|
Methomyl Synthesis 2 Of 3 V1
Methomyl is a carbamate insecticide introduced in 1966. It is highly toxic to humans, livestock, pets, and wildlife. The EU and UK imposed a pesticide residue limit of 20 µg/kg for apples and oranges. Methomyl is a common active ingredient in commercial fly bait, for which the label instructions in the United States warn that "It is a violation of Federal Law to use this product in a manner inconsistent with its labeling." "Off-label" uses and other uses not specifically targeted at problem insects are illegal, dangerous, and ill-advised. Use Methomyl is a broad-spectrum insecticide that is used to kill insect pests. Methomyl is registered for commercial/professional use under certain conditions on sites including field, vegetable, and orchard crops; turf (sod farms only); livestock quarters; commercial premises; and refuse containers. Products containing 1% Methomyl are available to the general public for retail sale, but more potent formulations are classified as restricted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
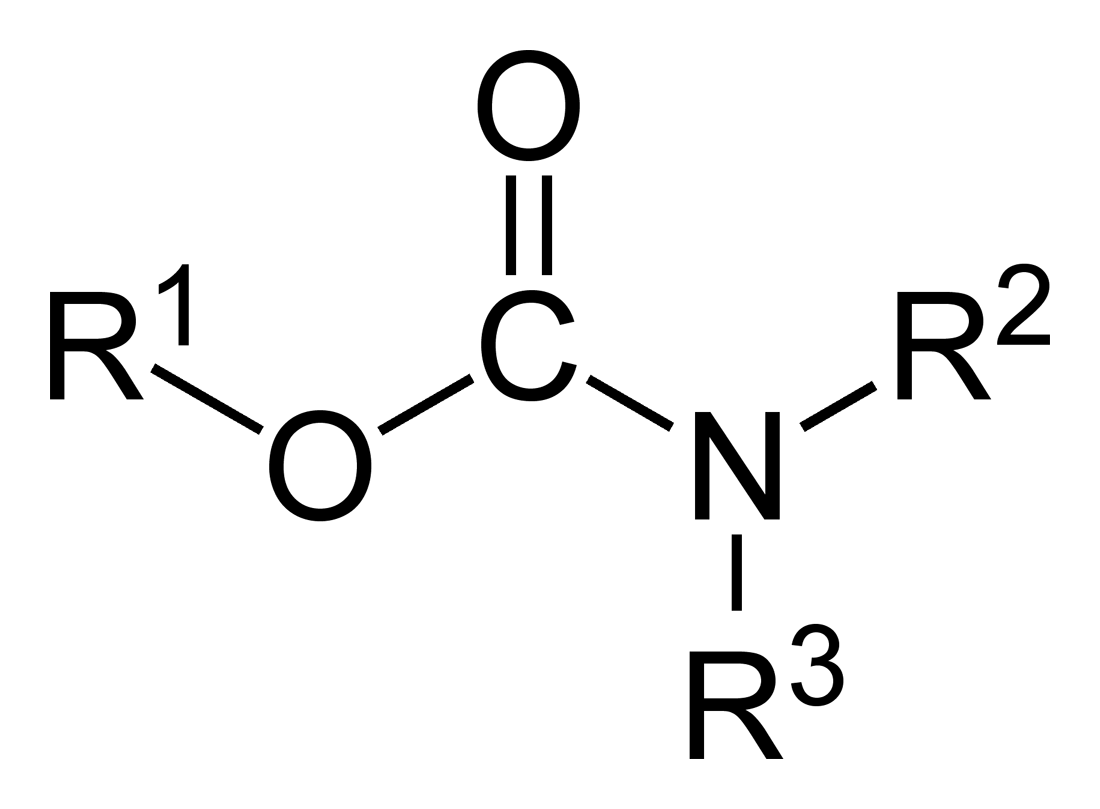
Carbamate
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose units are joined by carbamate groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters or ionic) are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate some calcium carbonate immediatel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable atoms survive. The term is also used more generally to characterize any type of exponential (or, rarely, non-exponential) decay. For example, the medical sciences refer to the biological half-life of drugs and other chemicals in the human body. The converse of half-life (in exponential growth) is doubling time. The original term, ''half-life period'', dating to Ernest Rutherford's discovery of the principle in 1907, was shortened to ''half-life'' in the early 1950s. Rutherford applied the principle of a radioactive element's half-life in studies of age determination of rocks by measuring the decay period of radium to lead-206. Half-life is constant over the lifetime of an exponentially decaying quantity, and it is a characteristic unit for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbamate Insecticides
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general Chemical formula, formula and Chemical structure, structure , which are formally Derivative (chemistry), derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salt (chemistry), salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose units are joined by carbamate groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters or salt (chemistry), ionic) are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like TEPP and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The active centre of cholinesterases feature two important sites, namely th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methomyl Synthesis 3 Of 3 V1
Methomyl is a carbamate insecticide introduced in 1966. It is highly toxic to humans, livestock, pets, and wildlife. The EU and UK imposed a pesticide residue limit of 20 µg/kg for apples and oranges. Methomyl is a common active ingredient in commercial fly bait, for which the label instructions in the United States warn that "It is a violation of Federal Law to use this product in a manner inconsistent with its labeling." "Off-label" uses and other uses not specifically targeted at problem insects are illegal, dangerous, and ill-advised. Use Methomyl is a broad-spectrum insecticide that is used to kill insect pests. Methomyl is registered for commercial/professional use under certain conditions on sites including field, vegetable, and orchard crops; turf (sod farms only); livestock quarters; commercial premises; and refuse containers. Products containing 1% Methomyl are available to the general public for retail sale, but more potent formulations are classified as restricted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Isocyanate
Methyl isocyanate (MIC) is an organic compound with the molecular formula CH3NCO. Synonyms are isocyanatomethane and methyl carbylamine. Methyl isocyanate is an intermediate chemical in the production of carbamate pesticides (such as carbaryl, carbofuran, methomyl, and aldicarb). It has also been used in the production of rubbers and adhesives. As an extremely toxic and irritating compound, it is very hazardous to human health. It was the principal toxicant involved in the infamous Bhopal gas disaster, which officially killed around 20,000 people in total. It is also a very potent lachrymatory agent. Physical properties Methyl isocyanate is a colorless, poisonous, lachrymatory (tearing agent), flammable liquid.Union Carbide Corporation "Methyl Isocyanate" Product Information Publication, F-41443, November 1967. It is soluble in water to 6–10 parts per 100 parts, but it also reacts with water (see Reactions below). Manufacture Methyl isocyanate is usually manufactured by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methomyl Synthesis 2 Of 3 V1
Methomyl is a carbamate insecticide introduced in 1966. It is highly toxic to humans, livestock, pets, and wildlife. The EU and UK imposed a pesticide residue limit of 20 µg/kg for apples and oranges. Methomyl is a common active ingredient in commercial fly bait, for which the label instructions in the United States warn that "It is a violation of Federal Law to use this product in a manner inconsistent with its labeling." "Off-label" uses and other uses not specifically targeted at problem insects are illegal, dangerous, and ill-advised. Use Methomyl is a broad-spectrum insecticide that is used to kill insect pests. Methomyl is registered for commercial/professional use under certain conditions on sites including field, vegetable, and orchard crops; turf (sod farms only); livestock quarters; commercial premises; and refuse containers. Products containing 1% Methomyl are available to the general public for retail sale, but more potent formulations are classified as restricted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxime
In organic chemistry, an oxime is a organic compound belonging to the imines, with the general formula , where R is an organic side-chain and R’ may be hydrogen, forming an aldoxime, or another organic group, forming a ketoxime. O-substituted oximes form a closely related family of compounds. Amidoximes are oximes of amides () with general structure . Oximes are usually generated by the reaction of hydroxylamine with aldehydes () or ketones (). The term ''oxime'' dates back to the 19th century, a combination of the words ''oxygen'' and ''imine''. Structure and properties If the two side-chains on the central carbon are different from each other—either an aldoxime, or a ketoxime with two different "R" groups—the oxime can often have two different geometric stereoisomeric forms according to the ''E''/''Z'' configuration. An older terminology of ''syn'' and ''anti'' was used to identify especially aldoximes according to whether the R group was closer or further from the hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methomyl Synthesis 1 Of 3 V1
Methomyl is a carbamate insecticide introduced in 1966. It is highly toxic to humans, livestock, pets, and wildlife. The EU and UK imposed a pesticide residue limit of 20 µg/kg for apples and oranges. Methomyl is a common active ingredient in commercial fly bait, for which the label instructions in the United States warn that "It is a violation of Federal Law to use this product in a manner inconsistent with its labeling." "Off-label" uses and other uses not specifically targeted at problem insects are illegal, dangerous, and ill-advised. Use Methomyl is a broad-spectrum insecticide that is used to kill insect pests. Methomyl is registered for commercial/professional use under certain conditions on sites including field, vegetable, and orchard crops; turf (sod farms only); livestock quarters; commercial premises; and refuse containers. Products containing 1% Methomyl are available to the general public for retail sale, but more potent formulations are classified as restricted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock become completely saturated with water is called the water table. Groundwater is recharged from the surface; it may discharge from the surface naturally at springs and seeps, and can form oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agricultural, municipal, and industrial use by constructing and operating extraction wells. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is hydrogeology, also called groundwater hydrology. Typically, groundwater is thought of as water flowing through shallow aquifers, but, in the technical sense, it can also contain soil moisture, perma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueous
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be represented as . The word ''aqueous'' (which comes from ''aqua'') means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved in, water. As water is an excellent solvent and is also naturally abundant, it is a ubiquitous solvent in chemistry. Since water is frequently used as the solvent in experiments, the word solution refers to an aqueous solution, unless the solvent is specified. A ''non-aqueous solution'' is a solution in which the solvent is a liquid, but is not water. (See also Solvent and Inorganic nonaqueous solvent.) Characteristics Substances that are ''hydrophobic'' ('water-fearing') do not dissolve well in water, whereas those that are ''hydrophilic'' ('water-friendly') do. An example of a hydrophilic substance is sodium chlori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to be a major factor behind the increase in the 20th-century's agricultural productivity. Nearly all insecticides have the potential to significantly alter ecosystems; many are toxic to humans and/or animals; some become concentrated as they spread along the food chain. Insecticides can be classified into two major groups: systemic insecticides, which have residual or long term activity; and contact insecticides, which have no residual activity. The mode of action describes how the pesticide kills or inactivates a pest. It provides another way of classifying insecticides. Mode of action can be important in understanding whether an insecticide will be toxic to unrelated species, such as fish, birds and mammals. Insecticides may be repellent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |