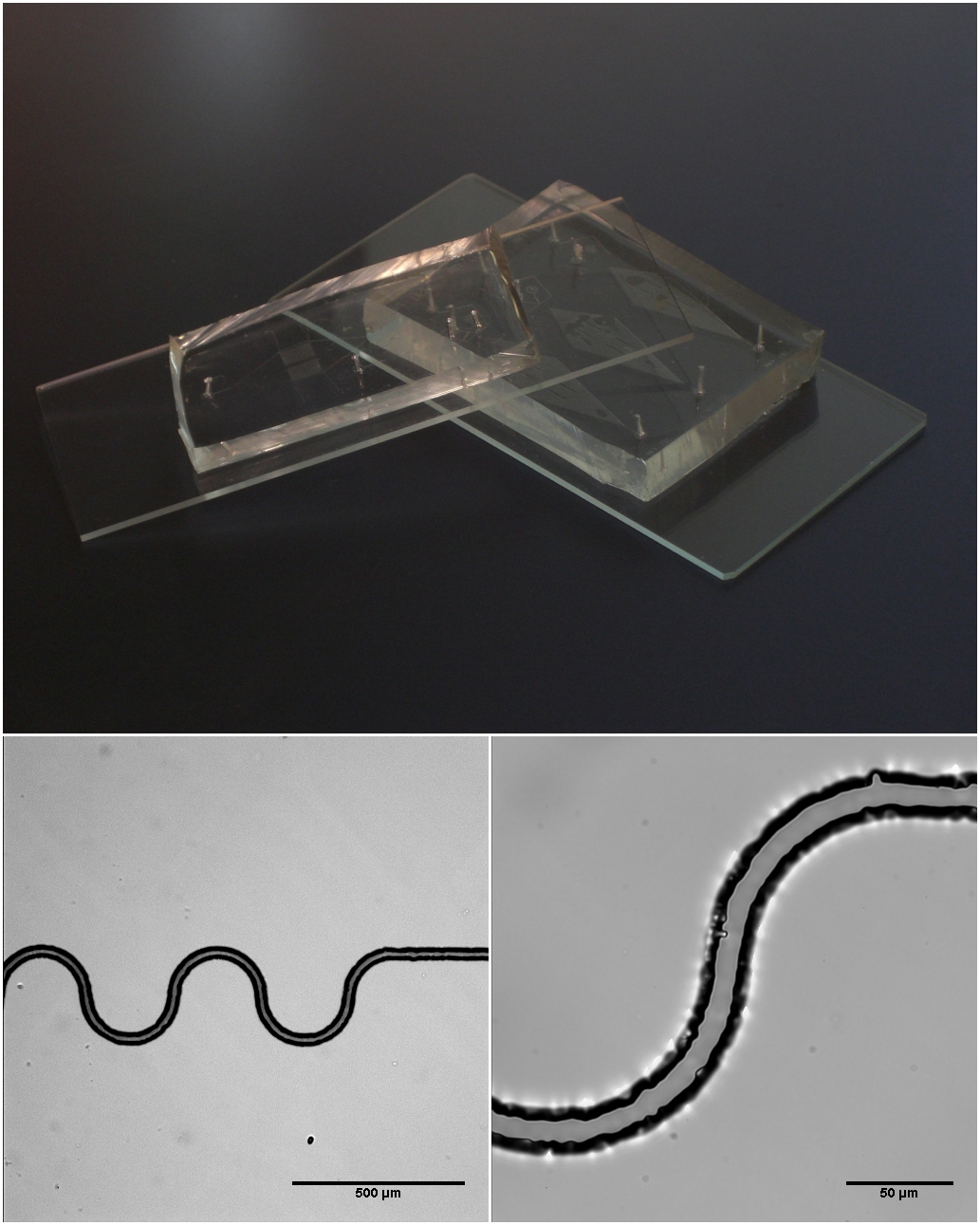
|
Micro-scale Actuator Schematic
Microscale is defined at the micrometre level spanning 0.1–100μm. Microscale may also refer to: *Microscale meteorology * Microscale chemistry * Kolmogorov microscales In fluid dynamics, Kolmogorov microscales are the smallest scales in the turbulent flow of fluids. At the Kolmogorov scale, viscosity dominates and the turbulence kinetic energy is dissipated into thermal energy. They are defined by where * i ... * Micro-scale heat exchangers * Micro-scale fluidics * Micro-scale reactor * Microscale and macroscale models * Micro-scale MOSFETs, used in certain commercial products {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscale
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI) equalling (SI standard prefix "micro-" = ); that is, one millionth of a metre (or one thousandth of a millimetre, , or about ). The nearest smaller common SI unit is the nanometre, equivalent to one thousandth of a micrometre, one millionth of a millimetre or one billionth of a metre (). The micrometre is a common unit of measurement for wavelengths of infrared radiation as well as sizes of biological cells and bacteria, and for grading wool by the diameter of the fibres. The width of a single human hair ranges from approximately 20 to . The longest human chromosome, chromosome 1, is approximately in length. Examples Between 1 μm and 10 μm: * 1–10 μm – length of a typical bacterium * 3–8 μm – width of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscale Meteorology
Microscale meteorology or micrometeorology is the study of short-lived atmospheric phenomena smaller than mesoscale, about or less. These two branches of meteorology are sometimes grouped together as "mesoscale and microscale meteorology" (MMM) and together study all phenomena smaller than synoptic scale; that is they study features generally too small to be depicted on a standard weather map. These include small and generally fleeting cloud "puffs" and other small cloud features. Microscale meteorology controls the most important mixing and dilution processes in the atmosphere. Important topics in microscale meteorology include heat transfer and gas exchange between soil, vegetation, and/or surface water and the atmosphere caused by near-ground turbulence. Measuring these transport processes involves use of micrometeorological (or flux) towers. Variables often measured or derived include net radiation, sensible heat flux, latent heat flux, ground heat storage, and fluxes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscale Chemistry
Microscale chemistry (often referred to as small-scale chemistry, in German: Chemie im Mikromaßstab) is an analytical method and also a teaching method widely used at school and at university levels, working with small quantities of chemical substances. While much of traditional chemistry teaching centers on multi-gramme preparations, milligrammes of substances are sufficient for microscale chemistry. In universities, modern and expensive lab glassware is used and modern methods for detection and characterization of the produced substances are very common. In schools and in many countries of the Southern hemisphere, small-scale working takes place with low-cost and even no-cost material. There has always been a place for small-scale working in qualitative analysis, but the new developments can encompass much of chemistry a student is likely to meet. History There are two main strands of the modern approach. One is based on the idea that many of the experiments associated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolmogorov Microscales
In fluid dynamics, Kolmogorov microscales are the smallest scales in the turbulent flow of fluids. At the Kolmogorov scale, viscosity dominates and the turbulence kinetic energy is dissipated into thermal energy. They are defined by where * is the average rate of dissipation of turbulence kinetic energy per unit mass, and * is the kinematic viscosity of the fluid. Typical values of the Kolmogorov length scale, for atmospheric motion in which the large eddies have length scales on the order of kilometers, range from 0.1 to 10 millimeters; for smaller flows such as in laboratory systems, may be much smaller. In 1941, Andrey Kolmogorov introduced the hypothesis that the smallest scales of turbulence are universal (similar for every turbulent flow) and that they depend only on and . The definitions of the Kolmogorov microscales can be obtained using this idea and dimensional analysis. Since the dimension of kinematic viscosity is length2/time, and the dimension of the energy d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micro Heat Exchanger
Micro heat exchangers, Micro-scale heat exchangers, or microstructured heat exchangers are heat exchangers in which (at least one) fluid flows in lateral confinements with typical dimensions below 1 mm. The most typical such confinement are microchannels, which are channels with a hydraulic diameter below 1 mm. Microchannel heat exchangers can be made from metal or ceramic. Microchannel heat exchangers can be used for many applications including: * high-performance aircraft gas turbine engines * heat pumps * Microprocessor and microchip cooling * air conditioning Background Investigation of microscale thermal devices is motivated by the single phase internal flow correlation for convective heat transfer: :h=\mathit_c \frac Where h is the heat transfer coefficient, \mathit_c is the Nusselt number, k is the thermal conductivity of the fluid and d is the hydraulic diameter of the channel or duct. In internal laminar flows, the Nusselt number becomes a constant. This is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microfluidics
Microfluidics refers to the behavior, precise control, and manipulation of fluids that are geometrically constrained to a small scale (typically sub-millimeter) at which surface forces dominate volumetric forces. It is a multidisciplinary field that involves engineering, physics, chemistry, biochemistry, nanotechnology, and biotechnology. It has practical applications in the design of systems that process low volumes of fluids to achieve multiplexing, automation, and high-throughput screening. Microfluidics emerged in the beginning of the 1980s and is used in the development of inkjet printheads, DNA chips, lab-on-a-chip technology, micro-propulsion, and micro-thermal technologies. Typically, micro means one of the following features: * Small volumes (μL, nL, pL, fL) * Small size * Low energy consumption * Microdomain effects Typically microfluidic systems transport, mix, separate, or otherwise process fluids. Various applications rely on passive fluid control using capillary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microreactor
A microreactor or microstructured reactor or microchannel reactor is a device in which chemical reactions take place in a confinement with typical lateral dimensions below 1 mm; the most typical form of such confinement are microchannels.''Recent advances in synthetic micro reaction technology'' Paul Watts and Charlotte Wiles Chem. Commun., 2007, 443 - 467, Microreactors are studied in the field of micro process engineering, together with other devices (such as micro heat exchangers) in which physical processes occur. The microreactor is usually a continuous flow reactor (contrast with/to a batch reactor). Microreactors offer many advantages over conventional scale reactors, including vast improvements in energy efficiency, reaction speed and yield, safety, reliability, scalability, on-site/on-demand production, and a much finer degree of process control. History Gas-phase microreactors have a long history but those involving liquids started to appear in the late 1990s. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscale And Macroscale Models
Microscale models form a broad class of computational models that simulate fine-scale details, in contrast with macroscale models, which amalgamate details into select categories. Microscale and macroscale models can be used together to understand different aspects of the same problem. Applications Macroscale models can include ordinary, partial, and integro-differential equations, where categories and flows between the categories determine the dynamics, or may involve only algebraic equations. An abstract macroscale model may be combined with more detailed microscale models. Connections between the two scales are related to multiscale modeling. One mathematical technique for multiscale modeling of nanomaterials is based upon the use of multiscale Green's function. In contrast, microscale models can simulate a variety of details, such as individual bacteria in biofilms, individual pedestrians in simulated neighborhoods, individual light beams in ray-tracing imagery, indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |