|
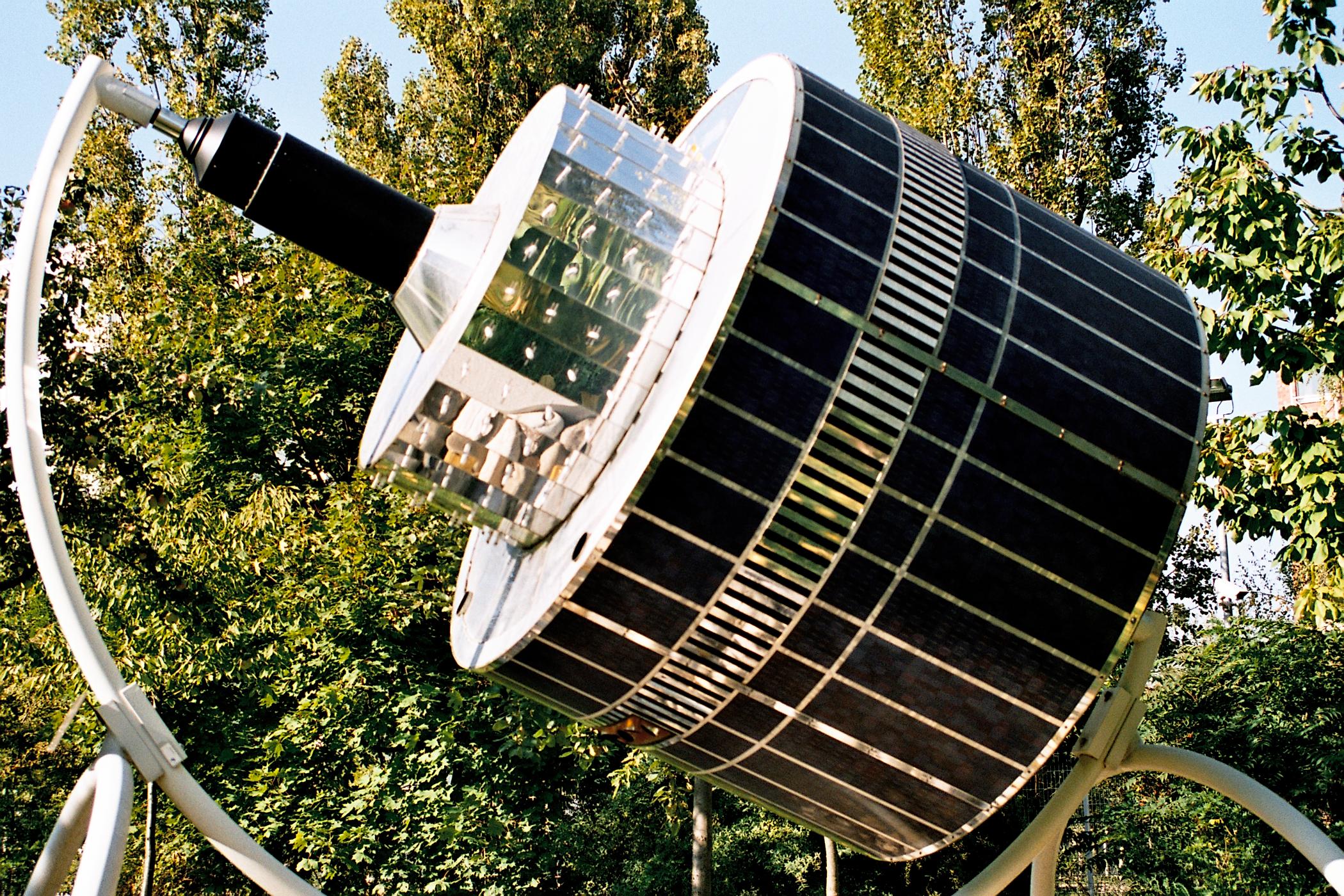
Meteosat 3
The Meteosat series of satellites are geostationary meteorological satellites operated by EUMETSAT under the Meteosat Transition Programme (MTP) and the Meteosat Second Generation (MSG) program. The MTP program was established to ensure the operational continuity between the end of the successful Meteosat Operational Programme in 1995 and Meteosat Second Generation (MSG), which came into operation at the start of 2004 using improved satellites. The MSG program will provide service until the MTG (Meteosat Third Generation) program takes over. __TOC__ First generation The first generation of Meteosat satellites, Meteosat-1 to Meteosat-7, provided continuous and reliable meteorological observations from space to a large user community. Meteosat-1 to -7 have all now retired. When operational, the Meteosat First Generation provided images every half-hour in three spectral channels (Visible, Infrared) and Water vapor, Water Vapour, via the Meteosat Visible and Infrared Imager (MVIRI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
METEOSAT
The Meteosat series of satellites are geostationary meteorological satellites operated by EUMETSAT under the Meteosat Transition Programme (MTP) and the Meteosat Second Generation (MSG) program. The MTP program was established to ensure the operational continuity between the end of the successful Meteosat Operational Programme in 1995 and Meteosat Second Generation (MSG), which came into operation at the start of 2004 using improved satellites. The MSG program will provide service until the MTG (Meteosat Third Generation) program takes over. __TOC__ First generation The first generation of Meteosat satellites, Meteosat-1 to Meteosat-7, provided continuous and reliable meteorological observations from space to a large user community. Meteosat-1 to -7 have all now retired. When operational, the Meteosat First Generation provided images every half-hour in three spectral channels (Visible, Infrared) and Water Vapour, via the Meteosat Visible and Infrared Imager (MVIRI) instrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteosat Geostasjonær Satellitt
The Meteosat series of satellites are geostationary meteorological satellites operated by EUMETSAT under the Meteosat Transition Programme (MTP) and the Meteosat Second Generation (MSG) program. The MTP program was established to ensure the operational continuity between the end of the successful Meteosat Operational Programme in 1995 and Meteosat Second Generation (MSG), which came into operation at the start of 2004 using improved satellites. The MSG program will provide service until the MTG (Meteosat Third Generation) program takes over. __TOC__ First generation The first generation of Meteosat satellites, Meteosat-1 to Meteosat-7, provided continuous and reliable meteorological observations from space to a large user community. Meteosat-1 to -7 have all now retired. When operational, the Meteosat First Generation provided images every half-hour in three spectral channels (Visible, Infrared) and Water Vapour, via the Meteosat Visible and Infrared Imager (MVIRI) instrumen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EUMETSAT MSG Control
The European Organization for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) is an intergovernmental organisation created through an international convention agreed by a current total of 30 European Member States. EUMETSAT's primary objective is to establish, maintain and exploit European systems of operational meteorological satellites. EUMETSAT is responsible for the launch and operation of the satellites and for delivering satellite data to end-users as well as contributing to the operational monitoring of climate and the detection of global climate changes. The activities of EUMETSAT contribute to a global meteorological satellite observing system coordinated with other space-faring nations. Satellite observations are an essential input to numerical weather prediction systems and also assist the human forecaster in the diagnosis of potentially hazardous weather developments. Of growing importance is the capacity of weather satellites to gather long-term measurem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
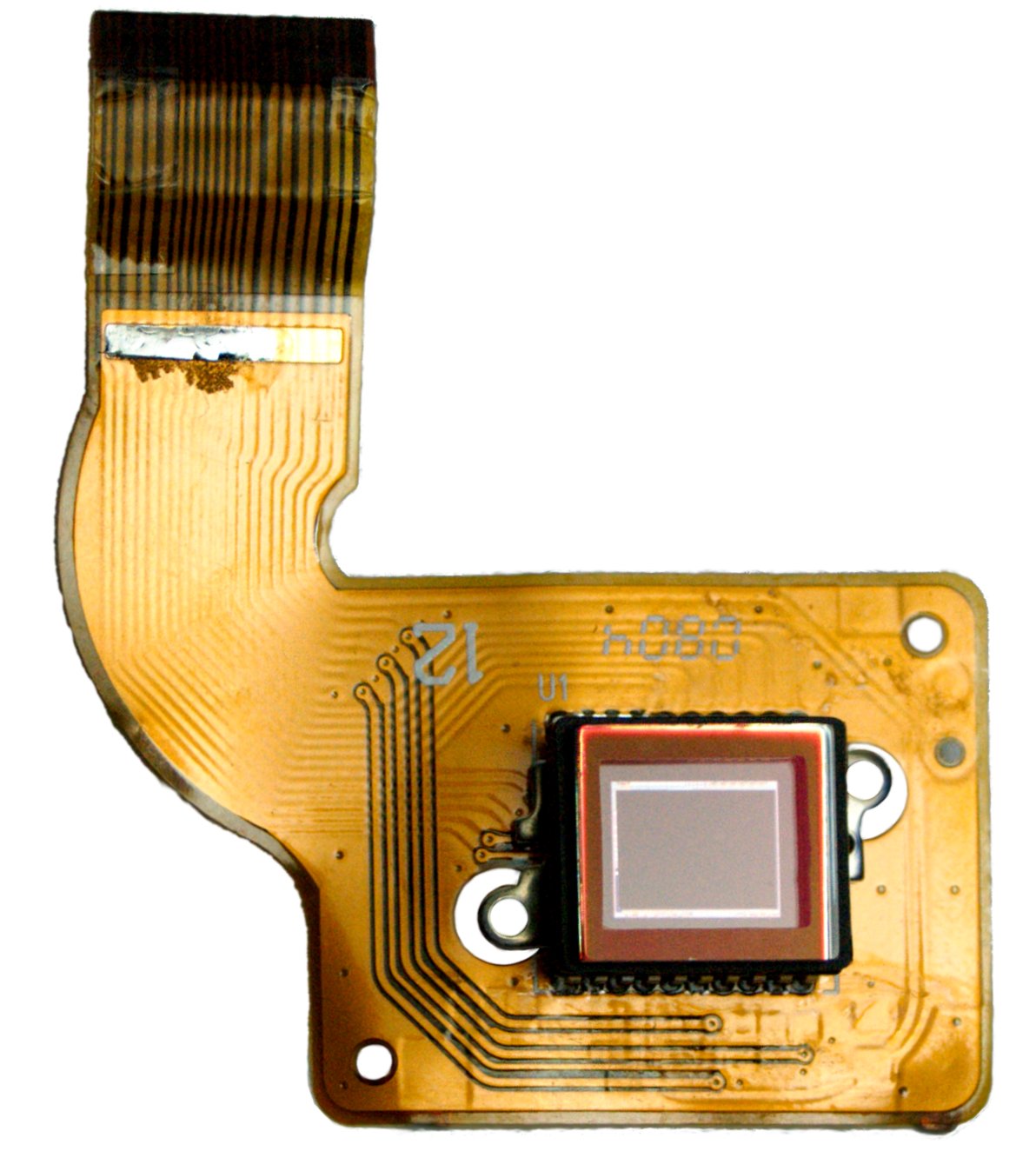
Electronic Imager
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they pass through or reflect off objects) into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging. The two main types of electronic image sensors are the charge-coupled device (CCD) and the active-pixel sensor (CMOS sensor). Both CCD and CMOS sensors are based on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology, with CCDs based on MOS capacitors and CMOS sensors based on MO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteosat 8
Meteosat 8 is a weather satellite, also known as MSG 1. The Meteosat series are operated by EUMETSAT under the Meteosat Transition Programme (MTP) and the Meteosat Second Generation (MSG) program. Notable for imaging the first meteor to be predicted to strike the earth, 2008 TC3. Launched 28 Aug 2002 by an Ariane V155, this European Meteorology satellite is in a Geostationary orbit. While Meteosat 8 meteorological instruments are working, solid state power amplifier SSPA-C failed in October 2002. On 22 May 2007, the satellite experienced an unexpected orbit change. This was initially assessed as due to a hit by an unknown object, but that was later assessed not to be credible. The thermal protection was damaged at the same time as the orbit change. Subsequent investigation assessed the Meteosat-8 spinning spacecraft's orbit change due to the mass release of thermal covering whose attachment failed. Meteosat-8 is still operating, and as of April 2013 is providing a backup capabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geostationary Earth Radiation Budget
The Geostationary Earth Radiation Budget (GERB) is an instrument aboard EUMETSAT's Meteosat Second Generation geostationary satellites designed to make accurate measurements of the Earth radiation budget. It was produced by a European consortium consisting of the United Kingdom, Belgium and Italy. The first, known as GERB 2, was launched on 28 August 2002 on an Ariane 5 rocket. The second, GERB 1, was launched on 21 December 2005, and the third, GERB3, on 5 July 2012. The last GERB 4 device was launched 14 July 2015. The first launched GERB 2 on MSG 1 is currently situated over the Indian Ocean at 41.5°E, while GERBs 1 and 3 on MSG 2 and 3 are still located over the standard Africa EUMETSAT position. GERB 4 on MSG is yet to become operational. Scientific motivations and objectives The unprecedented rate of atmospheric increase occurring since the industrial revolution due to human activity is of much concern to scientists as it has occurred an order of magnitude faster than pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerical Weather Prediction
Numerical weather prediction (NWP) uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic results. A number of global and regional forecast models are run in different countries worldwide, using current weather observations relayed from radiosondes, weather satellites and other observing systems as inputs. Mathematical models based on the same physical principles can be used to generate either short-term weather forecasts or longer-term climate predictions; the latter are widely applied for understanding and projecting climate change. The improvements made to regional models have allowed for significant improvements in tropical cyclone track and air quality forecasts; however, atmospheric models perform poorly at handling processes that occur in a relatively const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nowcasting (meteorology)
Nowcasting is weather forecasting on a very short term mesoscale period of up to 2 hours according to the World Meteorological Organization and up to six hours according to other authors in the field. This forecast is an extrapolation in time of known weather parameters, including those obtained by means of remote sensing, using techniques that take into account a possible evolution of the air mass. This type of forecast therefore includes details that cannot be solved by numerical weather prediction (NWP) models running over longer forecast periods. Principle Nowcasting in meteorology uses surface weather station data, wind profiler data, and any other weather data available to initialize the current weather situation and forecast by extrapolation for a period of 0 to 6 hours. In this time range it is possible to forecast small features such as individual storms with reasonable accuracy. Weather radar echoes and satellite data, giving cloud coverage, are particularly important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alenia Spazio
Thales Alenia Space () is a Franco-Italian aerospace manufacturer. A joint venture between the French technology corporation Thales Group (67%) and Italian defense conglomerate Leonardo (33%), the company is the largest satellite manufacturer in Europe. It is headquartered in Cannes, France. Thales Alenia Space designs and builds various space-related products, notably manufacturing numerous ranges of satellites for telecommunications, navigation, earth observation and space exploration purposes. The company is the second largest industrial participant in the International Space Station (ISS), having produced the European Space Agency's (ESA) modules for the ISS. It is also building satellites for Galileo, a European global satellite navigation system (GSNS). History Thales Alenia Space arose as a result of the French defense electronics specialist Thales Group deciding to buy out the participation of Alcatel in two joint-ventures between France's Alcatel and Italy's Finm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messerschmitt
Messerschmitt AG () was a German share-ownership limited, aircraft manufacturing corporation named after its chief designer Willy Messerschmitt from mid-July 1938 onwards, and known primarily for its World War II fighter aircraft, in particular the Bf 109 and Me 262. The company survived in the post-war era, undergoing a number of mergers and changing its name from Messerschmitt to Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm before being bought by Deutsche Aerospace (DASA, now part of Airbus) in 1989. History Background In February 1916, the south German engineering company MAN AG and several banks purchased the unprofitable aircraft builder Otto-Flugzeugwerke, starting a new company, ''Bayerische Flugzeugwerke AG'' (abbreviated ''B.F.W.''). The articles of association were drawn up on 19 and 20 February, and completed on 2 March 1916. Details of the company were recorded in the Commercial Register with an equity capital of RM 1,000,000 on 7 March 1916. 36% of the capital was provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thales Alenia Space
Thales Alenia Space () is a Franco-Italian aerospace manufacturer. A joint venture between the French technology corporation Thales Group (67%) and Italian defense conglomerate Leonardo (33%), the company is the largest satellite manufacturer in Europe. It is headquartered in Cannes, France. Thales Alenia Space designs and builds various space-related products, notably manufacturing numerous ranges of satellites for telecommunications, navigation, earth observation and space exploration purposes. The company is the second largest industrial participant in the International Space Station (ISS), having produced the European Space Agency's (ESA) modules for the ISS. It is also building satellites for Galileo, a European global satellite navigation system (GSNS). History Thales Alenia Space arose as a result of the French defense electronics specialist Thales Group deciding to buy out the participation of Alcatel in two joint-ventures between France's Alcatel and Italy's Finm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |