|
Metellus
The gens Caecilia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are mentioned in history as early as the fifth century BC, but the first of the Caecilii who obtained the consulship was Lucius Caecilius Metellus Denter, in 284 BC.''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', vol. I, p. 526 ("Caecilia Gens"). The Caecilii Metelli were one of the most powerful families of the late Republic, from the decades before the First Punic War down to the time of Augustus. Origin Like other Roman families in the later times of the Republic, the Caecilii traced their origin to a mythical personage, Caeculus, the founder of Praeneste. He was said to be the son of Vulcan, and engendered by a spark; a similar story was told of Servius Tullius. He was exposed as an infant, but preserved by his divine father, and raised by maidens. He grew up amongst the shepherds, and became a highwayman. Coming of age, he called upon the people of the countryside to build a new town, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasdrubal, Son Of Hanno
Hasdrubal ( 255250 BC) was a Carthaginian general who served during the middle years of the First Punic War, fought between Carthage and Rome, and took a leading part in three of the four major field battles of the war. He was a citizen of the city state of Carthage, which was in what is now Tunisia. His date of birth and age at death are both unknown, as are his activities prior to his coming to prominence in 255 BC. Modern historians distinguish him from other Carthaginians named Hasdrubal by the cognomen "son of Hanno". Hasdrubal was one of three Carthaginian generals, possibly the senior, who took command of the army raised when the Romans invaded North Africa in 255 BC. He was responsible for the decision to march against the Romans late in the year and was present at the Battle of Adys where the Carthaginians were routed. Early in 254 BC the triumvirate of Carthaginian generals gave control of the army to the Spartan mercenary commander, Xanthippus, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Caecilius Metellus (consul 251 BC)
Lucius Caecilius Metellus (221 BC) was the son of Lucius Caecilius Metellus Denter. He was Consul in 251 BC and 247 BC, Pontifex Maximus in 243 BC and Dictator in 224 BC. He defeated the Carthaginian general Hasdrubal at the celebrated Battle of Panormus, a turning point of the First Punic War which led to Roman domination of Sicily. In that battle, after which he received the Honours of the Triumph, he defeated thirteen enemy generals and captured one hundred and twenty elephants, some of which he exhibited to the Roman people. In this battle, so decisive for Rome, the Carthaginian advantage was subdued by luring the enemy to terrain where staked ditches had been dug. This, coupled with the element of surprise and a quick counter-attack, allowed the Roman infantry to rout the attacking Carthaginians. While Metellus was Pontifex Maximus, a fire destroyed the Temple of Vesta and threatened to destroy the ''Palladium'' and other sacred objects. Lucius Caecilius Metellus, witho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
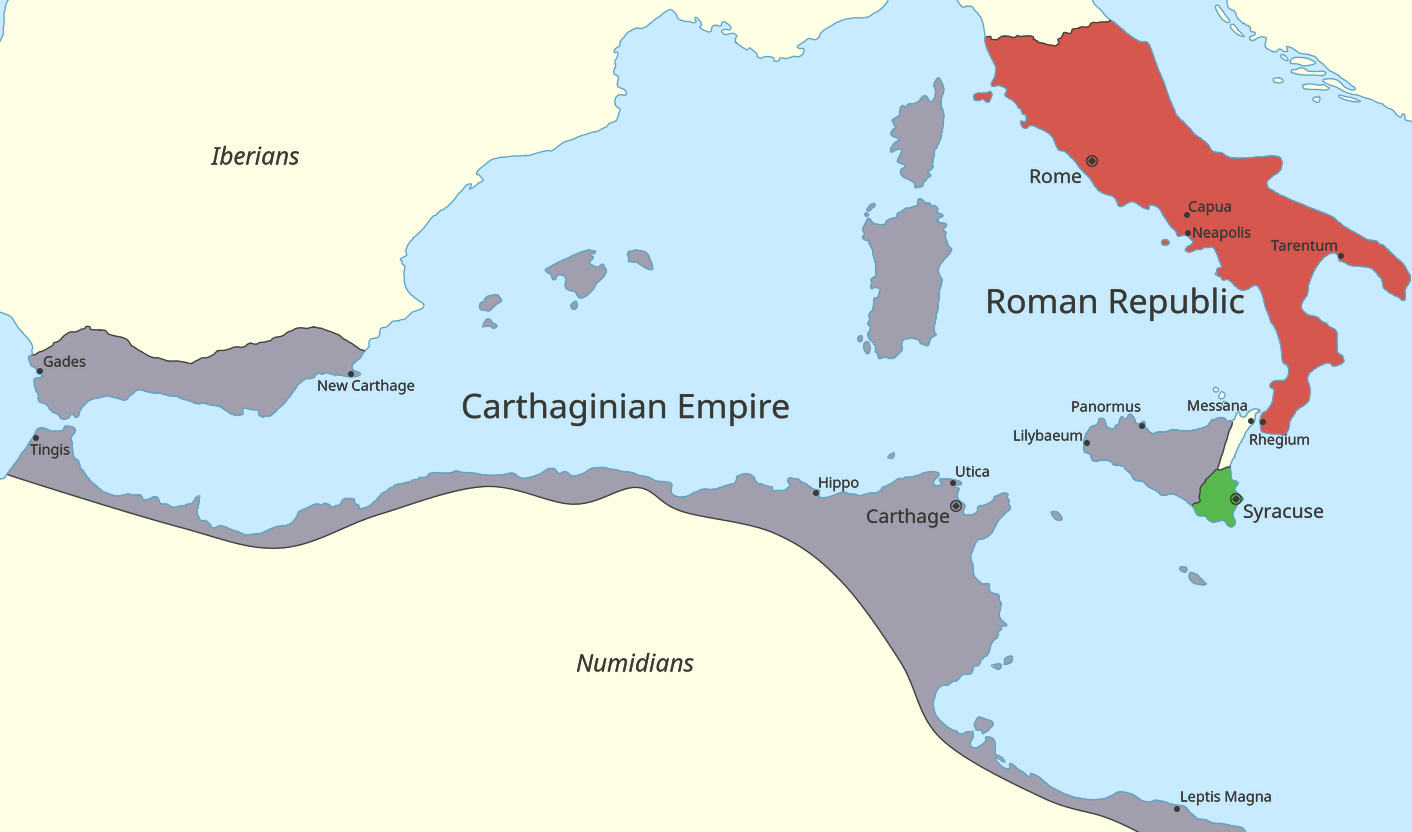
First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated. The war began in 264 BC with the Romans gaining a foothold on Sicily at Messana (modern Messina). The Romans then pressed Syracuse, the only significant independent power on the island, into allying with them and laid siege to Carthage's main base at Akragas. A large Carthaginian army attempted to lift the siege in 262 BC but was heavily defeated at the Battle of Akragas. The Romans then built a navy to challenge the Carthaginians', and using novel tactics inflicted severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period—from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. Roman society under the Republic was primarily a cultural mix of Latin and Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Roman Pantheon. Its political organization developed, at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by a senate. The top magistrates were the two consuls, who had an extensive range of executive, legislative, judicial, military, and religious powers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Caecilius Metellus Denter
