|
Methanobrevibacter Gottschalkii
Methanobrevibacter gottschalkii is a species of methanogen archaeon, named after Gerhard Gottschalk. Description It is a coccobacillus with rounded ends, about 0.7 micrometres in width and 0.9 micrometres in length, occurring in pairs or short chains. Gram-positive reaction. Its cell wall is composed of pseudomurein Pseudopeptidoglycan (also known as pseudomurein;White, David. (1995) ''The Physiology and Biochemistry of Prokaryotes'', pages 6, 12-21. (Oxford: Oxford University Press). . PPG hereafter) is a major cell wall component of some Archaea that differ .... It is a strict anaerobe and its type strain is HOT (=DSM 11977T =OCM 813T). It was first isolated from horse and pig faeces. References Further reading *Hackstein, Johannes HP, ed. (endo) symbiotic methanogenic archaea. Vol. 19. Springer, 2010. * * *Bignell, David Edward, Yves Roisin, and Nathan Lo, eds. Biology of termites: A modern synthesis. Springer, 2011. External linksLPSN*Type strain of ''Methanobrevibacter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of '' Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euryarchaeota
Euryarchaeota (from Ancient Greek ''εὐρύς'' eurús, "broad, wide") is a phylum of archaea. Euryarchaeota are highly diverse and include methanogens, which produce methane and are often found in intestines, halobacteria, which survive extreme concentrations of salt, and some extremely thermophilic aerobes and anaerobes, which generally live at temperatures between 41 and 122 °C. They are separated from the other archaeans based mainly on rRNA sequences and their unique DNA polymerase. Description The ''Euryarchaeota'' are diverse in appearance and metabolic properties. The phylum contains organisms of a variety of shapes, including both rods and cocci. ''Euryarchaeota'' may appear either gram-positive or gram-negative depending on whether pseudomurein is present in the cell wall. ''Euryarchaeota'' also demonstrate diverse lifestyles, including methanogens, halophiles, sulfate-reducers, and extreme thermophiles in each. Others live in the ocean, suspended with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanobacteria
In taxonomy, the Methanobacteria are a class of the Euryarchaeota. Several of the classes of the Euryarchaeota are methanogens and the Methanobacteria are one of these classes. Applications Methanobacteria can be used in biomass conversion as well as energy production through Anaerobic digestion (AD) process. Microbial community is used in Anaerobic digestion(AD) to convert organic wastes into clean energy by reducing chemical and biological oxygen demand in the wastes. Solid-state anaerobic digestion, which contains six genera of methanogens including Methanobacteria, can ferment rice straw and then produce methane. Since conventional treatment is burning rice straw in field, applying Methanobacteria to waste disposal process can reduce the air pollution caused by straw burning and also alleviate energy shortage problem, especially in rural areas. During biomethanation process, insoluble organic material and higher molecular mass compounds will first be transformed into simple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanobacteriales
In taxonomy, the Methanobacteriales are an order of the Methanobacteria. Species within this order differ from other methanogens in that they can use fewer catabolic substrates and have distinct morphological characteristics, lipid compositions, and RNA sequences. Their cell walls are composed of pseudomurein. Most species are Gram-positive with rod-shaped bodies and some can form long filaments. Most of them use formate to reduce carbon dioxide, but those of the genus ''Methanosphaera'' use hydrogen to reduce methanol to methane. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). See also * List of Archaea genera This article lists the genera of the Archaea. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Phylogeny National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanobacteriaceae
In taxonomy, the Methanobacteriaceae are a family of the Methanobacteriales. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). See also * List of Archaea genera This article lists the genera of the Archaea. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Phylogeny National Center for ... References Further reading Scientific journals * * * Scientific books Scientific databases External links {{Taxonbar, from=Q6823582 Archaea taxonomic families Euryarchaeota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanobrevibacter
In taxonomy, ''Methanobrevibacter'' is a genus of the Methanobacteriaceae.See the NCBIbr>webpage on Methanobrevibacter Data extracted from the The species within ''Methanobrevibacter'' are strictly anaerobic archaea that produce methane, for the most part through the reduction of carbon dioxide via hydrogen. Most species live in the intestines of larger organisms, such as termites and are responsible for the large quantities of greenhouse gases that they produce. ''Mbr. smithii'', found in the human intestine, may play a role in obesity. Nomenclature The name ''Methanobrevibacter'' has Latin and Greek roots. ''Methanum'' is Latin for methane, ''brevi'' is Latin for short, and ''bacter'' is Greek for bar. Professional publications use the abbreviations ''M.'', ''Mbb.'', and ''Mbr.'', as in ''M. smithii'', ''Mbb. smithii'', and ''Mbr. smithii''. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and Nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanogen
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are common in wetlands, where they are responsible for marsh gas, and in the digestive tracts of animals such as ruminants and many humans, where they are responsible for the methane content of belching in ruminants and flatulence in humans. In marine sediments, the biological production of methane, also termed methanogenesis, is generally confined to where sulfates are depleted, below the top layers. Moreover, methanogenic archaea populations play an indispensable role in anaerobic wastewater treatments. Others are extremophiles, found in environments such as hot springs and submarine hydrothermal vents as well as in the "solid" rock of Earth's crust, kilometers below the surface. Physical description Methanogens are coccoid (sph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeon
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccobacillus
A coccobacillus (plural coccobacilli), or bacilluscocco, is a type of bacterium with a shape intermediate between cocci (spherical bacteria) and bacilli (rod-shaped bacteria). Coccobacilli, then, are very short rods which may be mistaken for cocci. ''Haemophilus influenzae'', ''Gardnerella vaginalis'', and ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' are coccobacilli. ''Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans'' is a Gram-negative coccobacillus prevalent in subgingival plaques. ''Acinetobacter'' strains may grow on solid media as coccobacilli. ''Bordetella pertussis'' is a Gram-negative coccobacillus responsible for causing whooping cough. ''Yersinia pestis'', the bacterium that causes plague (disease), plague, is also coccobacillus. ''Coxiella burnetii'' is also a coccobacillus. Bacteria from the genus ''Brucella'' are medically important coccobacilli that cause brucellosis. ''Haemophilus ducreyi'', another medically important Gram-negative coccobacillus, is observed in sexually transmitted disease, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI) equalling (SI standard prefix " micro-" = ); that is, one millionth of a metre (or one thousandth of a millimetre, , or about ). The nearest smaller common SI unit is the nanometre, equivalent to one thousandth of a micrometre, one millionth of a millimetre or one billionth of a metre (). The micrometre is a common unit of measurement for wavelengths of infrared radiation as well as sizes of biological cells and bacteria, and for grading wool by the diameter of the fibres. The width of a single human hair ranges from approximately 20 to . The longest human chromosome, chromosome 1, is approximately in length. Examples Between 1 μm and 10 μm: * 1–10 μm – length of a typical bacterium * 3–8 μm � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. Gram-positive bacteria take up the crystal violet stain used in the test, and then appear to be purple-coloured when seen through an optical microscope. This is because the thick peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it is washed away from the rest of the sample, in the decolorization stage of the test. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage degrades the outer membrane of gram-negative cells, making the cell wall more porous and incapable of retaining the crystal violet stain. Their peptidoglycan layer is much thinner and sandwiched between an inner cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane, causing them to take up the counterstain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
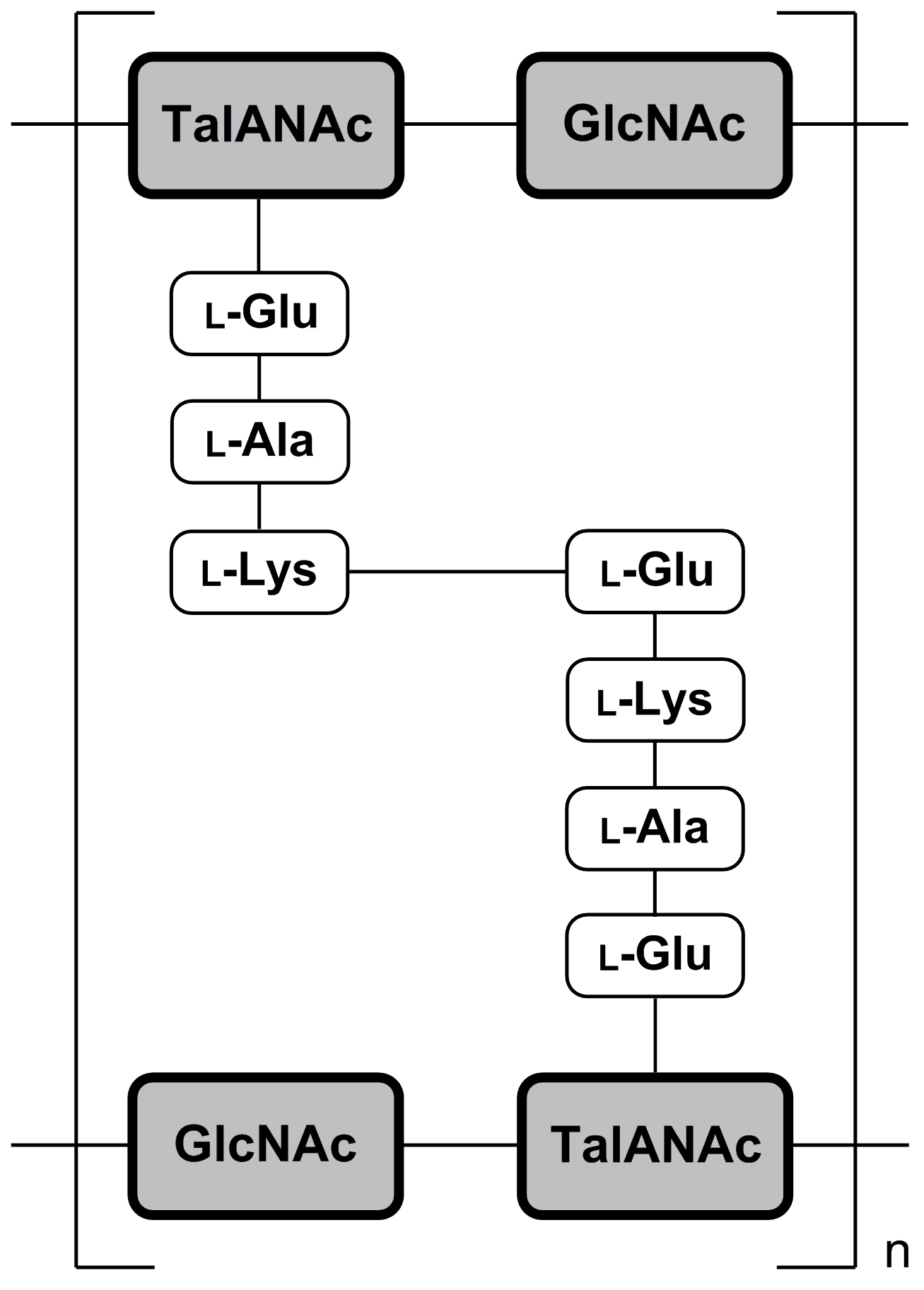
Pseudomurein
Pseudopeptidoglycan (also known as pseudomurein;White, David. (1995) ''The Physiology and Biochemistry of Prokaryotes'', pages 6, 12-21. (Oxford: Oxford University Press). . PPG hereafter) is a major cell wall component of some Archaea that differs from bacterial peptidoglycan in chemical structure, but resembles bacterial peptidoglycan in function and physical structure. Pseudopeptidoglycan, in general, is only present in a few methanogenic archaea. The basic components are N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetyltalosaminuronic acid (bacterial peptidoglycan containing ''N''-acetylmuramic acid instead), which are linked by β-1,3-glycosidic bonds. Lysozyme, a host defense mechanism present in human secretions (e.g. saliva and tears) breaks β-1,4-glycosidic bonds to degrade peptidoglycan. However, because pseudopeptidoglycan has β-1,3-glycosidic bonds, lysozyme is ineffective. It was thought from these large differences in cell wall chemistry that archaeal cell walls and bacterial cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)