|
Midger
Midger () is a biological Site of Special Scientific Interest straddling the border of Gloucestershire and South Gloucestershire, notified in 1966 and renotified in 1984. Since the last revision in 1974, the size has been reduced to a site. It lies east of Hillesley, Gloucestershire and north of Hawkesbury Upton, South Gloucestershire. It is at the head of the Kilcott Valley. There are six units of assessment. Part of the site () is part owned (and managed) by the Gloucestershire Wildlife Trust. The Wildlife Trust reserve Fuller information is available from the Wildlife Trust reserves handbook, the Midger reserve publication and the Nature Reserves Guide for 2011. The reserve comprises Midger Wood which was purchased by the trust in 1965, Back Common, Whitewell Wood, Twizzle Well Piece, Wedgewood and Saddlewood Roughs, which is part of the Badminton Estate. Woodland This is ancient woodland and has a canopy comprising mainly ash (including coppiced stools), pedunculate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midger
Midger () is a biological Site of Special Scientific Interest straddling the border of Gloucestershire and South Gloucestershire, notified in 1966 and renotified in 1984. Since the last revision in 1974, the size has been reduced to a site. It lies east of Hillesley, Gloucestershire and north of Hawkesbury Upton, South Gloucestershire. It is at the head of the Kilcott Valley. There are six units of assessment. Part of the site () is part owned (and managed) by the Gloucestershire Wildlife Trust. The Wildlife Trust reserve Fuller information is available from the Wildlife Trust reserves handbook, the Midger reserve publication and the Nature Reserves Guide for 2011. The reserve comprises Midger Wood which was purchased by the trust in 1965, Back Common, Whitewell Wood, Twizzle Well Piece, Wedgewood and Saddlewood Roughs, which is part of the Badminton Estate. Woodland This is ancient woodland and has a canopy comprising mainly ash (including coppiced stools), pedunculate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloucestershire Wildlife Trust
The Gloucestershire Wildlife Trust is the Gloucestershire local partner in a conservation network of 46 Wildlife Trusts. The Wildlife Trusts are local charities with the specific aim of protecting the United Kingdom's natural heritage. The Gloucestershire Wildlife Trust is managed by a Board of Trustees elected from its membership who provide overall direction for the development of the trust and there are advisory committees. The work of the trust is carried out through staff and volunteers. History The trust