Lucius Caecilius Metellus Denter was consul in 284 BC, and praetor the year after. In this capacity, he fell in the war against the Senones and was succeeded by Manius Curius Dentatus. Fischer, in his ''Römische Zeittafeln'', has him as praetor and also dying in 285 BC, and in the year following he has him again as consul. Wilhelm Drumann denies the identity of the consul and the praetor, on the ground that it was not customary for a person to hold the praetorship the year after his consulship; but examples of such a mode of proceeding do occur, so Drumann's objection fails. Denter may have been the father of Lucius Caecilius Metellus, consul in 251 and 247 BC. The latter's filiation is given as "L. f. C. n.", the son of Lucius and grandson of Gaius. In this case, Denter's father would have been Gaius Caecilius Metellus. An alternative hypothesis makes him the son or nephew of a Quintus Caecilius, supposedly tribune of the plebs in 316 BC. No corresponding individual appears i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognomina
A ''cognomen'' (; plural ''cognomina''; from ''con-'' "together with" and ''(g)nomen'' "name") was the third name of a citizen of ancient Rome, under Roman naming conventions. Initially, it was a nickname, but lost that purpose when it became hereditary. Hereditary ''cognomina'' were used to augment the second name, the ''nomen gentilicium'' (the family name, or clan name), in order to identify a particular branch within a family or family within a clan. The term has also taken on other contemporary meanings. Roman names Because of the limited nature of the Latin ''praenomen'', the ''cognomen'' developed to distinguish branches of the family from one another, and occasionally, to highlight an individual's achievement, typically in warfare. One example of this is Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, whose cognomen ''Magnus'' was earned after his military victories under Sulla's dictatorship. The ''cognomen'' was a form of distinguishing people who accomplished important feats, and those who alr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy ( Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Caecilius Iucundus, Plaster Cast Of Roman Bronze And Marble Original, House Of Caecilius Iucundus (V-i-26), Pompeii, C
Lucius ( el, Λούκιος ''Loukios''; ett, Luvcie) is a male given name derived from ''Lucius'' (abbreviated ''L.''), one of the small group of common Latin forenames (''praenomina'') found in the culture of ancient Rome. Lucius derives from Latin word ''Lux'' (gen. ''lucis''), meaning "light" (< PIE ''*leuk-'' "brightness", Latin verb ''lucere'' "to shine"), and is a cognate of the name Lucas. Another etymology proposed is a derivation from ''Lauchum'' (or ''Lauchme'') meaning "", wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praenomina
The ''praenomen'' (; plural: ''praenomina'') was a personal name chosen by the parents of a Roman child. It was first bestowed on the ''dies lustricus'' (day of lustration), the eighth day after the birth of a girl, or the ninth day after the birth of a boy. The praenomen would then be formally conferred a second time when girls married, or when boys assumed the ''toga virilis'' upon reaching manhood. Although it was the oldest of the ''tria nomina'' commonly used in Roman naming conventions, by the late republic, most praenomina were so common that most people were called by their praenomina only by family or close friends. For this reason, although they continued to be used, praenomina gradually disappeared from public records during imperial times. Although both men and women received praenomina, women's praenomina were frequently ignored, and they were gradually abandoned by many Roman families, though they continued to be used in some families and in the countryside. Backgroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optimates
Optimates (; Latin for "best ones", ) and populares (; Latin for "supporters of the people", ) are labels applied to politicians, political groups, traditions, strategies, or ideologies in the late Roman Republic. There is "heated academic discussion" as to whether Romans would have recognised an ideological content or political split in the label. Among other things, ''optimates'' have been seen as supporters of the continued authority of the Roman senate, senate, politicians who operated mostly in the senate, or opponents of the ''populares''. The ''populares'' have also been seen as focusing on operating before the Constitution of the Roman Republic#Assemblies, popular assemblies, generally in opposition to the Roman senate, senate, using "the populace, rather than the senate, as a means [for advantage]". References to optimates (also called ''boni'', "good men") and ''populares'' are found among the writings of Roman authors of the 1st century BC. The distinction bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextus Pompeius Festus
Sextus Pompeius Festus, usually known simply as Festus, was a Roman grammarian who probably flourished in the later 2nd century AD, perhaps at Narbo (Narbonne) in Gaul. Work He made a 20-volume epitome of Verrius Flaccus's voluminous and encyclopedic treatise ''De verborum significatione''. Flaccus had been a celebrated grammarian who flourished in the reign of Augustus. Festus gives the etymology as well as the meaning of many words, and his work throws considerable light on the language, mythology and antiquities of ancient Rome. He made a few alterations, and inserted some critical remarks of his own. He also omitted such ancient Latin words as had long been obsolete; these he apparently discussed in a separate work now lost, entitled ''Priscorum verborum cum exemplis''. Even incomplete, Festus' lexicon reflects at second hand the enormous intellectual effort that had been made in the Augustan Age to put together information on the traditions of the Roman world, which was alrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictionary Of Greek And Roman Biography And Mythology/Metellus
A dictionary is a listing of lexemes from the lexicon of one or more specific languages, often arranged alphabetically (or by radical and stroke for ideographic languages), which may include information on definitions, usage, etymologies, pronunciations, translation, etc.Webster's New World College Dictionary, Fourth Edition, 2002 It is a lexicographical reference that shows inter-relationships among the data. A broad distinction is made between general and specialized dictionaries. Specialized dictionaries include words in specialist fields, rather than a complete range of words in the language. Lexical items that describe concepts in specific fields are usually called terms instead of words, although there is no consensus whether lexicology and terminology are two different fields of study. In theory, general dictionaries are supposed to be semasiological, mapping word to definition, while specialized dictionaries are supposed to be onomasiological, first identifying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |