|
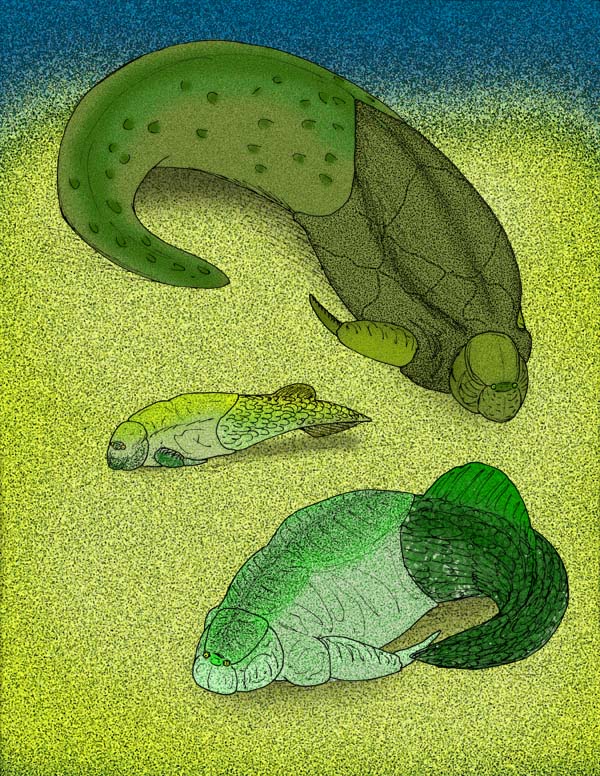
Microbrachius
''Microbrachius'' is an extinct genus of tiny, advanced antiarch placoderms closely related to the bothriolepids. Complete articulated specimens show that the armored section of the body had an average length of 2-4 cm. Species of ''Microbrachius'' are characterized by having large heads with short thoracic armor. Specimens of ''Microbrachius'' have been found in Scotland, Belarus, Estonia, and China. Specimens range in age from the Lower Devonian Late Emsian Stage (393.3 Ma) to the Middle Devonian Upper Givetian Stage (382.7 Ma). Although two of the four described species are known from Late Emsian-aged strata of Early Devonian China, the type and youngest species, ''M. dicki'', is known from upper Givetian freshwater strata of Scotland. The various species have short thoracic armor, and large heads. There are patterns of small, but noticeable tubercles on the armor, with the arrangement varying from species to species. Anatomy The bony armor of placoderms surrounds the he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Dick
Robert Dick (January 1811 – 24 December 1866), was a Scottish geologist and botanist. Life He was born at Tullibody, in Clackmannanshire. His father was an officer of excise in nearby Alloa. At the age of thirteen, after receiving a good elementary education at the parish school, Dick was apprenticed to a baker, and served for three years. In these early days he became interested in wildflowers—he made a collection of plants and gradually acquired some knowledge of their names from an old encyclopedia. When his time was up he left Tullibody and gained employment as a journeyman baker at Leith, Glasgow and Greenock. Meanwhile, his father, who in 1826 had been removed to Thurso, as supervisor of excise, advised his son to set up a baker's shop in that town. Dick went there in 1830, started a business as a baker, and worked laboriously until his death. Throughout this period he zealously devoted himself to studying and collecting the plants, mollusca and insects of a wide a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
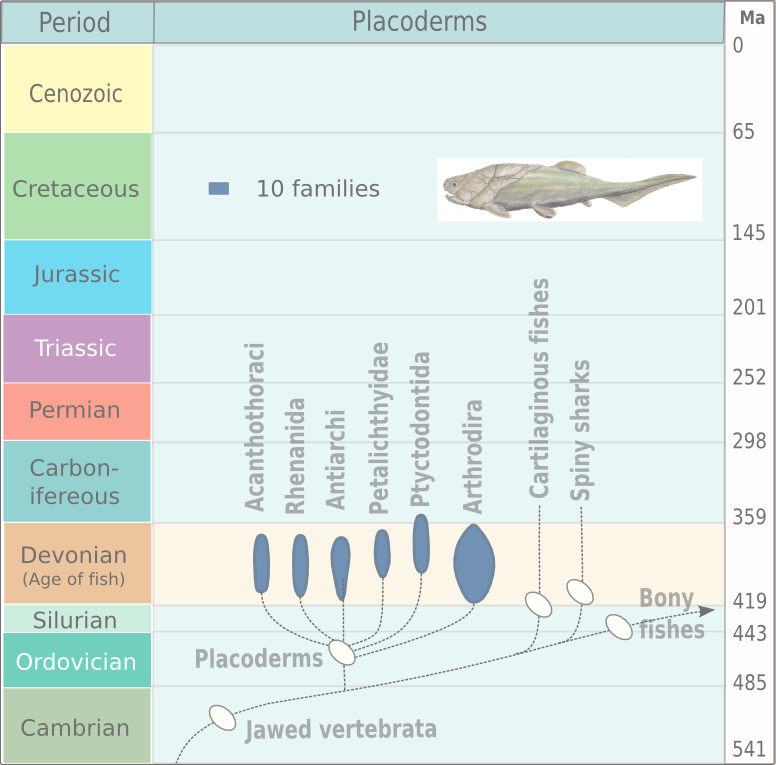
Antiarch
Antiarchi ("opposite anus") is an order of heavily armored placoderms. The antiarchs form the second-most successful group of placoderms after the arthrodires in terms of numbers of species and range of environments. The order's name was coined by Edward Drinker Cope, who, when examining some fossils that he thought were armored tunicates related to '' Chelysoma'', mistakenly thought that the orbital fenestra (i.e., the hole in the headshield for the eyes, nose and pineal foramen) was the opening for the mouth, or oral siphon, and that the opening for the anal siphon was on the other side of the body, as opposed to having both oral and anal siphons together at one end. The front portions of their bodies were heavily armored, to the point of literally resembling a box with eyes, with the sometimes scaled, sometimes naked rear portions often becoming sinuous, particularly with later forms. The pair of pectoral fins were modified into a pair of caliper-like, or arthropod-like l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiarchi
Antiarchi ("opposite anus") is an order (biology), order of heavily armored placoderms. The antiarchs form the second-most successful group of placoderms after the arthrodires in terms of numbers of species and range of environments. The order's name was coined by Edward Drinker Cope, who, when examining some fossils that he thought were armored tunicates related to ''Chelysoma'', mistakenly thought that the orbital fenestra (i.e., the hole in the headshield for the eyes, nose and pineal foramen) was the opening for the mouth, or oral siphon, and that the opening for the anal siphon was on the other side of the body, as opposed to having both oral and anal siphons together at one end. The front portions of their bodies were heavily armored, to the point of literally resembling a box with eyes, with the sometimes scaled, sometimes naked rear portions often becoming wiktionary:sinuous, sinuous, particularly with later forms. The pair of pectoral fins were modified into a pair of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bothriolepididae
Bothriolepididae is a family of antiarch placoderms, known from the Emsian, to Famennian. Taxonomy The cladogram is fromBothriolepid antiarchs (Vertebrata, Placodermi) from the Devonian of the north-western part of the East European Platform. {{Clade, style={{Clade , label1= Bothriolepidoidei , 1={{Clade , 1={{Clade , 1='' Microbrachius'' , 2='' Wudinolepis'' , 2={{Clade , 1={{Clade , 1=''Dianolepis'' , 2=''Jiangxilepis'' , 3='' Kirgisolepis'' , 4='' Tenizolepis'' , 2={{Clade , 1=''Monarolepis'' , 2={{Clade , 1=''Bothriolepis'' , 2=''Grossilepis Antiarchi ("opposite anus") is an order of heavily armored placoderms. The antiarchs form the second-most successful group of placoderms after the arthrodires in terms of numbers of species and range of environments. The order's name was coi ...'' , 3='' Vietnamaspis'' References {{Refl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Fertilization
Internal fertilization is the union of an egg and sperm cell during sexual reproduction inside the female body. Internal fertilization, unlike its counterpart, external fertilization, brings more control to the female with reproduction. For internal fertilization to happen there needs to be a method for the male to introduce the sperm into the female's reproductive tract. Most taxa that reproduce by internal fertilization are gonochoric. In mammals, reptiles, and certain other groups of animals, this is done by copulation, an intromittent organ being introduced into the vagina or cloaca. In most birds, the cloacal kiss is used, the two animals pressing their cloacas together while transferring sperm. Salamanders, spiders, some insects and some molluscs undertake internal fertilization by transferring a spermatophore, a bundle of sperm, from the male to the female. Following fertilization, the embryos are laid as eggs in oviparous organisms, or continue to develop inside the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of China
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian Placoderms
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began domi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placoderms Of Europe
Placodermi (from Greek πλάξ 'plate' and δέρμα 'skin', literally ' plate-skinned') is a class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates and the rest of the body was scaled or naked, depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish; their jaws likely evolved from the first of their gill arches. Placoderms are thought to be paraphyletic, consisting of several distinct outgroups or sister taxa to all living jawed vertebrates, which originated among their ranks. In contrast, one 2016 analysis concluded that placodermi are likely monophyletic, though these analyses have been further dismissed with more transitional taxa between placoderms and modern gnathosthomes, solidifying their paraphyletic status. Placoderms were also the first fish to develop pelvic fins, the precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placoderms Of Asia
Placodermi (from Greek πλάξ 'plate' and δέρμα 'skin', literally ' plate-skinned') is a class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates and the rest of the body was scaled or naked, depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish; their jaws likely evolved from the first of their gill arches. Placoderms are thought to be paraphyletic, consisting of several distinct outgroups or sister taxa to all living jawed vertebrates, which originated among their ranks. In contrast, one 2016 analysis concluded that placodermi are likely monophyletic, though these analyses have been further dismissed with more transitional taxa between placoderms and modern gnathosthomes, solidifying their paraphyletic status. Placoderms were also the first fish to develop pelvic fins, the precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods, as well as tru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bothriolepis
''Bothriolepis'' (from el, βόθρος , 'trench' and el, λεπίς 'scale') was a widespread, abundant and diverse genus of antiarch placoderms that lived during the Middle Devonian, Middle to Late Devonian period of the Paleozoic Era. Historically, ''Bothriolepis'' resided in an array of paleo-environments spread across every paleocontinent, including near shore marine and freshwater settings. Most species of ''Bothriolepis'' were characterized as relatively small, benthic, freshwater detritivores (organisms that obtain nutrients by consuming decomposing plant/animal material), averaging around in length. However, the largest species, ''B. rex'', had an estimated bodylength of . Although expansive with over 60 species found worldwide, comparatively ''Bothriolepis'' is not unusually more diverse than most modern bottom dwelling species around today. Classification ''Bothriolepis'' is a genus placed within the placoderm order Antiarchi. The earliest antiarch placoderms fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterichthyodes
''Pterichthyodes'' is a genus of antiarch placoderm fishes from the Devonian period. Its fossils have been discovered in Scotland. They were one of the first species recognized for what they were, as their fossils are common in the Old Red Sandstone formation studied by geologists in the early 19th century. Due to their extreme divergence from modern-day fish, they were a puzzle unsolved until Charles Darwin brought forward his theories on evolution. Description As with all other antiarchs, ''Pterichthyodes'' had heavily armored heads and forebodies, while their scaly tails were unarmored. Specimen length ranges from to . As placoderms, they were members of the Gnathostome, earliest known vertebrates to possess jaws, though they had grinding plates rather than teeth. The generic name of ''Pterichthyodes'' refers directly to their odd wing-like appendages ("pterichthys" being a compound crassis word from Ancient Greek language, Greek for "wing-fish"), which correspond to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austroptyctodus
''Austroptyctodus gardineri'' is a small ptyctodontid placoderm fish from the Upper Devonian Gogo Formation of Western Australia. First described by Miles & Young (1977) as a new species of the German genus '' Ctenurella''. Long (1997) redescribed the German material and found major differences in the skull roof pattern so assigned it to a new genus, ''Austroptyctodus''. This genus lacks spinal plates and has ''Ptyctodus''-like toothplates. The most significant discovery about ''Austroptyctodus'' is that one specimen depicts a female pregnant with 3 unborn embryos inside her, showing that like ''Materpiscis'', also from Gogo, this genus was a live bearer that reproduced through internal fertilization Internal fertilization is the union of an egg and sperm cell during sexual reproduction inside the female body. Internal fertilization, unlike its counterpart, external fertilization, brings more control to the female with reproduction. For inter ....Long, J.A., Trinajstic, K., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |