|
Microwave Radiometer (Juno)
Microwave Radiometer (MWR) is an instrument on the ''Juno'' orbiter sent to planet Jupiter. MWR is a multi-wavelength microwave radiometer for making observations of Jupiter's deep atmosphere. MWR can observe radiation from 1.37 to 50 cm in wavelength, from 600 MHz to 22 GHz in frequencies. This supports its goal of observing the previously unseen atmospheric features and chemical abundances hundreds of miles/km into Jupiter's atmosphere. MWR is designed to detect six different frequencies in that range using separate antennas. MWR views Jupiter's microwave radiation so it can see up to hundreds of miles deep into the planet. In August 2016, as ''Juno'' swung closely by the planet MWR achieved a penetration of 200 to 250 miles (350 to 400 kilometers) below the surface cloud layer. MWR is designed to make observations below the cloud-tops, especially detecting the abundances of certain chemicals and determine dynamic features. These depths have not been observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juno Lifted By Overhead Crane
Juno commonly refers to: *Juno (mythology), the Roman goddess of marriage and queen of the gods * ''Juno'' (film), 2007 Juno may also refer to: Arts, entertainment and media Fictional characters *Juno, in the film '' Jenny, Juno'' *Juno, in the film '' Beetlejuice'' *Juno, in the manga series ''Beastars'' *Sailor Juno, a character in the manga series ''Sailor Moon'' * Juno (''Dune''), in the ''Dune'' universe *Juno Boyle, in the play ''Juno and the Paycock'' *Juno, in the book ''Juno of Taris'' by Fleur Beale * Juno, a game character in ''Assassin's Creed'' * Juno, in '' The Banner Saga'' game * Juno Eclipse, in ''The Force Unleashed'' game * Mega Man Juno, in '' Mega Man Legends'' game Music Musicians and groups * Juno (band), an American musical group * Juno (rapper), Finnish hip hop artist * Juno (singer), South Korean singer Songs * "Juno", a song by Life Without Buildings from ''Any Other City'', 2001 * "Juno", a song by Running Touch, 2021 * "Juno", a song by Tesseract fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, particularly among aquatic organisms, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to 45% of the world's food and fertilizers. Around 70% of ammonia is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and Diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many pharmaceutical products and is used in many commercial cleaning products. It is mainly collected by downward displacement of both air and water. Although common in nature—both terrestrially and in the outer planets of the Solar System—and in wide use, ammonia i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter's Great Red Spot In Microwave
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Jupiter is the third brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky after the Moon and Venus, and it has been observed since prehistoric times. It was named after the Roman god Jupiter, the king of the gods. Jupiter is primarily composed of hydrogen, but helium constitutes one-quarter of its mass and one-tenth of its volume. It probably has a rocky core of heavier elements, but, like the other giant planets in the Solar System, it lacks a well-defined solid surface. The ongoing contraction of Jupiter's interior generates more heat than it receives from the Sun. Because of its rapid rotation, the planet's shape is an oblate spheroid: it has a slight but noticeable bulge around the equator. The outer atmosphere is div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
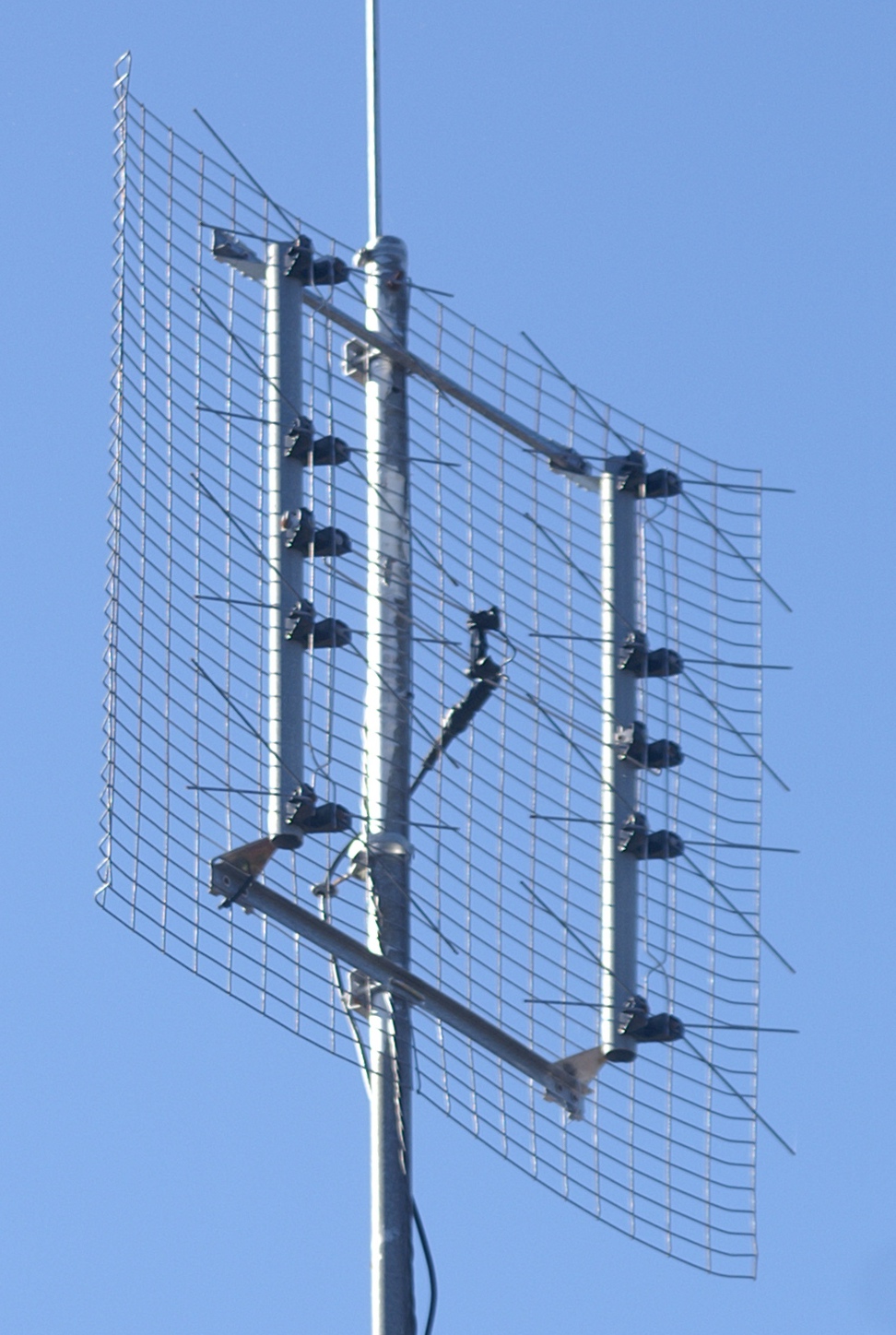
Slot Antenna
A slot antenna consists of a metal surface, usually a flat plate, with one or more holes or slots cut out. When the plate is driven as an antenna by an applied radio frequency current, the slot radiates electromagnetic waves in a way similar to a dipole antenna. The shape and size of the slot, as well as the driving frequency, determine the radiation pattern. Slot antennas are usually used at UHF and microwave frequencies at which wavelengths are small enough that the plate and slot are conveniently small. At these frequencies, the radio waves are often conducted by a waveguide, and the antenna consists of slots in the waveguide; this is called a slotted waveguide antenna. Multiple slots act as a directive array antenna and can emit a narrow fan-shaped beam of microwaves. They are used in standard laboratory microwave sources used for research, UHF television transmitting antennas, antennas on missiles and aircraft, sector antennas for cellular base stations, and partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflective Array Antenna
In telecommunications and radar, a reflective array antenna is a class of directive antennas in which multiple driven elements are mounted in front of a flat surface designed to reflect the radio waves in a desired direction. They are a type of array antenna. They are often used in the VHF and UHF frequency bands. VHF examples are generally large and resemble a highway billboard, so they are sometimes called billboard antennas. Other names are bedspring array and bowtie array depending on the type of elements making up the antenna. The curtain array is a larger version used by shortwave radio broadcasting stations. Reflective array antennas usually have a number of identical driven elements, fed in phase, in front of a flat, electrically large reflecting surface to produce a unidirectional beam of radio waves, increasing antenna gain and reducing radiation in unwanted directions. The larger the number of elements used, the higher the gain; the narrower the beam is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horn Antenna
A horn antenna or microwave horn is an antenna that consists of a flaring metal waveguide shaped like a horn to direct radio waves in a beam. Horns are widely used as antennas at UHF and microwave frequencies, above 300 MHz. They are used as feed antennas (called feed horns) for larger antenna structures such as parabolic antennas, as standard calibration antennas to measure the gain of other antennas, and as directive antennas for such devices as radar guns, automatic door openers, and microwave radiometers. Their advantages are moderate directivity, low standing wave ratio (SWR), broad bandwidth, and simple construction and adjustment. One of the first horn antennas was constructed in 1897 by Bengali-Indian radio researcher Jagadish Chandra Bose in his pioneering experiments with microwaves. reprinted in The modern horn antenna was invented independently in 1938 by Wilmer Barrow and G. C. Southworth The development of radar in World War 2 stimul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
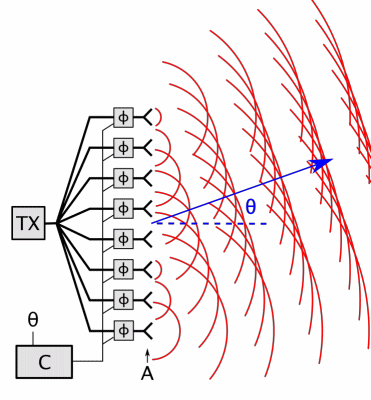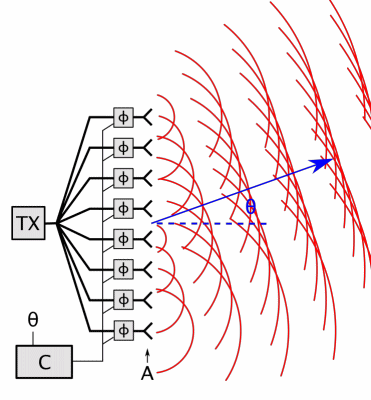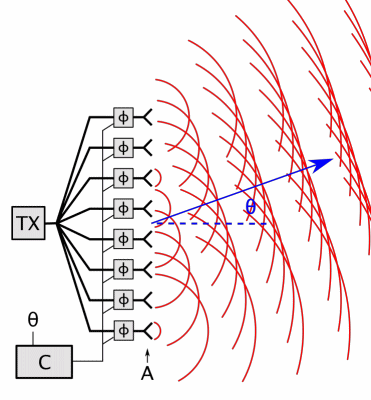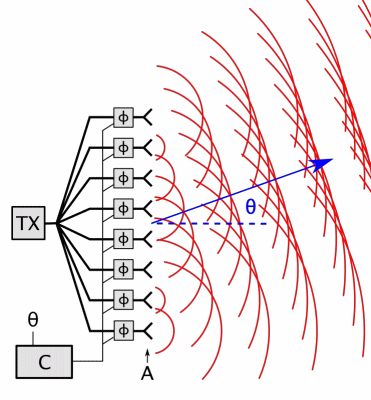
Antenna Array
An antenna array (or array antenna) is a set of multiple connected antennas which work together as a single antenna, to transmit or receive radio waves. The individual antennas (called ''elements'') are usually connected to a single receiver or transmitter by feedlines that feed the power to the elements in a specific phase relationship. The radio waves radiated by each individual antenna combine and superpose, adding together ( interfering constructively) to enhance the power radiated in desired directions, and cancelling ( interfering destructively) to reduce the power radiated in other directions. Similarly, when used for receiving, the separate radio frequency currents from the individual antennas combine in the receiver with the correct phase relationship to enhance signals received from the desired directions and cancel signals from undesired directions. More sophisticated array antennas may have multiple transmitter or receiver modules, each connected to a separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patch Antenna
A patch antenna is a type of antenna with a low profile, which can be mounted on a surface. It consists of a planar rectangular, circular, triangular, or any geometrical sheet or "patch" of metal, mounted over a larger sheet of metal called a ground plane. They are the original type of microstrip antenna described by Howell in 1972; the two metal sheets together form a resonant piece of microstrip transmission line with a length of approximately one-half wavelength of the radio waves. The radiation mechanism arises from fringing fields along the radiating edges. The radiation at the edges causes the antenna to act slightly larger electrically than its physical dimensions, so in order for the antenna to be resonant, a length of microstrip transmission line slightly shorter than one-half the wavelength at the frequency is used. The patch antenna is mainly practical at microwave frequencies, at which wavelengths are short enough that the patches are conveniently small. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin-stabilisation
Spin stabilization is the method of stabilizing a satellite or launch vehicle by means of spin, i.e. rotation along the longitudinal axis. The concept originates from ballistics, where the spin is commonly obtain by means of rifling. For most satellite applications this approach has been superseded by three-axis stabilization. Despinning can be achieved by various techniques, including yo-yo de-spin. Use On rockets with a solid motor upper stage, spin stabilization is used to keep the motor from drifting off course as they don't have their own thrusters. Usually small rockets are used to spin up the spacecraft and rocket then fire the rocket and send the craft off. Some rockets, like the Jupiter-C, Delta II, Minotaur V and the satellite Aryabhata are spin-stabilised. The Pioneer 4 spacecraft, the second object sent on a lunar flyby in 1959, maintained its attitude using spin-stabilization. The Schiaparelli EDM lander was spun up to 2.5 RPM before being ejected from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo Probe
''Galileo'' was an American robotic space probe that studied the planet Jupiter and its moons, as well as the asteroids Gaspra and Ida. Named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei, it consisted of an orbiter and an entry probe. It was delivered into Earth orbit on October 18, 1989, by , during STS-34. ''Galileo'' arrived at Jupiter on December 7, 1995, after gravitational assist flybys of Venus and Earth, and became the first spacecraft to orbit an outer planet. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory built the ''Galileo'' spacecraft and managed the ''Galileo'' program for NASA. West Germany Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm supplied the propulsion module. NASA's Ames Research Center managed the atmospheric probe, which was built by Hughes Aircraft Company. At launch, the orbiter and probe together had a mass of and stood tall. Spacecraft are normally stabilized either by spinning around a fixed axis or by maintaining a fixed orientation with reference to the Sun and a star. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

-3D-balls.png)