was founded in 1961 and was then named the Gloucestershire Trust for Nature Conservation. Founder members included Sir Peter Scott, Christopher Cadbury and a group of other local people with the shared interest of nature conservation. The name was changed to the Gloucestershire Wildlife Trust in 1991. In 1990 Lady Scott became the trust's patron succeeding her late husband, Sir Peter Scott. Originally the trust headquarters was at Church House, Standish, which was opene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
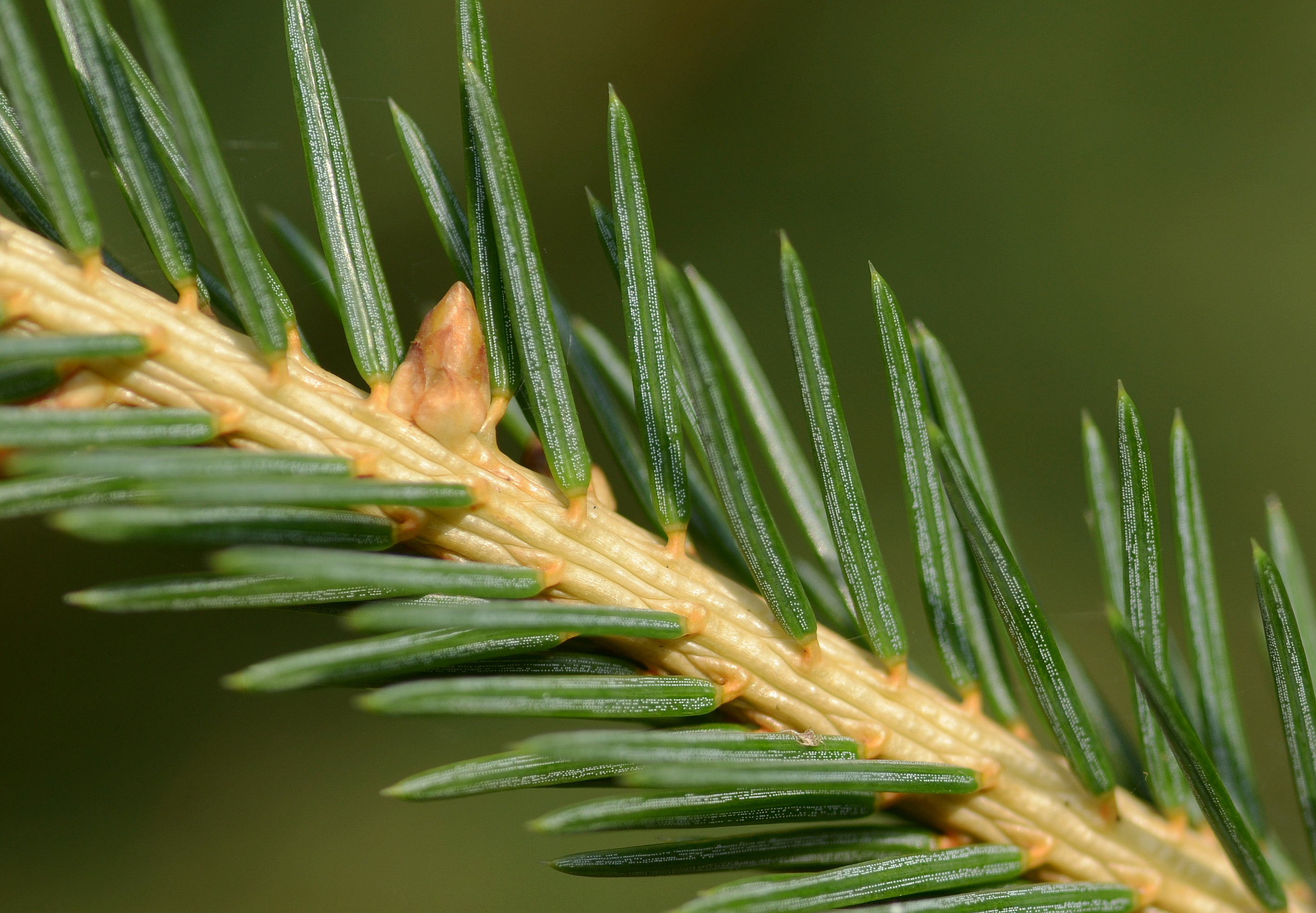
Spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Piceoideae. Spruces are large trees, from about 20 to 60 m (about 60–200 ft) tall when mature, and have whorled branches and conical form. They can be distinguished from other members of the pine family by their needles (leaves), which are four-sided and attached singly to small persistent peg-like structures (pulvini or sterigmata) on the branches, and by their cones (without any protruding bracts), which hang downwards after they are pollinated. The needles are shed when 4–10 years old, leaving the branches rough with the retained pegs. In other similar genera, the branches are fairly smooth. Spruce are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera (moth and butterfly) species, such as the eastern spruce budwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opposite-leaved Golden-saxifrage
''Chrysosplenium oppositifolium'', the opposite-leaved golden-saxifrage, is a species of flowering plant in the family Saxifragaceae, native to Europe (Belgium, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, France, Germany, Great Britain, Ireland, Italy, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and former Yugoslavia). It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753. References oppositifolium Flora of Europe Plants described in 1753 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus {{Saxifragaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood-sorrel
''Oxalis'' ( (American English) or (British English)) is a large genus of flowering plants in the wood-sorrel family Oxalidaceae, comprising over 550 species. The genus occurs throughout most of the world, except for the polar areas; species diversity is particularly rich in tropical Brazil, Mexico, and South Africa. Many of the species are known as wood sorrels (sometimes written "woodsorrels" or "wood-sorrels") as they have an acidic taste reminiscent of the sorrel proper (''Rumex acetosa''), which is only distantly related. Some species are called yellow sorrels or pink sorrels after the color of their flowers instead. Other species are colloquially known as false shamrocks, and some called sourgrasses. For the genus as a whole, the term oxalises is also used. Description and ecology These plants are annual or perennial. The leaves are divided into three to ten or more obovate and top-notched leaflets, arranged palmately with all the leaflets of roughly equal size. The majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
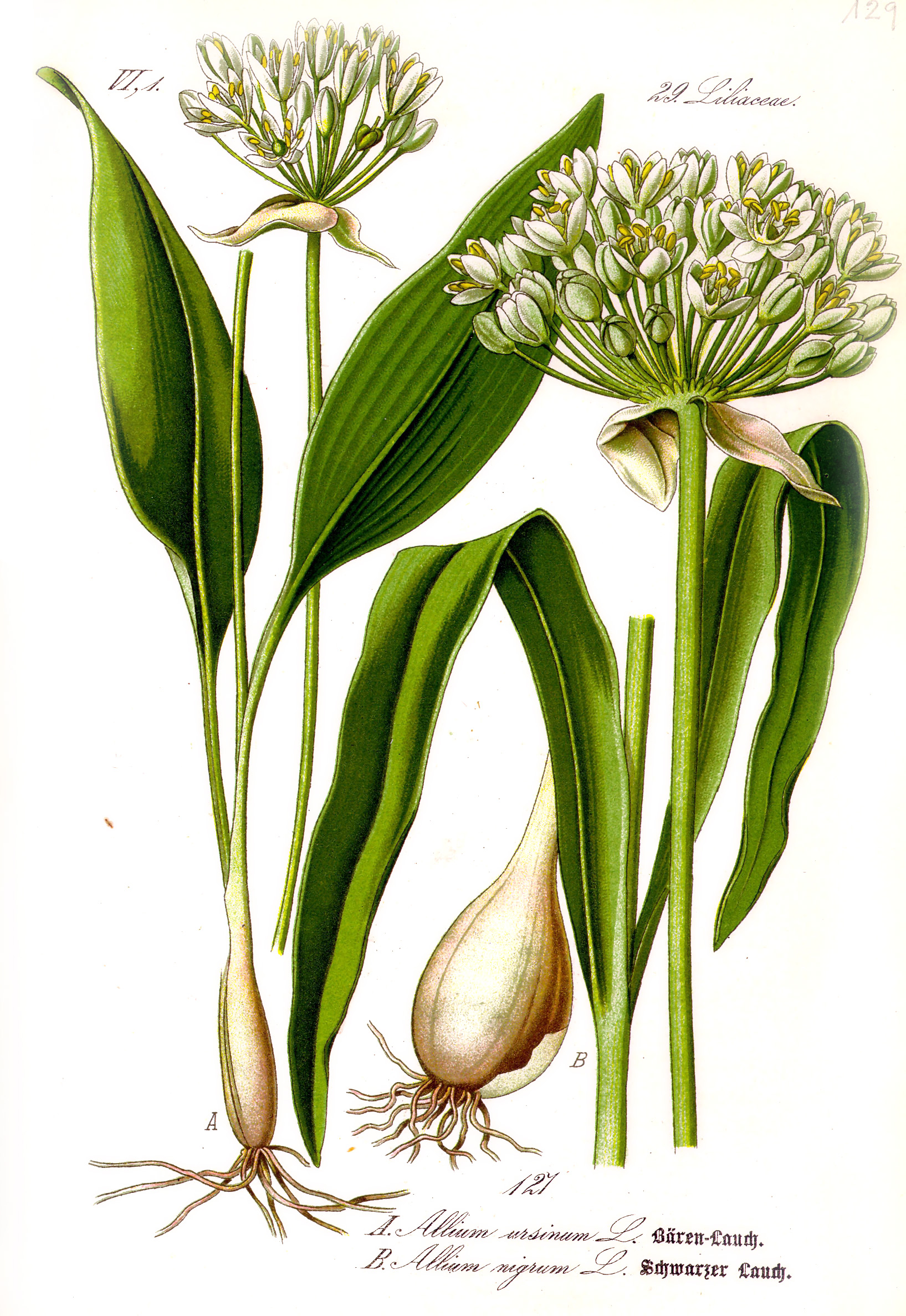
Ramsons
''Allium ursinum'', known as wild garlic, ramsons, cowleekes, cows's leek, cowleek, buckrams, broad-leaved garlic, wood garlic, bear leek, Eurasian wild garlic or bear's garlic, is a bulbous perennial flowering plant in the amaryllis family Amaryllidaceae. It is native to Europe and Asia, where it grows in moist woodland. It is a wild relative of onion and garlic, all belonging to the same genus, ''Allium''. There are two recognized subspecies: ''A. ursinum'' subsp. ''ursinum'' and ''A. ursinum'' subsp. ''ucrainicum''. Etymology The Latin specific name ''ursinum'' translates to 'bear' and refers to the supposed fondness of the brown bear for the bulbs; folk tales describe the bears consuming them after awakening from hibernation. Another theory is that the "''ursinum''" may refer to Ursa Major, as ''A. ursinum'' was perhaps one of the most northerly distributed ''Allium'' species known to the ancient Greeks, though this hypothesis is disputed. Common names for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemone Nemorosa
''Anemonoides nemorosa'' (syn. ''Anemone nemorosa''), the wood anemone, is an early-spring flowering plant in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae, native to Europe. Other common names include windflower, European thimbleweed, and smell fox, an allusion to the musky smell of the leaves. It is a perennial herbaceous plant growing tall. Description ''Anemonoides nemorosa'' is a rhizomatous herbaceous perennial plant less than in height. The compound basal leaves are palmate or ternate (divided into three lobes). They grow from underground root-like stems called rhizomes and die back down by mid summer (summer dormant). The plants start blooming in spring, March to May in the British Isles soon after the foliage emerges from the ground. The flowers are solitary, held above the foliage on short stems, with a whorl of three palmate or palmately-lobed leaflike bracts beneath. The flowers are diameter, with six or seven (and on rare occasions eight to ten) tepals (petal-like segments) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Archangel
''Lamium galeobdolon'', commonly known as yellow archangel, artillery plant, aluminium plant, or yellow weasel-snout, is a widespread wildflower in Europe, and has been introduced elsewhere as a garden plant. It displays the zygomorphic flower morphology, opposite leaves, and square stems typical of the mint family, Lamiaceae. The flowers are soft yellow and borne in axial clusters, with a prominent 'hood' (the dorsal lobe of the corolla). It spreads easily and so has been commonly used as an ornamental ground cover. It can be invasive in places where it is not native and caution must be taken when planting in these areas. Description Yellow archangel is a large-leaved perennial plant with underground runners growing to a height of about . The paired opposite leaves are stalked, broadly ovate with a cordate base and toothed margin. The underside of the leaves is often purplish. The flowers grow in whorls in a terminal spike. The calyx is five-lobed. The corolla is yellow, lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyacinthoides Non-scripta
''Hyacinthoides non-scripta'' (formerly ''Endymion non-scriptus'' or ''Scilla non-scripta'') is a bulbous perennial plant, found in Atlantic areas from north-western Spain to the British Isles, and also frequently used as a garden plant. It is known in English as the common bluebell or simply bluebell, a name which is used in Scotland to refer to the harebell, ''Campanula rotundifolia''. In spring, ''H. non-scripta'' produces a nodding, one-sided inflorescence of 5–12 tubular, sweet-scented violet–blue flowers, with strongly recurved tepals, and 3–6 long, linear, basal leaves. ''H. non-scripta'' is particularly associated with ancient woodland where it may dominate the understorey to produce carpets of violet–blue flowers in "bluebell woods", but also occurs in more open habitats in western regions. It is protected under UK law, and in some other parts of its range. A related species, '' H. hispanica'' has also been introduced to the British Isles and hyb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
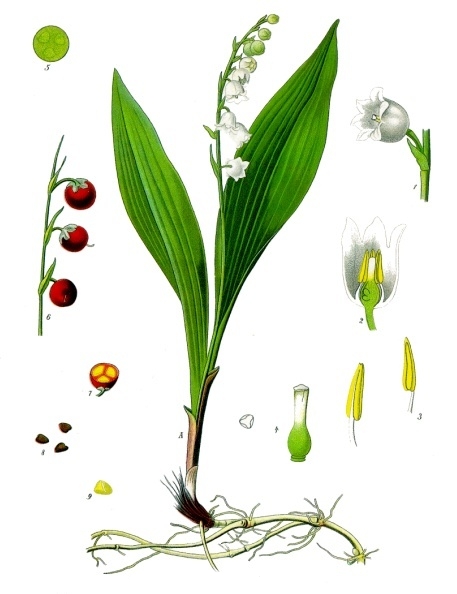
Lily Of The Valley
Lily of the valley (''Convallaria majalis'' (), sometimes written lily-of-the-valley, is a woodland flowering plant with sweetly scented, pendent, bell-shaped white flowers borne in sprays in spring. It is native throughout the cool temperate Northern Hemisphere in Asia and Europe. ''Convallaria majalis'' var. ''montana'', also known as the American lily of the valley, is native to North America. Due to the concentration of cardiac glycosides (cardenolides), it is highly poisonous if consumed by humans or other animals. Other names include May bells, Our Lady's tears, and Mary's tears. Its French name, ''muguet'', sometimes appears in the names of perfumes imitating the flower's scent. In pre-modern England, the plant was known as glovewort (as it was a wort used to create a salve for sore hands), or Apollinaris (according to a legend that it was discovered by Apollo). Description ''Convallaria majalis'' is an herbaceous perennial plant that often forms extensive colonies by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellebore
Commonly known as hellebores (), the Eurasian genus ''Helleborus'' consists of approximately 20 species of herbaceous or evergreen perennial flowering plants in the family Ranunculaceae, within which it gave its name to the tribe of Helleboreae. Despite names such as "winter rose", "Christmas rose" and "Lenten rose", hellebores are not closely related to the rose family (Rosaceae). Many hellebore species are poisonous. Description The flowers have five petal-like sepals surrounding a ring of small, cup-like nectaries which are actually petals modified to hold nectar. The sepals do not fall as petals would, but remain on the plant, sometimes for many months. Recent research in Spain suggests that the persistence of the sepals contributes to the development of the seeds. Taxonomy The genus was established by Carl Linnaeus in volume one of his ''Species Plantarum'' in 1753. The scientific name ''Helleborus'' could derive from the Ancient Greek word (), the common name for '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herb Paris
''Paris quadrifolia'', the herb Paris or true lover's knot, is a species of flowering plant in the family Melanthiaceae. It occurs in temperate and cool areas throughout Eurasia, from Spain to Yakutia, and from Iceland to Mongolia. It prefers calcareous soils and lives in damp and shady places, especially old established woods and stream banks. ''P. quadrifolia'' is in decline in Europe due to loss of habitat. In Iceland, for example, it is on the red list. Characteristics ''P. quadrifolia'' is a perennial herbaceous plant that is tall. It may have 3–8 leaves but typically there are four leaves arranged as opposing pairs. The flowers are wispy and inconspicuous. The plant flowers during the months of June and July. It has a solitary flower with four narrow greenish filiform (threadlike) petals, four green petaloid sepals, eight golden yellow stamens, and a round purple to red ovary. The flower is borne above a single whorl of four leaves. Each plant produces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(d.j.b.).jpg)
.jpg)


