|
Midi E 3301
Midi E 3301 was a prototype electric locomotive of Class E 3300 designed for the Chemins de fer du Midi, France. Because of poor performance, it was refused by the Compagnie du Midi and was re-deployed to Swiss railways. On 1 May 1919, it was classified Fb 2/5 11001 and, in 1920, it became experimental locomotive Be 2/5 11001 of the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB). Overview Many lines of the Midi network being mountain lines, the company began an electrification programme in 1909. The system chosen was single phase alternating current at 12 kV and 16⅔ Hz. Six prototype locomotives were ordered for the Perpignan - Villefranche-de-Conflent line. They were: * E 3001 from Thomson and General Electric * E 3101 from AEG and Henschel * E 3201 from Westinghouse, later SNCF 1C1 3900 * E 3301 from Brown-Boveri and SLM Winterthur * E 3401 from Ateliers du Nord et de l'Est * E 3501 from Schneider The E 3301 locomotive was expected to perform the following tasks: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1C1 3900
1C1 3900 was a class of SNCF electric locomotive. The class had only one member, 1C1 3901. It was built in 1912 for the Chemins de fer du Midi and its Midi class was E 3200. It was one of six different prototype electric locomotives ordered by the Midi. It was withdrawn in 1959 and one motor from it is preserved. Overview Many lines of the Midi network being mountain lines, the company began an electrification programme in 1909. The system chosen was single phase alternating current at 12 kV and 16⅔ Hz. Six prototype locomotives were ordered for the Perpignan - Villefranche-de-Conflent line. They were: * E 3001 from Thomson and General Electric * E 3101 from AEG and Henschel * E 3201 from Westinghouse, later SNCF 1C1 3900 * E 3301 from Brown-Boveri and SLM Winterthurbr>* E 3401 from Ateliers du nord de la france, Ateliers du Nord et de l'Est * E 3501 from Schneider Only the E 3201 really worked well. The company also ordered railcars E ABD 1 to 30, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1′C1′
Rigid-framed electric locomotives were some of the first generations of electric locomotive design. When these began the traction motors of these early locomotives, particularly with AC motors, were too large and heavy to be mounted directly to the axles and so were carried on the frame. One of the initial simplest wheel arrangements for a mainline electric locomotive, from around 1900, was the 1′C1′ arrangement, in UIC classification. Some of these locomotives had their driving wheels coupled with coupling rods, as for steam locomotives. Others had individual motors for each axle, as would later become universal. By the middle of the century, the bogie arrangement for locomotives became more popular and rigid-framed locomotives are now rare, except for small shunters. 1′C1′ 1′C1′ is the UIC classification for a railway locomotive with a wheel arrangement of three coupled driving wheels, with a leading and trailing articulated pony truck. The driving wheels are coup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
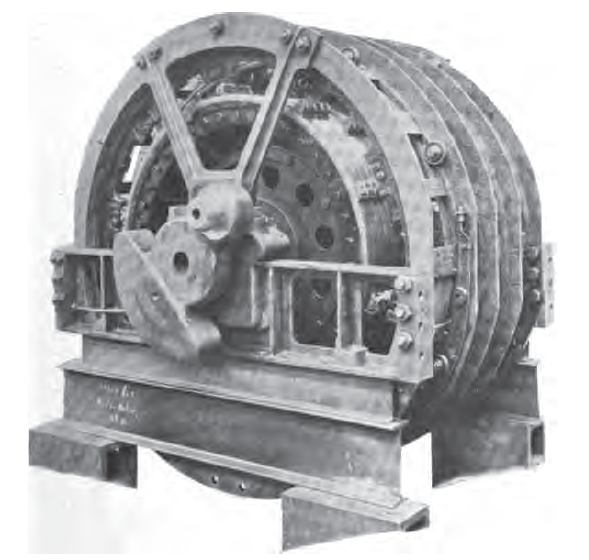
Deri Repulsion Type Motor Midi E 3301
Deri may refer to : People * Aryeh Deri (born 1959), an Israeli politician * Frances Deri (1880–1971), an Austrian psychoanalyst * Miksa Déri (1854–1938), a Hungarian electrical engineer * Shlomo Deri (fl. 2000s), an Israeli politician * Yehuda Deri (fl. 1990s/2000s), an Israeli rabbi Other uses * Deri, Caerphilly, a village in South Wales ** Deri RFC, a rugby club * Afon Deri, a river in Mid Wales * Digital Enterprise Research Institute The Digital Enterprise Research Institute (DERI) is a former research institute at NUI Galway. It is now part of the Insight Centre for Data Analytics. Insight was established in 2013 by Science Foundation Ireland with funding of €75m. DERI's ... (DERI), Ireland See also * Dari (other) {{disambig, geo, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lötschberg Railway Line
The Lötschberg is an Alpine mountain massif and usually associated with a major, historically important transit axis of the Alps in Switzerland with, at its core, the Lötschen Pass (german: Lötschenpass, Swiss German: ''Lötschepass''). The mountain pass, which culminates at nearly 2,700 metres above sea level, are part of the eastern Bernese Alps, whose main crest straddles the border between the cantons of Berne and Valais. The valleys concerned by the Lötschberg are those of the Kander in the Berner Oberland, with Kandersteg at the head of it, and a secluded side-valley of the Upper Valais, the Lötschental, with Ferden at the valley's entrance and at the bottom of the pass. Although the Lötschberg is one of the main north-south axes through the Alps, it is not on the main chain of the Alps, the Pennine Alps, further south, making up the main water divide. As a main north-south axis through the Alps, the Lötschberg is thus completed by the Simplon, between Brig and Domod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB-CFF-FFS Ae 4/8
The Ae 4/8 was a prototype locomotive of the Schweizerischen Bundesbahnen (Swiss Federal Railways) (SBB) for the testing of electrical operation. The locomotive was equipped with two different drives, therefore acquiring the nickname ''Bastard''. Because of its three-part locomotive body it also acquired the nickname '' Tatzelwurm''. History During the First World War the SBB decided to establish electric operation on their main lines as fast as possible, in order to become independent of coal supplies which had to be obtained from their warring neighbouring countries. Since electric traction technology was still new, suitable locomotive configurations had to be found. Therefore, the SBB ordered several prototype locomotives. In addition to the Be 3/5 12201, Be 4/6 12301, Be 4/6 12302 and Ce 6/8I 14201 with coupling rods, the SBB procured the Be 2/5 prototype locomotive with fully spring-loaded drives. When tested in the operational environment, this locomotive turned out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buchli Drive
The Buchli drive is a transmission system used in electric locomotives. It was named after its inventor, Swiss engineer Jakob Buchli. The drive is a fully spring-loaded drive, in which each floating axle has an individual motor, that is placed in the spring mounted locomotive frame. The weight of the driving motors is completely disconnected from the driving wheels, which are exposed to movement of the rails. First used in electric locomotives from the 1920s, the Buchli drive made possible the construction of faster and more powerful locomotives that required larger and heavier traction motors. The system minimises the impact on rail tracks due to the reduction in the overall unsprung weight. Although the drive was very successful though the 1930s, it is little used in modern locomotives, having been replaced with smaller, simpler drives that exhibit less imbalance and allow higher speeds. Construction In a Buchli drive a driven gear wheel is securely fixed to the locomotive f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tschanz Drive
The Tschanz drive or Oerlikon single-axle drive is a fully sprung single-axle drive for electric locomotives named after its inventor Otto Tschanz or after Maschinenfabrik Oerlikon. The drive was not widely used because its competitor, the Buchli drive, was cheaper and lighter. Construction The Tschanz drive is a fully sprung drive, which means that the motors are housed in the sprung part of the locomotive and are thus less exposed to shocks from the rails. Also, the shocks from the wheelsets to the rail are reduced because there is less unsprung weight on them. The traction motor is firmly mounted in the locomotive frame and drives through a single-stage gearbox to a gear that is located to one side of the wheel. The power transmission from this gear to the axle is done with a cardan shaft which has universal joints at both ends and passes through a hollow axle. Use Rolling stock on which the Tschanz drive was used include: * SBB-CFF-FFS Be 2/5 * SBB-CFF-FFS Ae 4/8 * BTB BCe 2/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB CFF FFS Be 25 BBC SLM 1
SBB may refer to: Arts and entertainment * SBB (band), a Polish progressive rock band, or their self-titled albums: ** SBB (1974 album) ** SBB (1978 album, Amiga) * Seán Bán Breathnach, also known as SBB, Irish TV personality * ''Saas Bahu aur Betiyaan'', a television programme on the Indian channel Aaj Tak * Soldier Boy Ben, a superhero in the third season of the ''The Boys'' television series Companies * Swiss Federal Railways, (german: Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, links=no) * Serbia Broadband ( sr, Српске кабловске мреже, links=no, ), a cable television and broadband internet service provider in Serbia Technology * Solid bleached board, a paperboard grade * Storage Building Block, an individual tape or disk drive component used in a computer data storage array or library * SwiftBroadband, a satellite-based communication network for aircraft * Screened Bottom Board, also known as Open Mesh Floor, a device used to protect beehives from '' Varroa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNCF
The Société nationale des chemins de fer français (; abbreviated as SNCF ; French for "National society of French railroads") is France's national state-owned railway company. Founded in 1938, it operates the country's national rail traffic along with Monaco, including the TGV, on France's high-speed rail network. Its functions include operation of railway services for passengers and freight (through its subsidiaries SNCF Voyageurs and Rail Logistics Europe), as well as maintenance and signalling of rail infrastructure (SNCF Réseau). The railway network consists of about of route, of which are high-speed lines and electrified. About 14,000 trains are operated daily. In 2010 the SNCF was ranked 22nd in France and 214th globally on the Fortune Global 500 list. It is the main business of the SNCF Group, which in 2020 had €30 billion of sales in 120 countries. The SNCF Group employs more than 275,000 employees in France and around the world. Since July 2013, the SNCF Grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railcar
A railcar (not to be confused with a railway car) is a self-propelled railway vehicle designed to transport passengers. The term "railcar" is usually used in reference to a train consisting of a single coach (carriage, car), with a driver's cab at one or both ends. Some railway companies, such as the Great Western, termed such vehicles "railmotors" (or "rail motors"). Self-propelled passenger vehicles also capable of hauling a train are, in technical rail usage, more usually called "rail motor coaches" or "motor cars" (not to be confused with the motor cars, otherwise known as automobiles, that operate on roads). The term is sometimes also used as an alternative name for the small types of multiple unit which consist of more than one coach. That is the general usage nowadays in Ireland when referring to any diesel multiple unit (DMU), or in some cases electric multiple unit (EMU). In North America the term "railcar" has a much broader sense and can be used (as an abbr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frutigen
Frutigen is a municipality in the Bernese Oberland in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. It is the capital of the Frutigen-Niedersimmental administrative district. History The area around Frutigen may have been settled since possibly the Bronze Age or Roman times. It is first mentioned in 1234 as ''Frutingen''. During the Middle Ages there were three castles in the modern municipal border; Halten, Tellenburg and Bürg. By 1260 the scattered farmers of the valley floor had formed a political and business association. The association had its own seal in 1263 and in 1340 it negotiated a peace with an association in the Obersimmental. In 1391, the village of Frutigen gained the right to hold the low court in the village. In 1400, the expanding city-state of Bern annexed the entire valley. However, the association was powerful enough to force Bern to make concessions. The residents of the valley were freed from the obligation to pay taxes or provide labor for local lord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(14779577373).jpg)





.jpg)
