|
Microwave Oven
A microwave oven (commonly referred to as a microwave) is an electric oven that heats and cooks food by exposing it to electromagnetic radiation in the microwave frequency range. This induces polar molecules in the food to rotate and produce thermal energy in a process known as dielectric heating. Microwave ovens heat foods quickly and efficiently because excitation is fairly uniform in the outer of a homogeneous, high-water-content food item. The development of the cavity magnetron in the UK made possible the production of electromagnetic waves of a small enough wavelength ( microwaves). American engineer Percy Spencer is generally credited with inventing the modern microwave oven after World War II from radar technology developed during the war. Named the "Radarange", it was first sold in 1946. Raytheon later licensed its patents for a home-use microwave oven that was introduced by Tappan in 1955, but it was still too large and expensive for general home use. Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave 2022
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ranges as microwaves; the above broad definition includes both UHF and EHF ( millimeter wave) bands. A more common definition in radio-frequency engineering is the range between 1 and 100 GHz (wavelengths between 0.3 m and 3 mm). In all cases, microwaves include the entire SHF band (3 to 30 GHz, or 10 to 1 cm) at minimum. Frequencies in the microwave range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations. The prefix ' in ''microwave'' is not meant to suggest a wavelength in the micrometer range. Rather, it indicates that microwaves are "small" (having shorter wavelengths), compared to the radio waves used prior to microwave tech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amana Corporation
The Amana Corporation is an American brand of household appliances. It was founded in 1934 by George Foerstner as The Electrical Equipment Co. in Middle Amana, Iowa, to manufacture commercial walk-in coolers. The business was later owned by the Amana Society and became known as Amana Refrigeration, Inc. It is now owned by the Whirlpool Corporation. History In 1947, Amana manufactured the first upright freezer for the home, and in 1949 it added a side-by-side refrigerator. In 1950 the company was sold to a group of investors, including its founder, and became Amana Refrigeration, Inc. In 1954, it began making air conditioners. Amana was acquired in 1965 by Raytheon, which had invented the microwave oven in 1947, and introduced the commercial ''Radarange'' Model 1611 in 1954. In 1967, Amana introduced a consumer model of the ''Radarange'', the first popular microwave designed for home use. In 1997, the company was purchased by Goodman Global (now part of Daikin North America), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
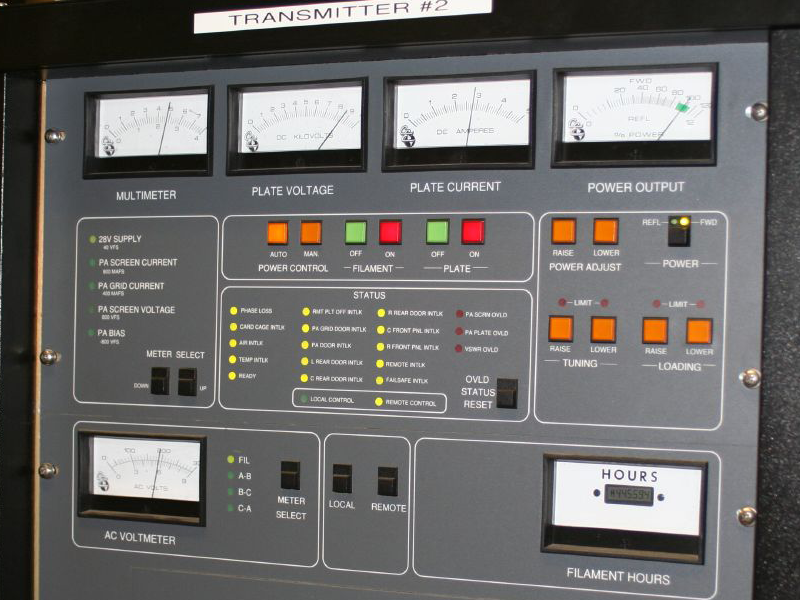
Transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary component parts of all electronic devices that communicate by radio, such as radio and television broadcasting stations, cell phones, walkie-talkies, wireless computer networks, Bluetooth enabled devices, garage door openers, two-way radios in aircraft, ships, spacecraft, radar sets and navigational beacons. The term ''transmitter'' is usually limited to equipment that generates radio waves for communication purposes; or radiolocation, such as radar and navigational transmitters. Generators of radio waves for heating or industrial purposes, such as microwave ovens or diathermy equipment, are not usually called transmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shortwave
Shortwave radio is radio transmission using shortwave (SW) radio frequencies. There is no official definition of the band, but the range always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz (100 to 10 metres); above the medium frequency band (MF), to the bottom of the VHF band. Radio waves in the shortwave band can be reflected or refracted from a layer of electrically charged atoms in the atmosphere called the ionosphere. Therefore, short waves directed at an angle into the sky can be reflected back to Earth at great distances, beyond the horizon. This is called skywave or "skip" propagation. Thus shortwave radio can be used for communication over very long distances, in contrast to radio waves of higher frequency, which travel in straight lines (line-of-sight propagation) and are limited by the visual horizon, about 64 km (40 miles). Shortwave broadcasts of radio programs played an important role in the early days of rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westinghouse Electric Corporation
The Westinghouse Electric Corporation was an American manufacturing company founded in 1886 by George Westinghouse. It was originally named "Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company" and was renamed "Westinghouse Electric Corporation" in 1945. The company acquired the CBS television network in 1995 and was renamed "CBS Corporation" until being acquired by Viacom in 1999, a merger completed in April 2000. The CBS Corporation name was later reused for one of the two companies resulting from the split of Viacom in 2006. The Westinghouse trademarks are owned by Westinghouse Electric Corporation, and were previously part of Westinghouse Licensing Corporation. The nuclear power business, Westinghouse Electric Company, was spun off from the Westinghouse Electric Corporation in 1999. History Westinghouse Electric was founded by George Westinghouse in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, on January 8, 1886. The firm became active in developing electric infrastructure throughou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diathermy
Diathermy is electrically induced heat or the use of high-frequency electromagnetic currents as a form of physical therapy and in surgical procedures. The earliest observations on the reactions of high-frequency electromagnetic currents upon the human organism were made by Jacques Arsene d'Arsonval. The field was pioneered in 1907 by German physician Karl Franz Nagelschmidt, who coined the term ''diathermy'' from the Greek words ''dia'' and θέρμη ''therma'', literally meaning "heating through" (adj., diather´mal, diather´mic). Diathermy is commonly used for muscle relaxation, and to induce deep heating in tissue for therapeutic purposes in medicine. It is used in physical therapy to deliver moderate heat directly to pathologic lesions in the deeper tissues of the body. Diathermy is produced by three techniques: ultrasound (''ultrasonic diathermy''), short-wave radio frequencies in the range 1–100 MHz (''shortwave diathermy'') or microwaves typically in the 915& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Wave
Shortwave radio is radio transmission using shortwave (SW) radio frequencies. There is no official definition of the band, but the range always includes all of the High frequency, high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz (100 to 10 metres); above the Medium frequency, medium frequency band (MF), to the bottom of the Very high frequency, VHF band. Radio waves in the shortwave band can be reflected or refracted from a layer of electrically charged atoms in the atmosphere called the ionosphere. Therefore, short waves directed at an angle into the sky can be reflected back to Earth at great distances, beyond the horizon. This is called skywave or "skip" radio propagation, propagation. Thus shortwave radio can be used for communication over very long distances, in contrast to radio waves of higher frequency, which travel in straight lines (line-of-sight propagation) and are limited by the visual horizon, about 64 km (40 miles). Shortwave broadcasts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary component parts of all electronic devices that communicate by radio, such as radio and television broadcasting stations, cell phones, walkie-talkies, wireless computer networks, Bluetooth enabled devices, garage door openers, two-way radios in aircraft, ships, spacecraft, radar sets and navigational beacons. The term ''transmitter'' is usually limited to equipment that generates radio waves for communication purposes; or radiolocation, such as radar and navigational transmitters. Generators of radio waves for heating or industrial purposes, such as microwave ovens or diathermy equipment, are not usually called transmitters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
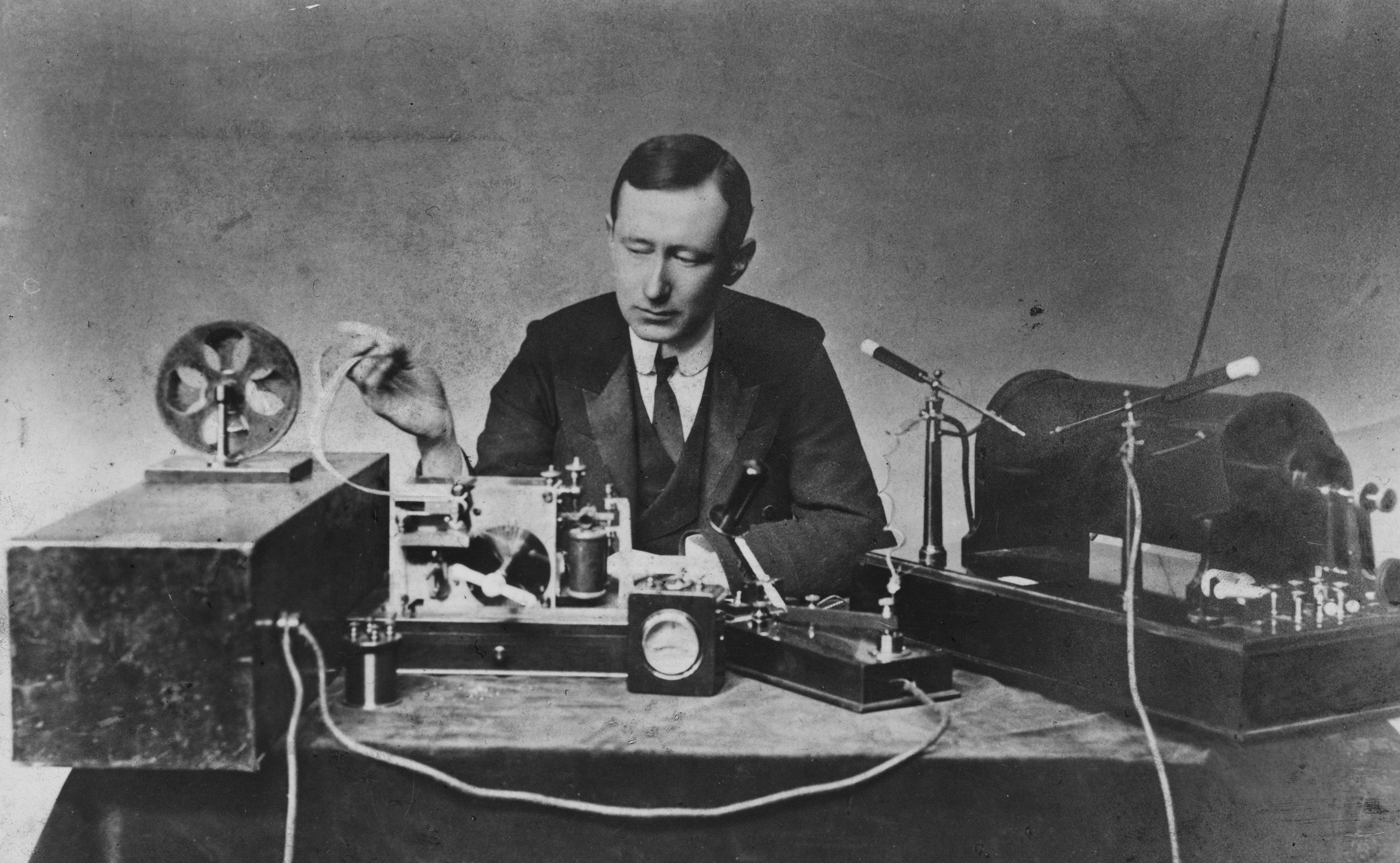
Radio Wave
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz ( GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1 mm (shorter than a grain of rice); at 30 Hz the corresponding wavelength is (longer than the radius of the Earth). Like all electromagnetic waves, radio waves in a vacuum travel at the speed of light, and in the Earth's atmosphere at a close, but slightly lower speed. Radio waves are generated by charged particles undergoing acceleration, such as time-varying electric currents. Naturally occurring radio waves are emitted by lightning and astronomical objects, and are part of the blackbody radiation emitted by all warm objects. Radio waves are generated artificially by an electronic device called a transmitter, which is connected to an antenna which radiates the waves. They are received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Century Of Progress
A Century of Progress International Exposition, also known as the Chicago World's Fair, was a world's fair held in the city of Chicago, Illinois, United States, from 1933 to 1934. The fair, registered under the Bureau International des Expositions (BIE), celebrated the city's centennial. The theme of the fair was technological innovation, and its motto was "Science Finds, Industry Applies, Man Adapts", trumpeting the message that science and American life were wedded. Its architectural symbol was the Sky Ride, a transporter bridge perpendicular to the shore on which one could ride from one side of the fair to the other. One description of the fair noted that the world, "then still mired in the malaise of the Great Depression, could glimpse a happier not-too-distant future, all driven by innovation in science and technology." Fair visitors saw the latest wonders in rail travel, automobiles, architecture and even cigarette-smoking robots. The exposition "emphasized technology a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maillard Reaction
The Maillard reaction ( ; ) is a chemical reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars that gives browned food its distinctive flavor. Seared steaks, fried dumplings, cookies and other kinds of biscuits, breads, toasted marshmallows, and many other foods undergo this reaction. It is named after French chemist Louis Camille Maillard, who first described it in 1912 while attempting to reproduce biological protein synthesis. The reaction is a form of non-enzymatic browning which typically proceeds rapidly from around . Many recipes call for an oven temperature high enough to ensure that a Maillard reaction occurs. At higher temperatures, caramelization (the browning of sugars, a distinct process) and subsequently pyrolysis (final breakdown leading to burning and the development of acrid flavors) become more pronounced. The reactive carbonyl group of the sugar reacts with the nucleophilic amino group of the amino acid and forms a complex mixture of poorly characterized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |