|
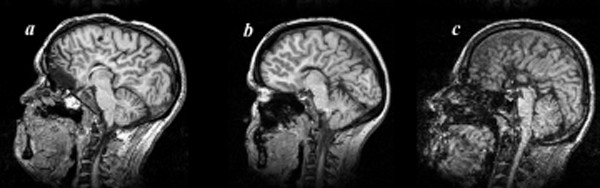
Microlissencephaly (cropped)
Microlissencephaly (MLIS) is a rare congenital brain disorder that combines severe microcephaly (small head) with lissencephaly (smooth brain surface due to absent sulci and gyri). Microlissencephaly is a heterogeneous disorder, i.e. it has many different causes and a variable clinical course. Microlissencephaly is a malformation of cortical development (MCD) that occurs due to failure of neuronal migration between the third and fifth month of gestation as well as stem cell population abnormalities. Numerous genes have been found to be associated with microlissencephaly, however, the pathophysiology is still not completely understood. The combination of lissencephaly with severe congenital microcephaly is designated as microlissencephaly only when the cortex is abnormally thick. If such combination exists with a normal cortical thickness (2.5 to 3 mm), it is known as " microcephaly with simplified gyral pattern" (MSGP). Both MLIS and MSGP have a much more severe clinical cours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestational Age (obstetrics)
In obstetrics, gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy which is taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method if available. Such methods include adding 14 days to a known duration since fertilization (as is possible in in vitro fertilization), or by obstetric ultrasonography. The popularity of using this definition of gestational age is that menstrual periods are essentially always noticed, while there is usually a lack of a convenient way to discern when fertilization occurred. Gestational age is contrasted with fertilization age which takes the date of fertilization as the start date of gestation. The initiation of pregnancy for the calculation of gestational age can differ from definitions of initiation of pregnancy in context of the abortion debate or beginning of human personhood. Methods According to American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem. The brainstem is very small, making up around only 2.6 percent of the brain's total weight. It has the critical roles of regulating cardiac, and respiratory function, helping to control heart rate and breathing rate. It also provides the main motor and sensory nerve supply to the face and neck via the cranial nerves. Ten pairs of cranial nerves come from the brainstem. Other roles include the regulation of the central nervous system and the body's sleep cycle. It is also of prime importance in the conveyance of motor and sensory pathways from the rest of the brain to the body, and from the body back to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coloboma
A coloboma (from the Greek , meaning defect) is a hole in one of the structures of the eye, such as the iris, retina, choroid, or optic disc. The hole is present from birth and can be caused when a gap called the choroid fissure, which is present during early stages of prenatal development, fails to close up completely before a child is born. Ocular coloboma is relatively uncommon, affecting less than one in every 10,000 births. The classical description in medical literature is of a keyhole-shaped defect. A coloboma can occur in one eye (unilateral) or both eyes (bilateral). Most cases of coloboma affect only the iris. The level of vision impairment of those with a coloboma can range from having no vision problems to being able to see only light or dark, depending on the position and extent of the coloboma (or colobomata if more than one is present). Signs and symptoms Visual effects may be mild to more severe depending on the size and location of the coloboma. If, for exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptosis (eyelid)
Ptosis, also known as blepharoptosis, is a drooping or falling of the upper eyelid. The drooping may be worse after being awake longer when the individual's muscles are tired. This condition is sometimes called "lazy eye", but that term normally refers to the condition amblyopia. If severe enough and left untreated, the drooping eyelid can cause other conditions, such as amblyopia or astigmatism. This is why it is especially important for this disorder to be treated in children at a young age, before it can interfere with vision development. The term is from Greek 'fall, falling'. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms typically seen in this condition include: * The eyelid(s) may appear to droop. * Droopy eyelids can give the face a false appearance of being fatigued, disinterested, or even sinister. * The eyelid may not protect the eye as effectively, allowing it to dry out. * Sagging upper eyelids can partially block the person's field of view. * Obstructed vision may cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthrogryposis
Arthrogryposis (AMC) describes congenital joint contracture in two or more areas of the body. It derives its name from Greek, literally meaning "curving of joints" (', "joint"; ', late Latin form of late Greek ', "hooking"). Children born with one or more joint contractures have abnormal fibrosis of the muscle tissue causing muscle shortening, and therefore are unable to perform active extension and flexion in the affected joint or joints. AMC has been divided into three groups: amyoplasia, distal arthrogryposis, and syndromic. Amyoplasia is characterized by severe joint contractures and muscle weakness. Distal arthrogryposis mainly involves the hands and feet. Types of arthrogryposis with a primary neurological or muscle disease belong to the syndromic group. Signs and symptoms Often, every joint in a patient with arthrogryposis is affected; in 84% all limbs are involved, in 11% only the legs, and in 4% only the arms are involved. Every joint in the body, when affected, displays ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with loss of consciousness ( tonic-clonic seizure), to shaking movements involving only part of the body with variable levels of consciousness (focal seizure), to a subtle momentary loss of awareness ( absence seizure). Most of the time these episodes last less than two minutes and it takes some time to return to normal. Loss of bladder control may occur. Seizures may be provoked and unprovoked. Provoked seizures are due to a temporary event such as low blood sugar, alcohol withdrawal, abusing alcohol together with prescription medication, low blood sodium, fever, brain infection, or concussion. Unprovoked seizures occur without a known or fixable cause such that ongoing seizures are likely. Unprovoked seizures may be exacerbated by stress or sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spasticity
Spasticity () is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance with a combination of paralysis, increased tendon reflex activity, and hypertonia. It is also colloquially referred to as an unusual "tightness", stiffness, or "pull" of muscles. Clinically, spasticity results from the loss of inhibition of motor neurons, causing excessive velocity-dependent muscle contraction. This ultimately leads to hyperreflexia, an exaggerated deep tendon reflex. Spasticity is often treated with the drug baclofen, which acts as an agonist at GABA receptors, which are inhibitory. Spastic cerebral palsy is the most common form of cerebral palsy, which is a group of permanent movement problems that do not get worse over time. GABA's inhibitory actions contribute to baclofen's efficacy as an anti-spasticity agent. Cause Spasticity mostly occurs in disorders of the central nervous system (CNS) affecting the upper motor neurons in the form of a lesion, such as spastic diplegia, or upper motor neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microlissencephaly (cropped)
Microlissencephaly (MLIS) is a rare congenital brain disorder that combines severe microcephaly (small head) with lissencephaly (smooth brain surface due to absent sulci and gyri). Microlissencephaly is a heterogeneous disorder, i.e. it has many different causes and a variable clinical course. Microlissencephaly is a malformation of cortical development (MCD) that occurs due to failure of neuronal migration between the third and fifth month of gestation as well as stem cell population abnormalities. Numerous genes have been found to be associated with microlissencephaly, however, the pathophysiology is still not completely understood. The combination of lissencephaly with severe congenital microcephaly is designated as microlissencephaly only when the cortex is abnormally thick. If such combination exists with a normal cortical thickness (2.5 to 3 mm), it is known as " microcephaly with simplified gyral pattern" (MSGP). Both MLIS and MSGP have a much more severe clinical cours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callosal Agenesis
Agenesis of the corpus callosum (ACC) is a rare birth defect in which there is a complete or partial absence of the corpus callosum. It occurs when the development of the corpus callosum, the band of white matter connecting the two hemispheres in the brain, in the embryo is disrupted. The result of this is that the fibers that would otherwise form the corpus callosum are instead longitudinally oriented along the ipsilateral ventricular wall and form structures called Probst bundles. In addition to agenesis, other degrees of callosal defects exist, including hypoplasia (underdevelopment or thinness), hypogenesis (partial agenesis) or dysgenesis (malformation). ACC is found in many syndromes and can often present alongside hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis. When this is the case, there can also be an enlarged fourth ventricle or hydrocephalus; this is called Dandy–Walker malformation. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of ACC and other callosal disorders vary greatly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agenesis Of Corpus Callosum
Agenesis of the corpus callosum (ACC) is a rare birth defect in which there is a complete or partial absence of the corpus callosum. It occurs when the development of the corpus callosum, the band of white matter connecting the two hemispheres in the brain, in the embryo is disrupted. The result of this is that the fibers that would otherwise form the corpus callosum are instead longitudinally oriented along the ipsilateral ventricular wall and form structures called Probst bundles. In addition to agenesis, other degrees of callosal defects exist, including hypoplasia (underdevelopment or thinness), hypogenesis (partial agenesis) or dysgenesis (malformation). ACC is found in many syndromes and can often present alongside hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis. When this is the case, there can also be an enlarged fourth ventricle or hydrocephalus; this is called Dandy–Walker malformation. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of ACC and other callosal disorders vary greatly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neopallium
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning and language. The neocortex is further subdivided into the true isocortex and the proisocortex. In the human brain, the neocortex is the largest part of the cerebral cortex (the outer layer of the cerebrum). The neocortex makes up the largest part of the cerebral cortex, with the allocortex making up the rest. The neocortex is made up of six layers, labelled from the outermost inwards, I to VI. Etymology The term is from ''cortex'', Latin, " bark" or "rind", combined with ''neo-'', Greek, "new". ''Neopallium'' is a similar hybrid, from Latin ''pallium'', "cloak". ''Isocortex'' and ''allocortex'' are hybrids with Greek ''isos'', "same", and ''allos'', "other". Anatomy The neocortex is the most developed in its organisa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.gif)