation Deep Freeze III", and so on. (There w ... 1958–1959 and 1959–1960, and in keeping with other ship names in the Convoy Range. References * Valleys of Victoria Land McMurdo Dry Valleys {{McMurdoDryValleys-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Morrison (Victoria Land)
Benson Glacier () is a glacier about long, draining the east part of Flight Deck Névé and continuing east between Fry Glacier and Mackay Glacier into the north part of Granite Harbour where it forms a floating tongue. Exploration and naming Benson Glacier was mapped in 1957 by the New Zealand Northern Survey Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–1958), and indicated as a somewhat longer glacier including the present Midship Glacier. It was named by the party after Noel Benson, formerly professor of geology at the University of Otago, New Zealand, whose publications include a major contribution to the petrology of Victoria Land. Location The Benson Glacier forms in the northeast end of Alatna Valley in the Convoy Range and flows northeast to the south of Mount Razorback, Dotson Ridge, Flagship Mountain, Mount Davidson (Antarctica) and Mount Nesbelan, which surround Flight Deck Névé. To the south the Benson Glacier flows past Mount Morrison, Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convoy Range
Convoy Range () is a broad mountain range in Antarctica. Much of the range has a nearly flat plateau-like summit, extending south from the Fry Saddle and ending at Mackay Glacier. The range has steep cliffs on its east side, but it slopes gently into the Cambridge Glacier on the western side. The New Zealand Northern Survey Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58) worked in this area in 1957. The party named the range for the main convoy into McMurdo Sound in the 1956–57 season, with the names of the various vessels being used for features in the range. Features Taff Y Bryn () is a ridgelike summit capped by dolerite (about 1,600 m), situated 1 nautical mile (1.9 km) west of Flagship Mountain in the Convoy Range. It is named after the River Taff in Wales, the toponym in Welsh literally means "Hill of the Taff." It was named by the 1976–77 Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) led by Christopher J. Burgess. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. The region includes ranges of the Transantarctic Mountains and the McMurdo Dry Valleys (the highest point being Mount Abbott in the Northern Foothills), and the flatlands known as the Labyrinth. The Mount Melbourne is an active volcano in Victoria Land. Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benson Glacier
Benson Glacier () is a glacier about long, draining the east part of Flight Deck Névé and continuing east between Fry Glacier and Mackay Glacier into the north part of Granite Harbour where it forms a floating tongue. Exploration and naming Benson Glacier was mapped in 1957 by the New Zealand Northern Survey Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–1958), and indicated as a somewhat longer glacier including the present Midship Glacier. It was named by the party after Noel Benson, formerly professor of geology at the University of Otago, New Zealand, whose publications include a major contribution to the petrology of Victoria Land. Location The Benson Glacier forms in the northeast end of Alatna Valley in the Convoy Range and flows northeast to the south of Mount Razorback, Dotson Ridge, Flagship Mountain, Mount Davidson (Antarctica) and Mount Nesbelan, which surround Flight Deck Névé. To the south the Benson Glacier flows past Mount Morrison, Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Antarctic Research Programme
The New Zealand Antarctic Research Programme (NZARP) was a research program that operated a permanent research facility in Antarctica from 1959 to 1996. It was created by the Geophysics Division of New Zealand's Department of Scientific and Industrial Research (New Zealand), Department of Scientific and Industrial Research (DSIR), originally based in Wellington. The programme promoted research in geochemistry, zoology, geology, botany, meteorology, and limnology. History NZARP began as a proposal by the New Zealand government, in 1953, for a research base in Antarctica. Its mission was to provide support for a variety of scientific fieldwork in Antarctica. Members worked as researchers, assistants, tour guides, operators, and administrators to Scott Base. Ground was broken for Scott Base on 10 January 1957. Assembly of the base began 12 January, conducted by the eight men who first assembled the base in Wellington, and was completed by 20 January. In 1959, the NZARP was establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trevor Chinn (glaciologist)
Trevor James Hill Chinn (9 August 1937 – 20 December 2018) was a New Zealand glaciologist, who conducted extensive surveys of the glaciers of New Zealand's Southern Alps. Early life Growing up near the town of Te Taho (about eight kilometers from Whataroa) in South Westland, near the Franz Josef Glacier, Trevor Chinn was fascinated by water and glaciers at an early age. While at the University of Canterbury Chinn joined the tramping club, and graduated with a BSc in geology. Trevor was the second of four children to Alfred and Myrtle (née Sweney) Chinn. Career During the early 1960s Chinn worked for the North Canterbury Catchment Board, near Christchurch. In his role as field hydrologist, Chinn quickly learned the elements of river gauging and meticulous record keeping. Following a training period with the Ministry of Works, Chinn was invited to apply for a field role carrying out snow surveys on the Tasman Glacier and in the wider Mackenzie Basin. This new job was with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jetsam Moraine
Benson Glacier () is a glacier about long, draining the east part of Flight Deck Névé and continuing east between Fry Glacier and Mackay Glacier into the north part of Granite Harbour where it forms a floating tongue. Exploration and naming Benson Glacier was mapped in 1957 by the New Zealand Northern Survey Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–1958), and indicated as a somewhat longer glacier including the present Midship Glacier. It was named by the party after Noel Benson, formerly professor of geology at the University of Otago, New Zealand, whose publications include a major contribution to the petrology of Victoria Land. Location The Benson Glacier forms in the northeast end of Alatna Valley in the Convoy Range and flows northeast to the south of Mount Razorback, Dotson Ridge, Flagship Mountain, Mount Davidson (Antarctica) and Mount Nesbelan, which surround Flight Deck Névé. To the south the Benson Glacier flows past Mount Morrison, Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Deck Névé
Flight Deck Névé () is an elevated and unusually flat glacier névé, about , between Flagship Mountain and Mount Razorback in the Convoy Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica. The feature is the primary source of ice to the east-flowing Benson Glacier at Scuppers Icefalls. It is one of a group of nautical names in the Convoy Range applied by the New Zealand Geographic Board The New Zealand Geographic Board Ngā Pou Taunaha o Aotearoa (NZGB) was established by the New Zealand Geographic Board Act 1946, which has since been replaced by the New Zealand Geographic Board (Ngā Pou Taunaha o Aotearoa) Act 2008. Althoug ... in 1994. References Snow fields of Victoria Land Scott Coast Névés of Antarctica {{ScottCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite Harbour
Granite Harbour () is a bay in the coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica, about long, entered between Cape Archer and Cape Roberts. It was discovered and named by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04) in the ''Discovery'' in January 1902, while searching for safe winter quarters for the ship. The name derives from the great granite boulders found on its shores. See also *First View Point *Stevens Cliff Granite Harbour () is a bay in the coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica, about long, entered between Cape Archer and Cape Roberts. It was discovered and named by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04) in the ''Discovery'' in January 19 ... References Bays of the Ross Dependency Landforms of Victoria Land Scott Coast Ports and harbours of the Ross Dependency {{ScottCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |