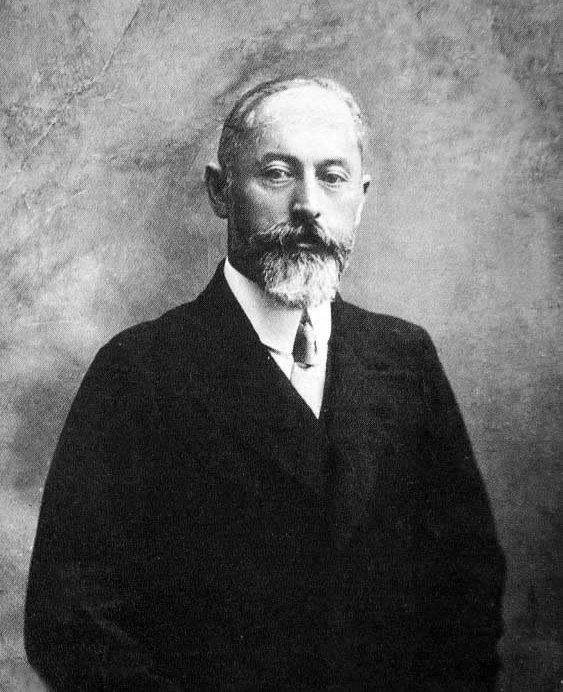|
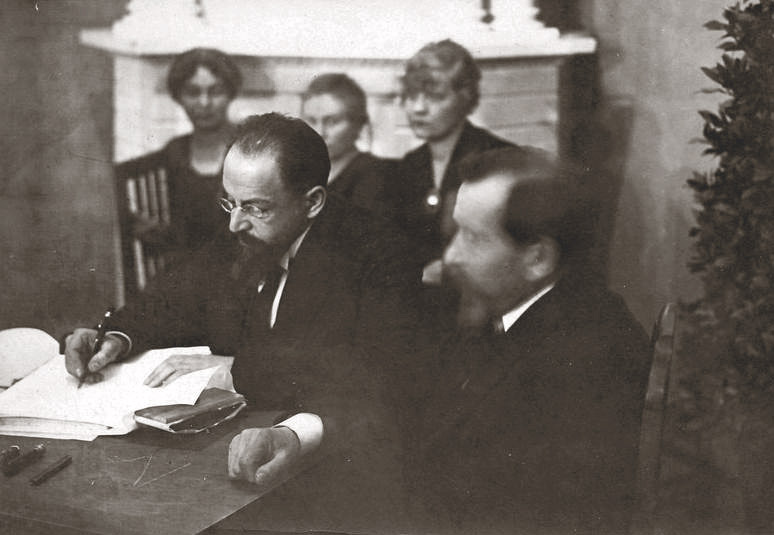
Mezhraiontsy
The Mezhraiontsy ( rus, межрайонцы, p=mʲɪʐrɐˈjɵnt͡sɨ), usually translated as the "Interdistrictites,"''Mezhraionka'' and ''Mezhraiontsy'' are derived from the Russian ''"mezh-"'' (meaning "inter-" or "between'") + ''"raion"'' (meaning "district" or "region"). were members of a small independent faction of the Russian Social Democratic Labor Party (RSDLP), which existed between 1913 and 1917. Although the formal name of this organization was Russian Social Democratic Labor Party (Internationalists), the names "Mezhraionka" for the organization and "Mezhraiontsy" for its participants were commonly used to indicate the group's intermediate ideological position between the rival Menshevik and Bolshevik wings of the divided RSDLP. The Mezhraiontsy merged with the Bolsheviks during the Russian Revolution of 1917. Organizational history Background Russian social democrats had been split into numerous factions along political and ethnic lines since at least 1903 when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstantin Yurenev
Konstantin Konstantinovich Yurenev (russian: Константи́н Константи́нович Юре́нев), also known as Konstantin Konstantinovich Krotovsky (russian: Константин Константинович Кротовский) (1888 – 1 August 1938), was a Russian revolutionary, Soviet politician and diplomat. Life and career Early revolutionary career Yurenev was born at Dvinsk station on the Riga-Orlov railway in the family of a railway watchman. He joined the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) in 1905 and later its Bolshevik faction in 1906. In 1908, he was arrested and sentenced to three years' exile in Arkhangelsk. When his term of exile was completed, he settled in St Petersburg, but split with the Bolsheviks their leader Vladimir Lenin pronounced that all Mensheviks were to be expelled from the RSDLP. In 1913, he co-founded the 'Inter-Borough Organisation' or Mezhraiontsy, who were neither Bolsheviks nor Mensheviks, but were inspi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmitry Manuilsky
Dmitriy Manuilsky, or Dmytro Zakharovych Manuilsky (Russian: Дми́трий Заха́рович Мануи́льский; Ukrainian: Дмитро Захарович Мануїльський; October 1883 in Sviatets near Kremenets – 22 February 1959 in Kiev) was an important Bolshevik revolutionary, Soviet politician and academic who was Secretary of the Executive Committee of Comintern, the Communist International, from December 1926 to its dissolution in May 1943. Life Background Manuilsky was born to a peasant family of an Orthodox priest in Kremenets. After secondary school, he enrolled at the University of St. Petersburg in 1903, and joined the Bolshevik faction of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party in 1904. During the 1905 revolution he was assigned by the Bolsheviks to the naval base in Kronstadt where he took part in the naval revolt in July. Arrested, he was held in Kronstadt prison in 1905-06, then exiled, but escaped, arriving in Kiev and then, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leon Trotsky
Lev Davidovich Bronstein. ( – 21 August 1940), better known as Leon Trotsky; uk, link= no, Лев Давидович Троцький; also transliterated ''Lyev'', ''Trotski'', ''Trotskij'', ''Trockij'' and ''Trotzky''. (), was a Russian Marxist revolutionary, political theorist and politician. Ideologically a Marxist, his developments to the ideology are called Trotskyism. Born to a wealthy Jewish family in Yanovka (now Bereslavka, Ukraine), Trotsky embraced Marxism after moving to Mykolaiv in 1896. In 1898, he was arrested for revolutionary activities and subsequently exiled to Siberia. He escaped from Siberia in 1902 and moved to London, where he befriended Vladimir Lenin. In 1903, he sided with Julius Martov's Mensheviks against Lenin's Bolsheviks during the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party's initial organisational split. Trotsky helped organize the failed Russian Revolution of 1905, after which he was again arrested and exiled to Siberia. He once again escape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Joffe
Adolph Abramovich Joffe (russian: Адо́льф Абра́мович Ио́ффе, alternative transliterations Adol'f Ioffe or, rarely, Yoffe) (10 October 1883 in Simferopol – 16 November 1927 in Moscow) was a Russian revolutionary, a Bolshevik politician and a Soviet diplomat of Karaite descent. Biography Revolutionary career Adolf Abramovich Joffe was born in Simferopol, Crimea, Russian Empire in a wealthy Karaite family.See Albert S. Lindemann. ''Esau's Tears: Modern Anti-Semitism and the Rise of the Jews'', Cambridge University Press, 1997; pg. 430. He became a social democrat in 1900 while still in high school, formally joining the Russian Social Democratic Labor Party in 1903. In 1904 Joffe was sent to Baku, which he had to flee to avoid arrest. He was then sent to Moscow, but had to flee again, this time abroad. After the events of Bloody Sunday on 9 January 1905, Joffe returned to Russia and took an active part in the Russian Revolution of 1905. In early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatoly Lunacharsky
Anatoly Vasilyevich Lunacharsky (russian: Анато́лий Васи́льевич Лунача́рский) (born Anatoly Aleksandrovich Antonov, – 26 December 1933) was a Russian Marxist revolutionary and the first Bolshevik Soviet People's Commissar (Narkompros) responsible for Ministry of Education as well as an active playwright, critic, essayist and journalist throughout his career. Background Lunacharsky was born on 23 or 24 November 1875 in Poltava, Ukraine (then part of the Russian Empire) as the illegitimate child of Alexander Antonov and Alexandra Lunacharskaya, née Rostovtseva. His mother was then married to statesman Vasily Lunacharsky, a nobleman of Polish origin, whence Anatoly's surname and patronym. She later divorced Vasily Lunacharsky and married Antonov, but Anatoly kept his former name. In 1890, at the age of 15, Lunacharsky became a Marxist. From 1894, he studied at the University of Zurich under Richard Avenarius for two years without taking a deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moisei Uritsky
Moisei Solomonovich Uritsky ( ua, Мойсей Соломонович Урицький; russian: Моисей Соломонович Урицкий; – 30 August 1918) was a Bolshevik revolutionary leader in Russia. After the October Revolution, he was Chief of Cheka of the Petrograd Soviet. Uritsky was assassinated by Leonid Kannegisser, a military cadet, who was executed shortly afterwards. Family Uritsky was born in the city of Cherkasy, Kiev Governorate, to a Jewish Litvak family. His father, a merchant, died when Moisei was little and his mother raised her son by herself. He attended the Bila Tserkva Gymnasium, supporting himself through teaching and became an active social democrat. Early political career Moisei studied law at the St. Vladimir Imperial University of Kiev. During his studies he joined the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party and organized an underground network for importing and distributing political literature. In 1897 he was arrested and exil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Riazanov
David Riazanov (russian: Дави́д Ряза́нов), born David Borisovich Goldendakh (russian: Дави́д Бори́сович Гольдендах; 10 March 1870 – 21 January 1938), was a Russian revolutionary, historian, bibliographer and archivist. Riazanov founded the Marx–Engels Institute and edited the first large-scale effort to publish the collected works of these two founders of the modern socialist movement. Riazanov was a prominent victim of the Great Terror of the late 1930s. Early years David Borisovich Goldendakh was born 10 March 1870 to a Jewish father and a Russian mother in Odessa, Ukraine, then part of the Russian empire.Colum Leckey, "David Riazanov and Russian Marxism," ''Russian History/Histoire Russe,'' vol. 22, no. 2 (Summer 1995), pg. 129. At the age of 15, the future David Riazanov joined the ranks of the Narodnik revolutionaries attempting to overthrow the autocracy of the Russian Tsar.Alexander Trachtenberg, "Introduction" to D. Riazanov, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factions Of The Russian Social Democratic Labour Party
In the course of the history of the RSDLP ( Russian Social Democratic Labour Party between 1898 and 1918), several political factions developed, as well as the major split between the Bolsheviks and the Mensheviks. * Bolsheviks formed in 1903 from the major split in the RSDLP which also produced the Mensheviks. The Bolshevik faction followed Vladimir Lenin, and organised a separate party, the Russian Social Democratic Workers Party, aka Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (Bolsheviks), in 1912. After the October Revolution of November 1917 it became the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks). * Mensheviks formed from the 1903 split with the Bolsheviks; the Mensheviks followed Julius Martov. With the formal severing of ties in 1912, the Mensheviks used the name Russian Social Democratic Party (Mensheviks), or sometimes without the qualifier. At the outbreak of World War I in 1914, the majority supporting the war ("Defencists") maintained control of the RSDLP(M) under Fyodor Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menshevik
The Mensheviks (russian: меньшевики́, from меньшинство 'minority') were one of the three dominant factions in the Russian socialist movement, the others being the Bolsheviks and Socialist Revolutionaries. The factions emerged in 1903 following a dispute within the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) between Julius Martov and Vladimir Lenin. The dispute originated at the 2nd Congress of the RSDLP, ostensibly over minor issues of party organization. Martov's supporters, who were in the minority in a crucial vote on the question of party membership, came to be called ''Mensheviks'', derived from the Russian ('minority'), while Lenin's adherents were known as ''Bolsheviks'', from ('majority'). Despite the naming, neither side held a consistent majority over the course of the entire 2nd Congress, and indeed the numerical advantage fluctuated between both sides throughout the rest of the RSDLP's existence until the Russian Revolution. The split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lev Karakhan
Lev Mikhailovich Karakhan (''Karakhanian'') Armenian Լևոն Միքայելի Կարախանյան, Russian Лев Михайлович Карахан (20 January 1889, Tiflis – 20 September 1937, Moscow) was a Russian revolutionary and a Soviet diplomat. A member of the RSDLP from 1904. At first a Menshevik, he joined the Bolsheviks in May 1917. In October 1917, he was member of the Revolutionary Military Council; then served as secretary of the Soviet delegation at the Brest-Litovsk peace talks together with Leon Trotsky and Adolph Joffe. In 1918-1920 and 1927–1934, he was the Deputy People's Commissar for Foreign Affairs. In 1919, he issued a statement concerning relations with China called the Karakhan Manifesto. In 1921, he was the Soviet Ambassador to Poland; in 1923–1926, the Ambassador to China; after 1934, the Ambassador to Turkey. Karakhan was known for his dandyish appearance; Karl Radek is quoted as having "maliciously described" him as "the Ass of Classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Social Democratic Labor Party
The Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP; in , ''Rossiyskaya sotsial-demokraticheskaya rabochaya partiya (RSDRP)''), also known as the Russian Social Democratic Workers' Party or the Russian Social Democratic Party, was a socialist political party founded in 1898 in Minsk (then in Northwestern Krai of the Russian Empire, present-day Belarus). Formed to unite the various revolutionary organizations of the Russian Empire into one party, the RSDLP split in 1903 into Bolsheviks ("majority") and Mensheviks ("minority") factions, with the Bolshevik faction eventually becoming the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. History Origins and early activities The RSDLP was not the first Russian Marxist group; the Emancipation of Labour group had been formed in 1883. The RSDLP was created to oppose the revolutionary populism of the Narodniks, which was later represented by the Socialist Revolutionary Party (SRs). The RSLDP was formed at an underground conference in Minsk in M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socialist Revolutionary Party
The Socialist Revolutionary Party, or the Party of Socialist-Revolutionaries (the SRs, , or Esers, russian: эсеры, translit=esery, label=none; russian: Партия социалистов-революционеров, ), was a major political party in late Imperial Russia, and both phases of the Russian Revolution and early Soviet Russia. The SRs were agrarian socialists and supporters of a democratic socialist Russian republic. The ideological heirs of the Narodniks, the SRs won a mass following among the Russian peasantry by endorsing the overthrow of the Tsar and the redistribution of land to the peasants. The SRs boycotted the elections to the First Duma following the Revolution of 1905 alongside the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, but chose to run in the elections to the Second Duma and received the majority of the few seats allotted to the peasantry. Following the 1907 coup, the SRs boycotted all subsequent Dumas until the fall of the Tsar in the February R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |